
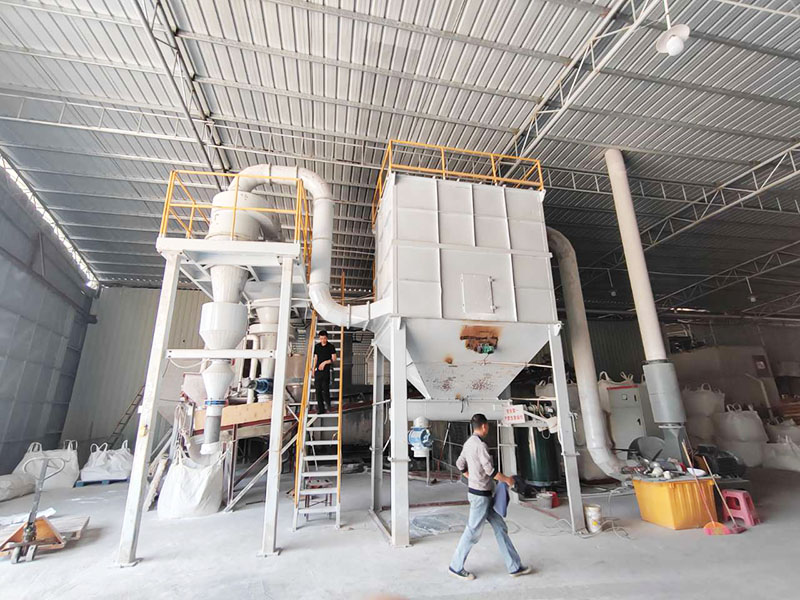
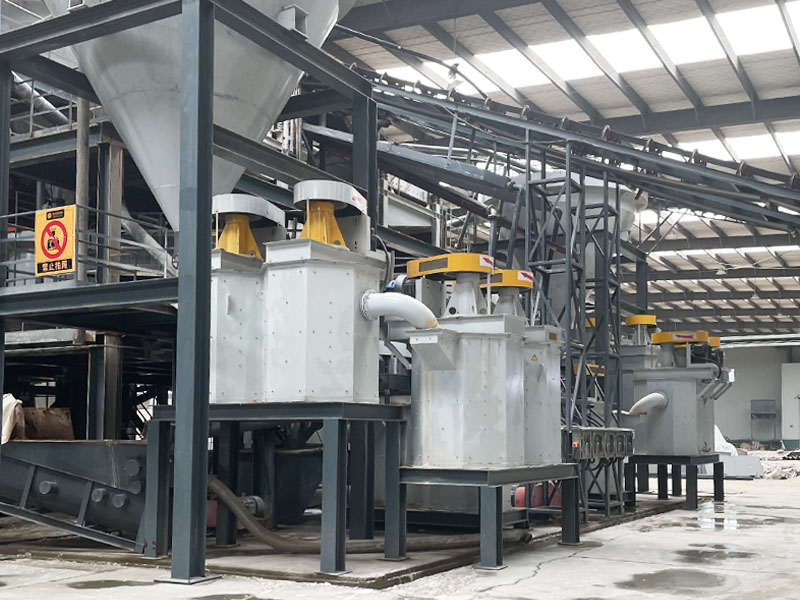
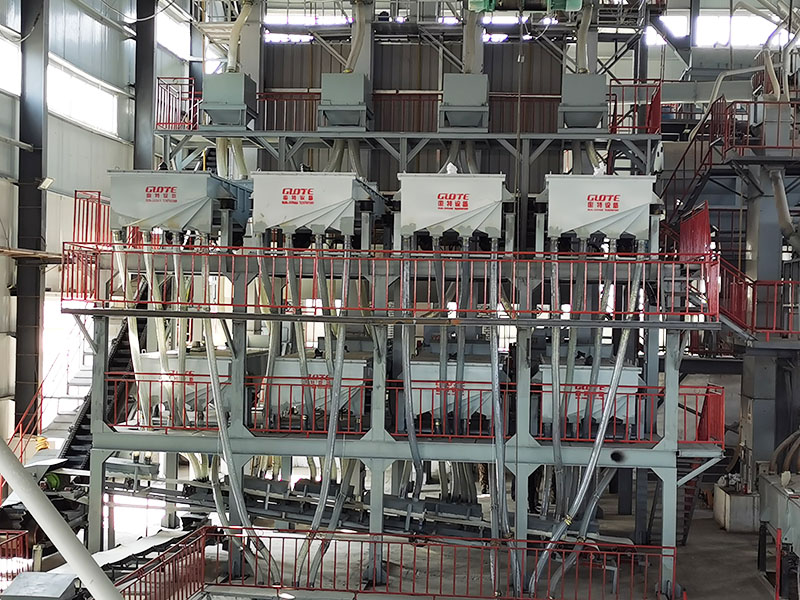
Magnetic separator is a device that uses the magnetic difference of materials to separate them in an uneven magnetic field. It is widely used in many fields such as mineral processing (ore dressing), coal washing, non-metallic mineral purification, metallurgy, building materials, chemicals, food, medicine, garbage disposal and waste material recycling. It is mainly used to separate magnetic minerals (such as magnetite, titanomagnetite, pyrrhotite, etc.) from non-magnetic minerals, or to remove ferromagnetic impurities (iron removal) in raw materials.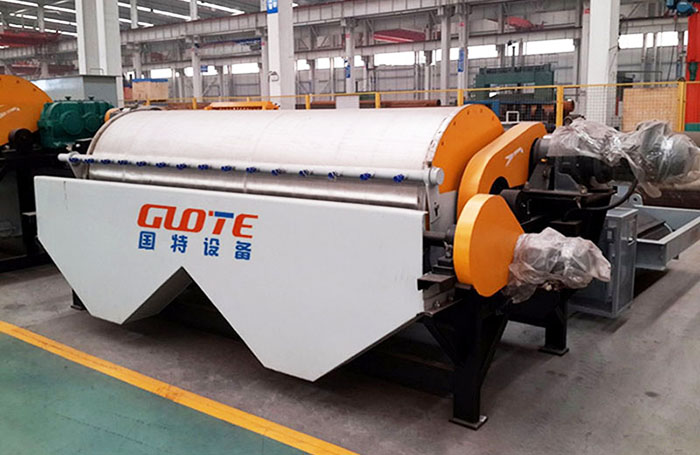
Understanding the principles and functions of different types of magnetic separators is essential for the efficient and economical application of magnetic separation technology in fields such as mineral processing, material purification, environmental protection and resource recovery.
There are many types of magnetic separators, which can be classified mainly from the following aspects.
Use the table of contents below to navigate through the guide:
1Classification by magnetic field source
1. Permanent magnetic separator:
●Magnetic field source: Use permanent magnetic materials (such as NdFeB, ferrite, aluminum nickel cobalt, etc.) to generate magnetic field.
●Advantages: Relatively simple structure, no excitation power supply required, low energy consumption, low operating cost, easy maintenance, stable magnetic field, not easy to heat up.
●Disadvantages: The magnetic field strength is relatively fixed (cannot be adjusted at will), which may be limited when processing extremely high or weak magnetic materials, and the price of strong permanent magnets is relatively high.
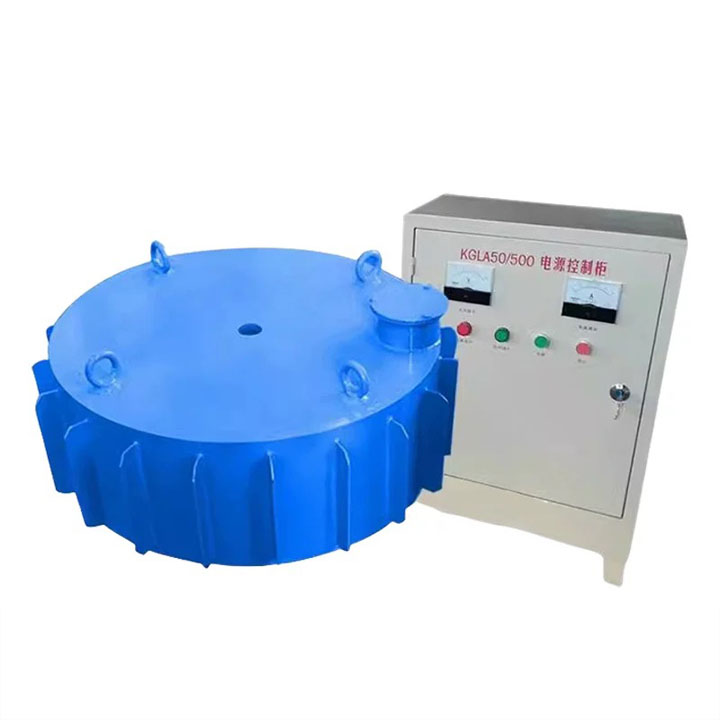
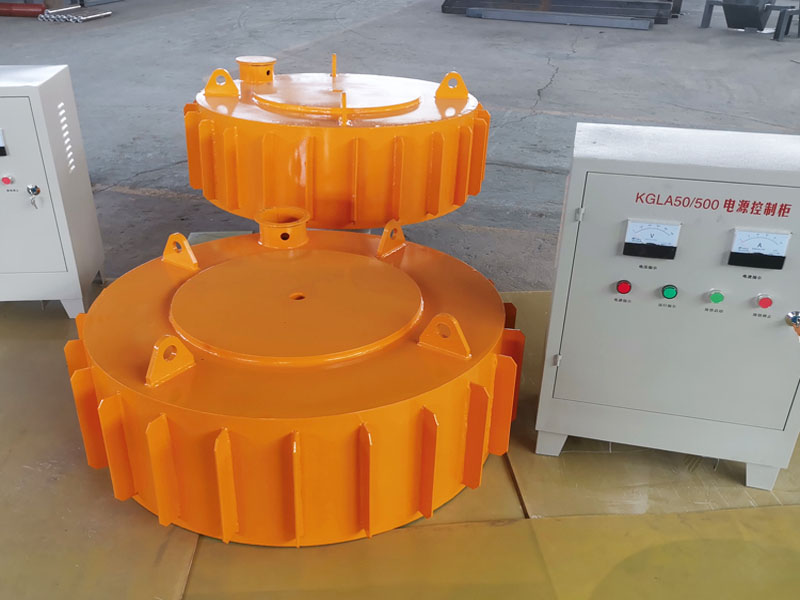
●Magnetic field source: Generate magnetic field through energized coil (electromagnet).
●Advantages: High and adjustable magnetic field strength (achieved by adjusting the current), magnetic field gradient can also be designed to be higher, magnetic field disappears after power failure (convenient for cleaning mechanical blockage), suitable for processing weak magnetic minerals.
●Disadvantages: Requires excitation power supply, high energy consumption, equipment heating requires cooling system, relatively complex structure, high cost, and high maintenance requirements.
●Magnetic field source: Use permanent magnetic materials (such as NdFeB, ferrite, aluminum nickel cobalt, etc.) to generate magnetic field.
●Advantages: Relatively simple structure, no excitation power supply required, low energy consumption, low operating cost, easy maintenance, stable magnetic field, not easy to heat up.
●Disadvantages: The magnetic field strength is relatively fixed (cannot be adjusted at will), which may be limited when processing extremely high or weak magnetic materials, and the price of strong permanent magnets is relatively high.
●Main applications: roughing, scavenging, iron removal (widely used), especially economical and efficient when processing highly magnetic minerals (such as magnetite).
●Magnetic field source: Generate magnetic field through energized coil (electromagnet).
●Advantages: High and adjustable magnetic field strength (achieved by adjusting the current), magnetic field gradient can also be designed to be higher, magnetic field disappears after power failure (convenient for cleaning mechanical blockage), suitable for processing weak magnetic minerals.
●Disadvantages: Requires excitation power supply, high energy consumption, equipment heating requires cooling system, relatively complex structure, high cost, and high maintenance requirements.
●Main applications: selection (high grade requirements for magnetic products), processing of weakly magnetic minerals (such as hematite, limonite, manganese ore, etc.), and occasions requiring high field strength or adjustable magnetic field.
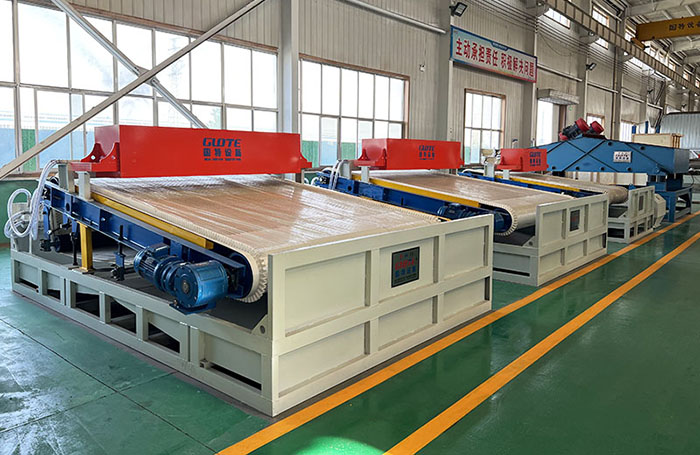

2Classification by selection medium
1. Dry magnetic separator:
●Working environment: sorting in the air.
●Advantages: no water is needed, suitable for arid and water-scarce areas or materials that cannot be exposed to water (such as certain chemical raw materials, coal), the process is relatively simple, and the product is dry.
●Disadvantages: sorting accuracy is usually not as good as wet type, dust is large (dust removal system is required), high requirements for material particle size uniformity, and poor sorting effect of fine-grained materials.
●Main applications: pre-selection and discarding of large ore (such as large magnetite), sorting of coarse-grained materials, coal gangue removal, non-metallic ore iron removal, construction waste/scrap steel recycling, abrasive/refractory material purification, etc.
2. Wet magnetic separator:
●Working environment: sorting in water or magnetic liquid.
●Advantages: high sorting accuracy, especially good at processing fine-grained and micro-fine-grained materials, low dust pollution, and good material fluidity.
●Disadvantages: water is required, tailings slurry needs to be treated, the equipment structure is relatively complex (involving slurry feeding, dehydration, etc.), and the product needs to be dehydrated and dried.
●Main applications: fine-grained iron ore selection, deep iron removal of non-metallic ores (such as quartz sand, feldspar, kaolin), seaside sand ore selection, sewage treatment (recovery of magnetic flocs), etc.
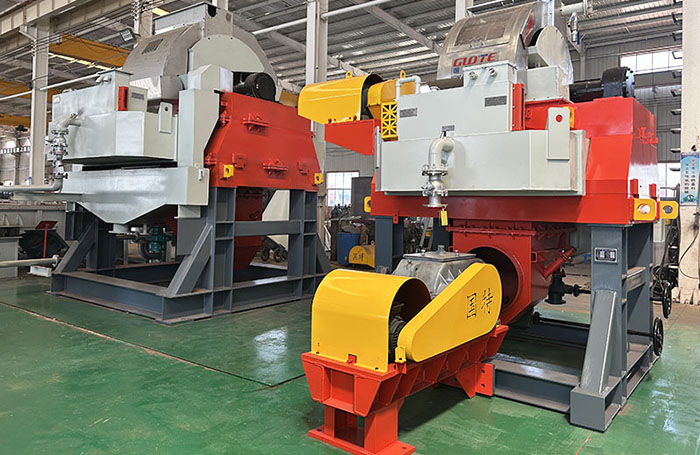

3Classification by magnetic field intensity
1. Weak magnetic field separator:
●Magnetic field strength: usually < 2000 Gauss (0.2 T).
●Function: mainly used for sorting strong magnetic minerals (such as magnetite, pyrrhotite) or iron removal.
●Typical equipment: permanent magnetic drum magnetic separator (wet/dry), permanent magnetic drum (magnetic pulley), belt iron remover, etc.
2. Medium magnetic field separator:
●Magnetic field strength: usually 2000 - 6000 Gauss (0.2 - 0.6 T).
●Function: used for sorting medium magnetic minerals or for more refined sorting (selection) of strong magnetic minerals.
●Typical equipment: some specially designed permanent magnetic drum magnetic separators, electromagnetic drum magnetic separators, some permanent magnetic roller magnetic separators, etc.
3. Strong magnetic field separator:
●Magnetic field strength: usually > 6000 Gauss (0.6 T), up to tens of thousands or even 200,000 Gauss (2 T).
●Function: Specially used for sorting weakly magnetic minerals (such as hematite, limonite, siderite, manganese ore, wolframite, ilmenite, etc.) and removing extremely fine weakly magnetic iron and titanium impurities from non-metallic ores.
●Typical equipment: electromagnetic induction magnetic separator, flat plate wet high-intensity magnetic separator, vertical ring high-gradient magnetic separator, etc.
●Magnetic field strength: usually < 2000 Gauss (0.2 T).
●Function: mainly used for sorting strong magnetic minerals (such as magnetite, pyrrhotite) or iron removal.
●Typical equipment: permanent magnetic drum magnetic separator (wet/dry), permanent magnetic drum (magnetic pulley), belt iron remover, etc.
2. Medium magnetic field separator:
●Magnetic field strength: usually 2000 - 6000 Gauss (0.2 - 0.6 T).
●Function: used for sorting medium magnetic minerals or for more refined sorting (selection) of strong magnetic minerals.
●Typical equipment: some specially designed permanent magnetic drum magnetic separators, electromagnetic drum magnetic separators, some permanent magnetic roller magnetic separators, etc.
3. Strong magnetic field separator:
●Magnetic field strength: usually > 6000 Gauss (0.6 T), up to tens of thousands or even 200,000 Gauss (2 T).
●Function: Specially used for sorting weakly magnetic minerals (such as hematite, limonite, siderite, manganese ore, wolframite, ilmenite, etc.) and removing extremely fine weakly magnetic iron and titanium impurities from non-metallic ores.
●Typical equipment: electromagnetic induction magnetic separator, flat plate wet high-intensity magnetic separator, vertical ring high-gradient magnetic separator, etc.
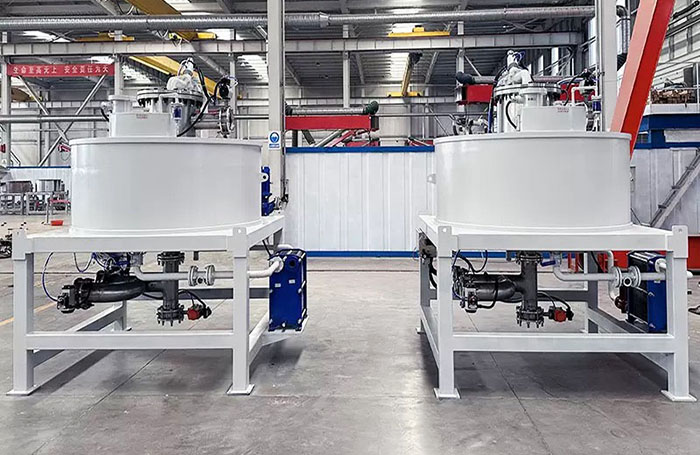

4Classification by magnetic system structure and working mode
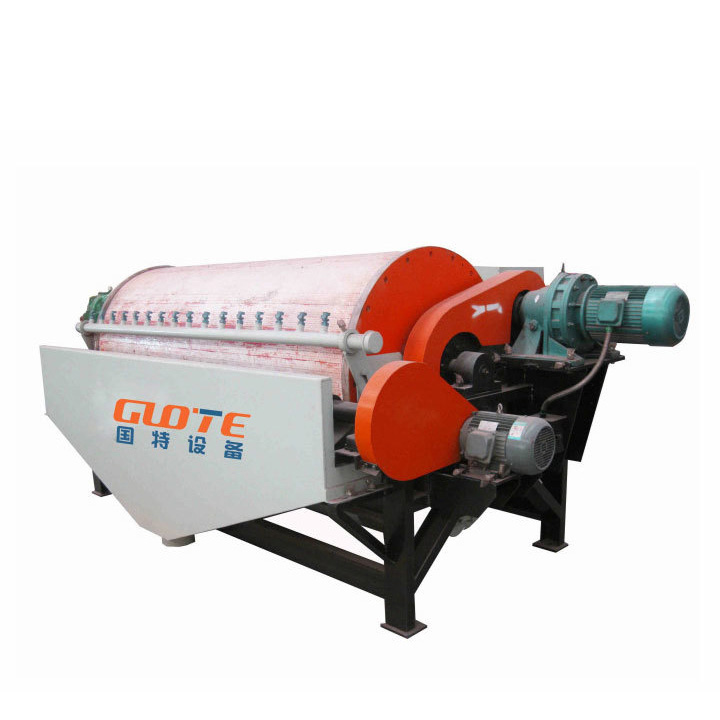
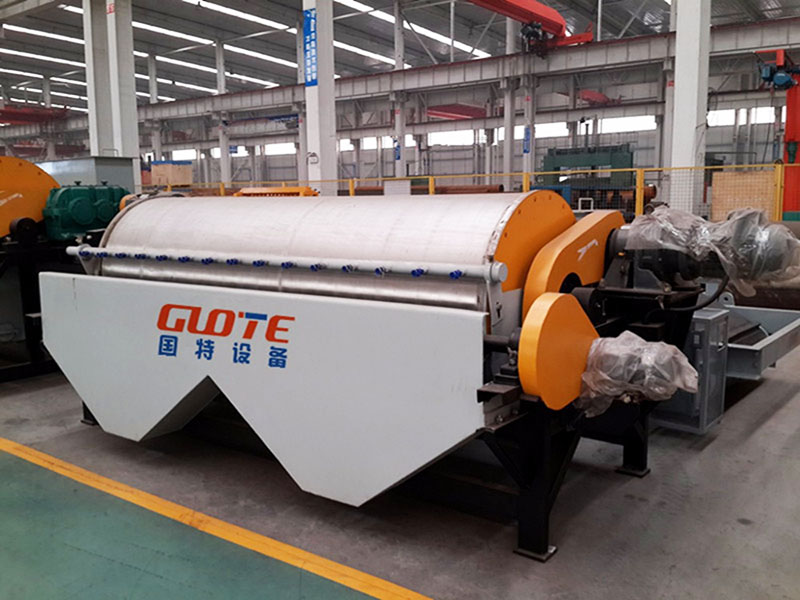
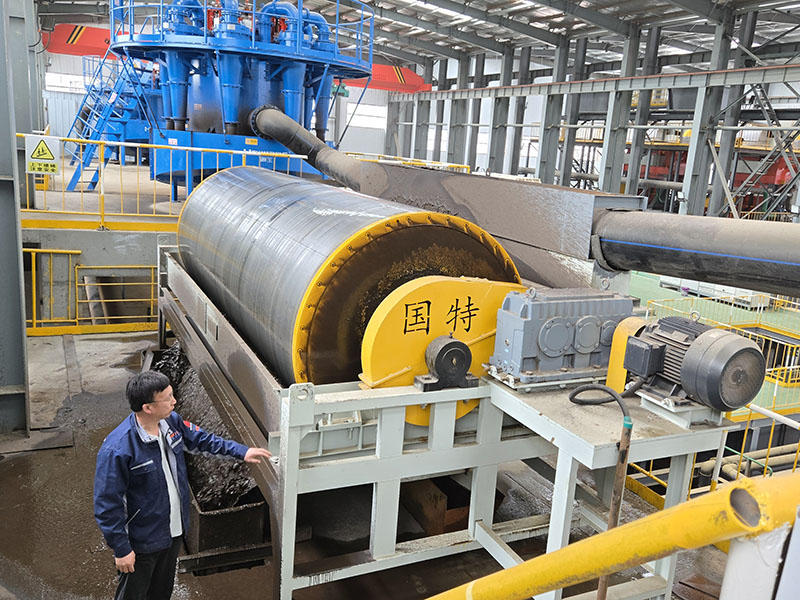
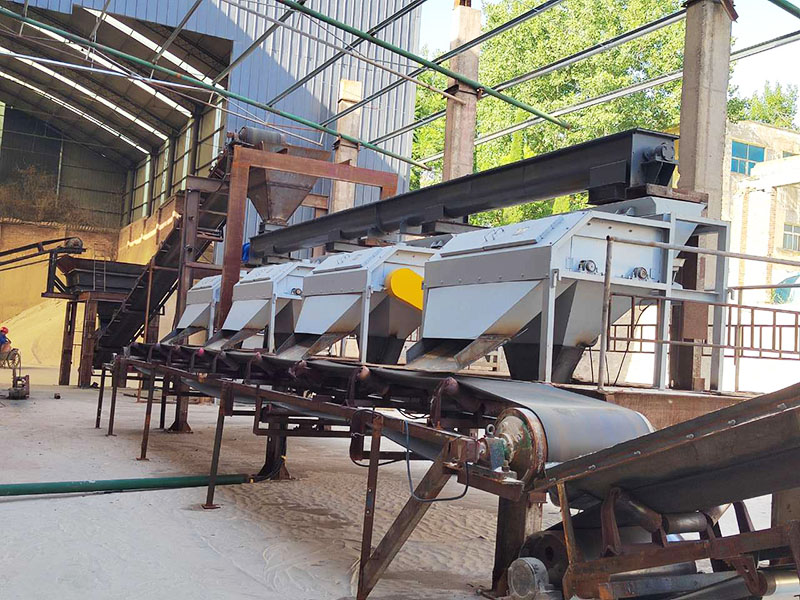
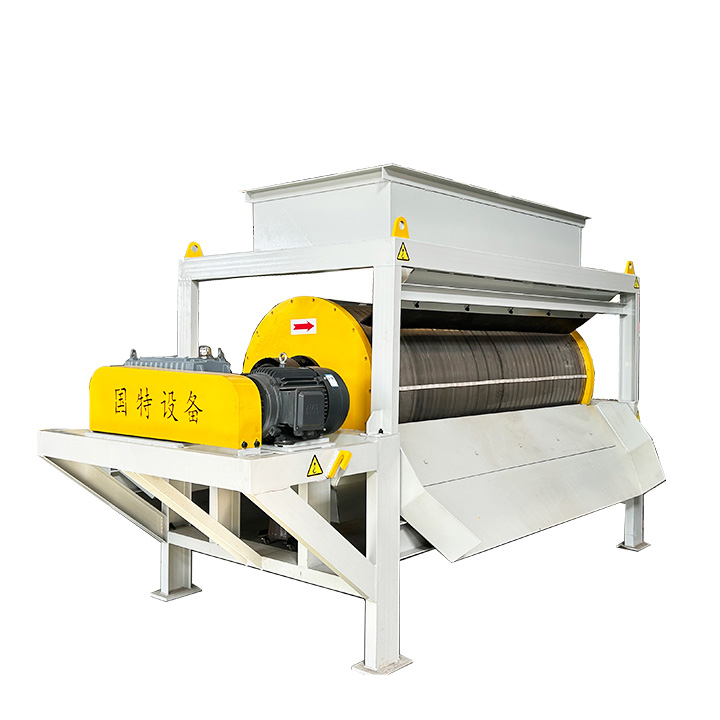
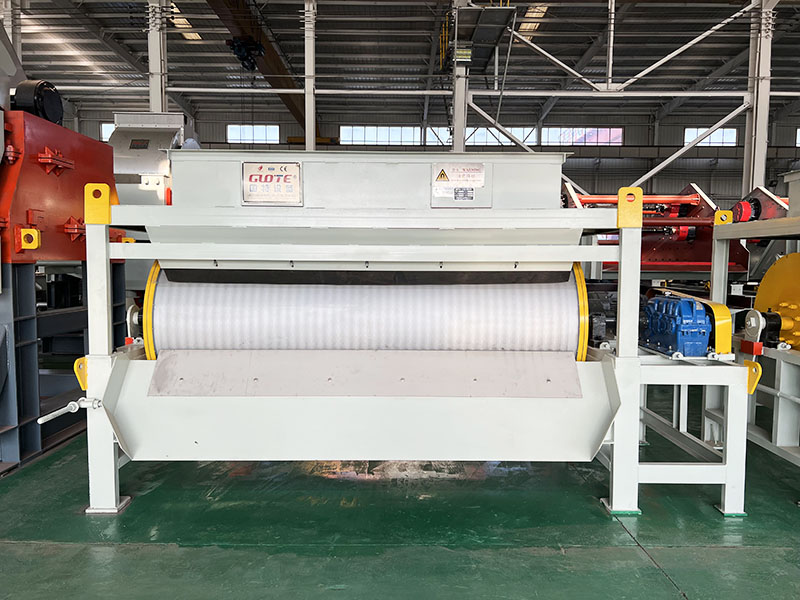
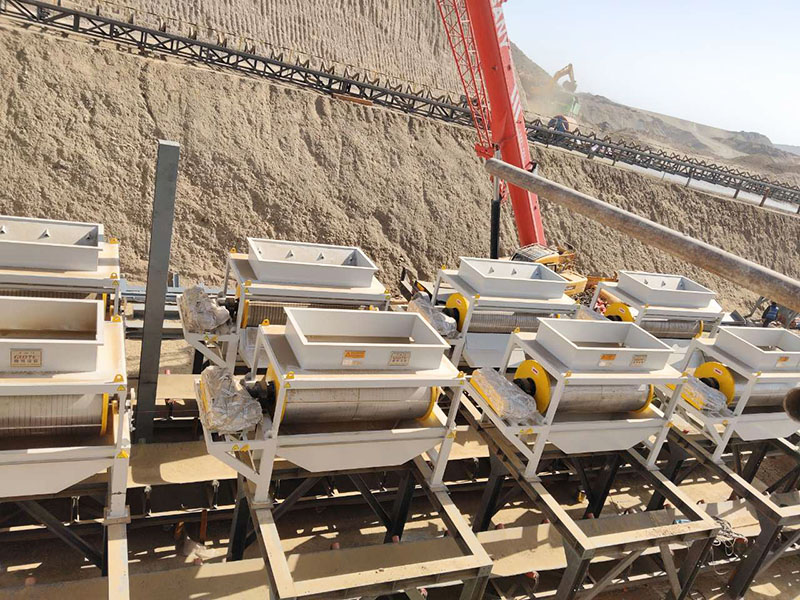
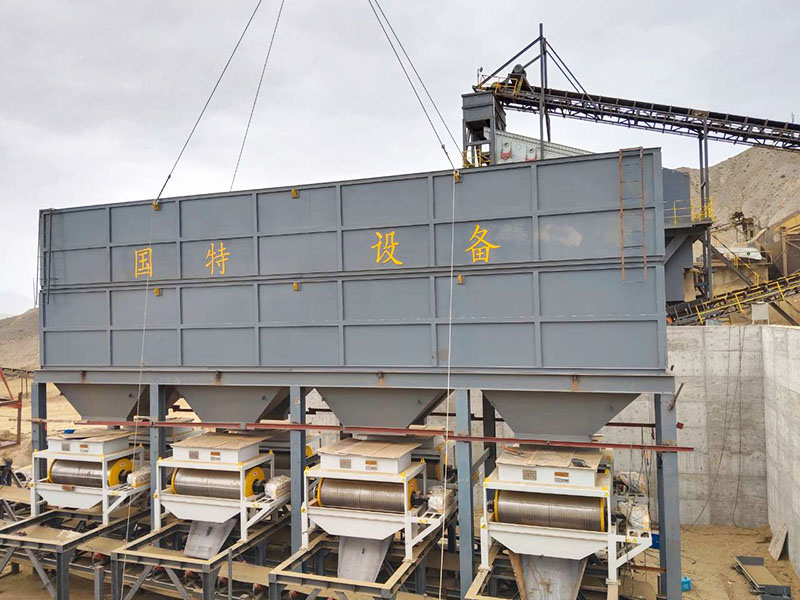
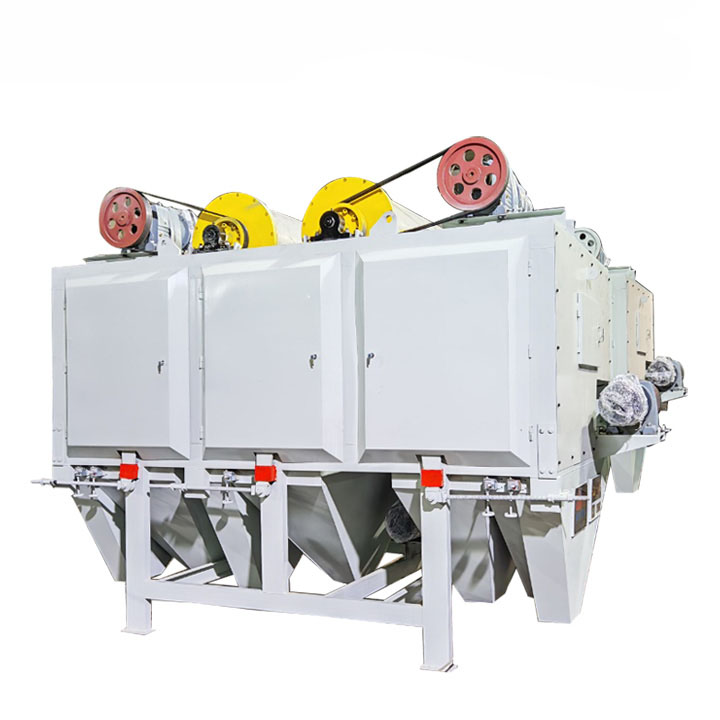
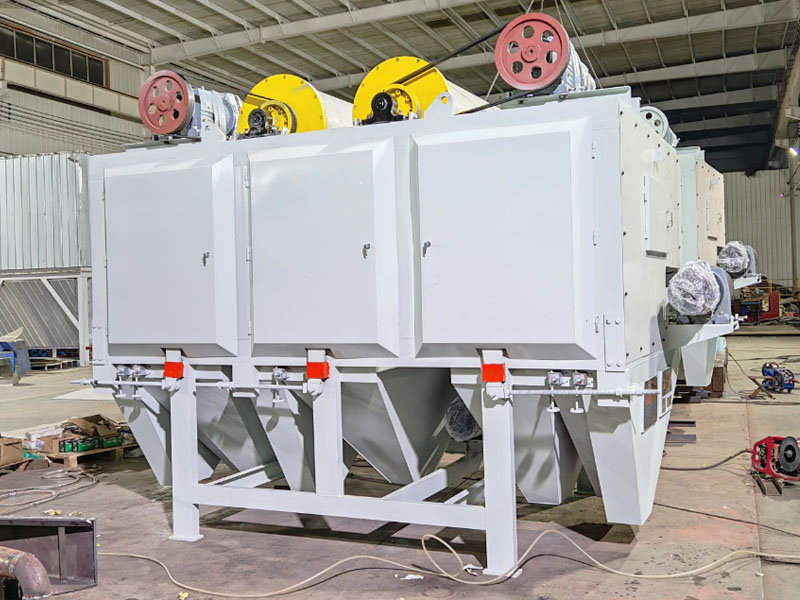
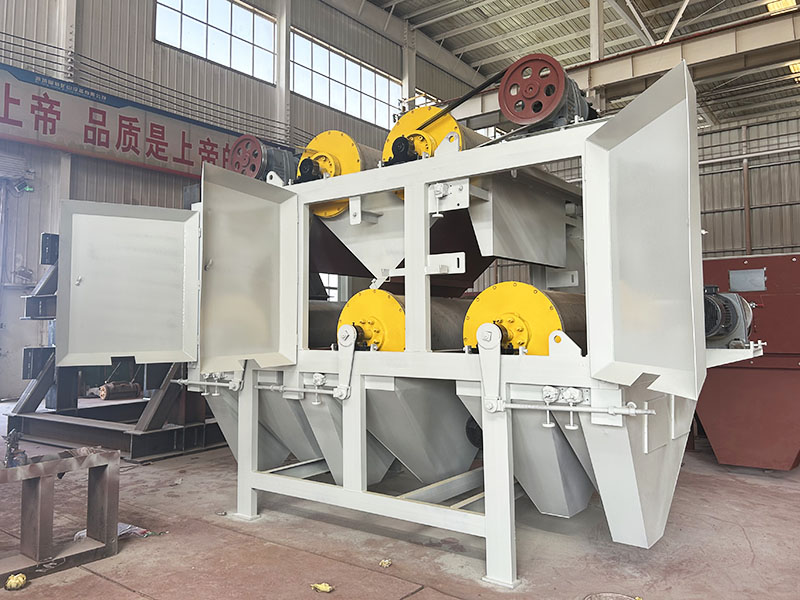
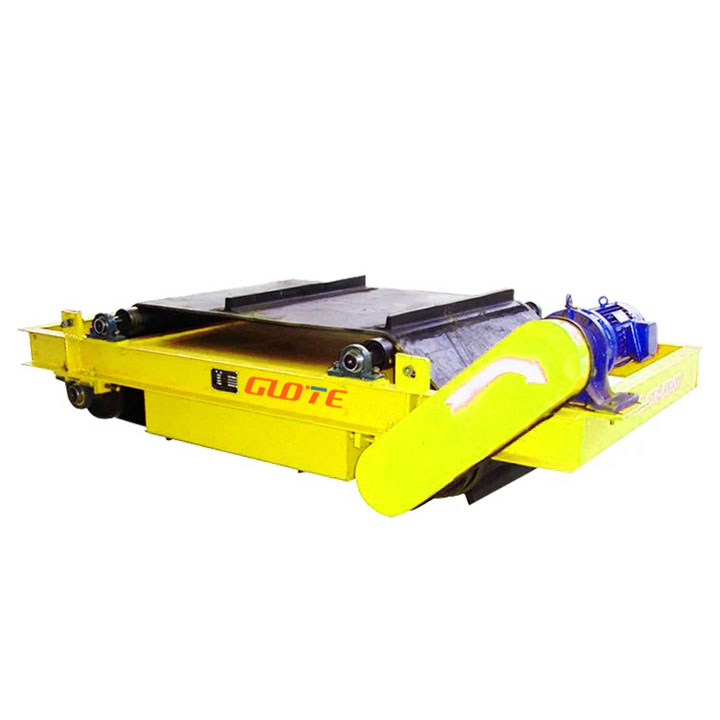
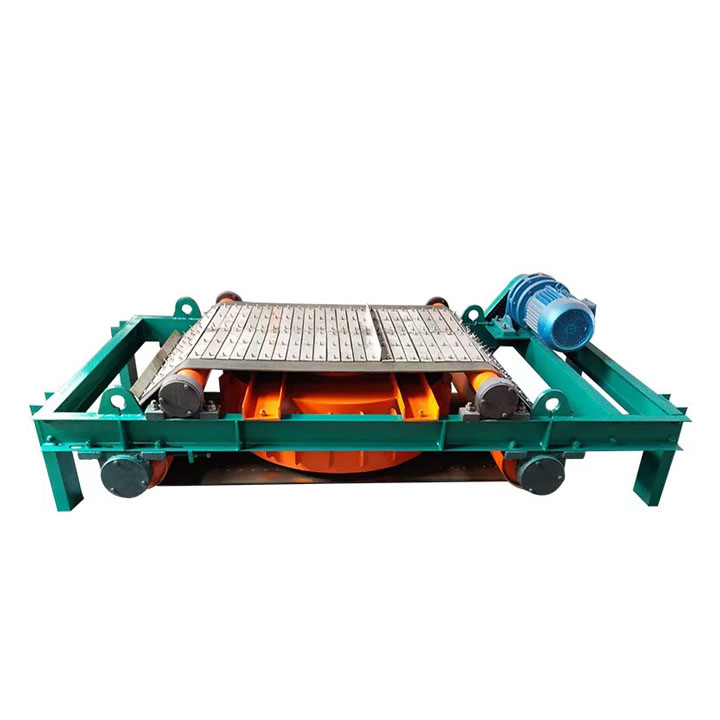
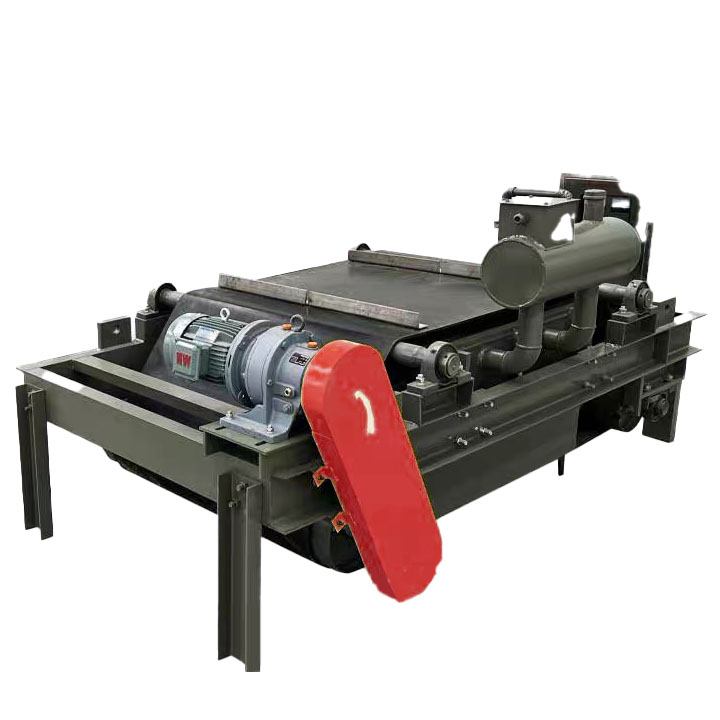
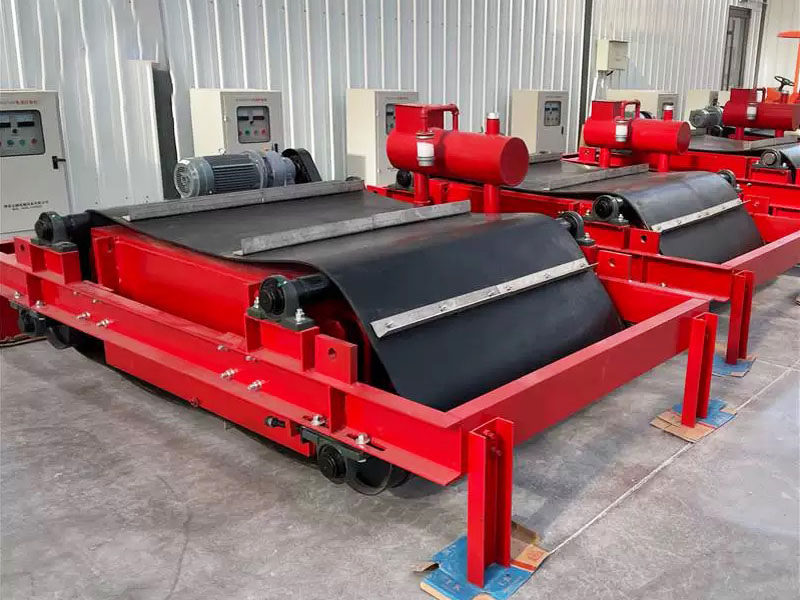
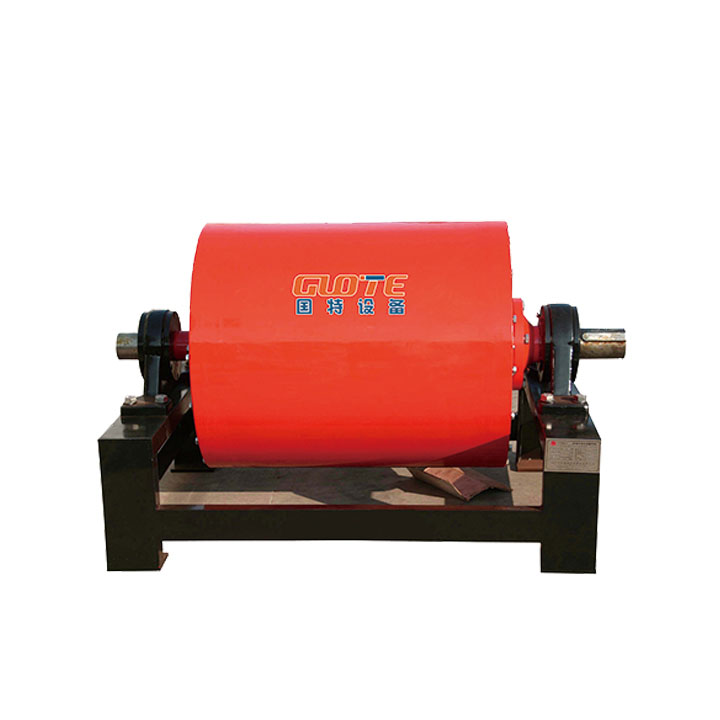
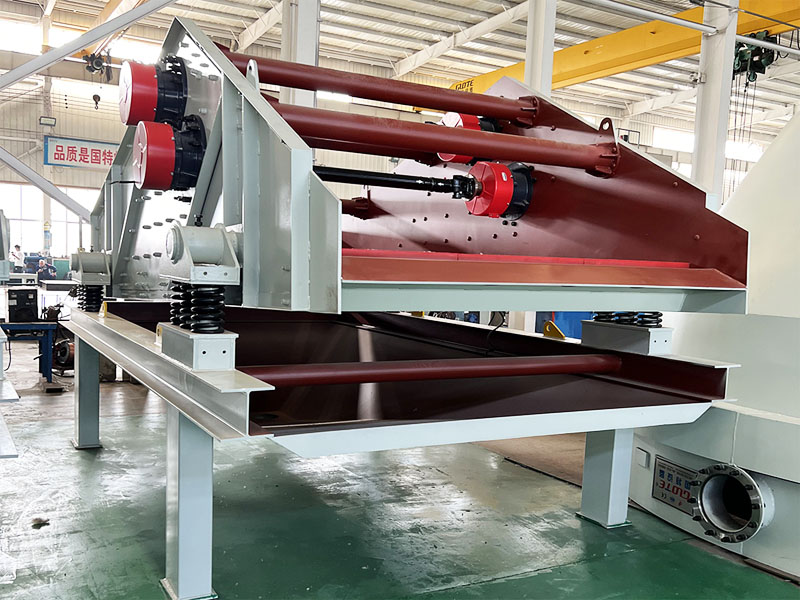
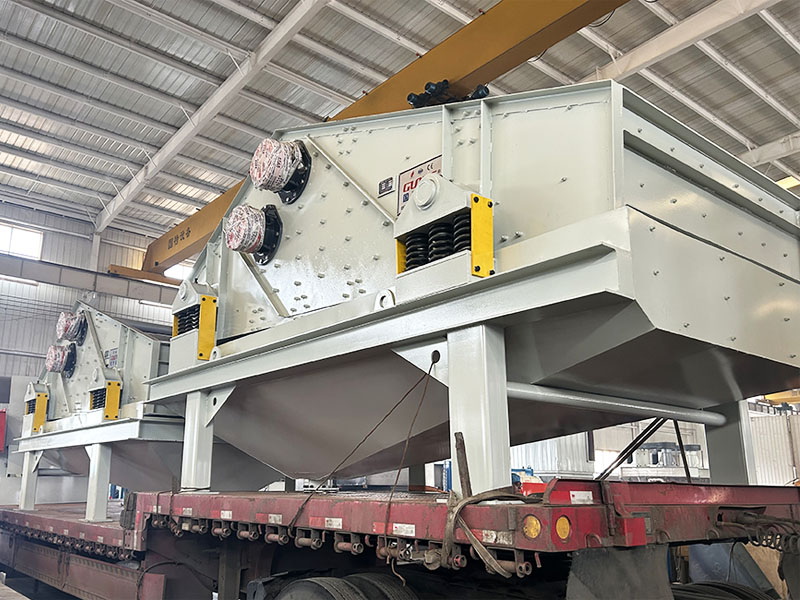
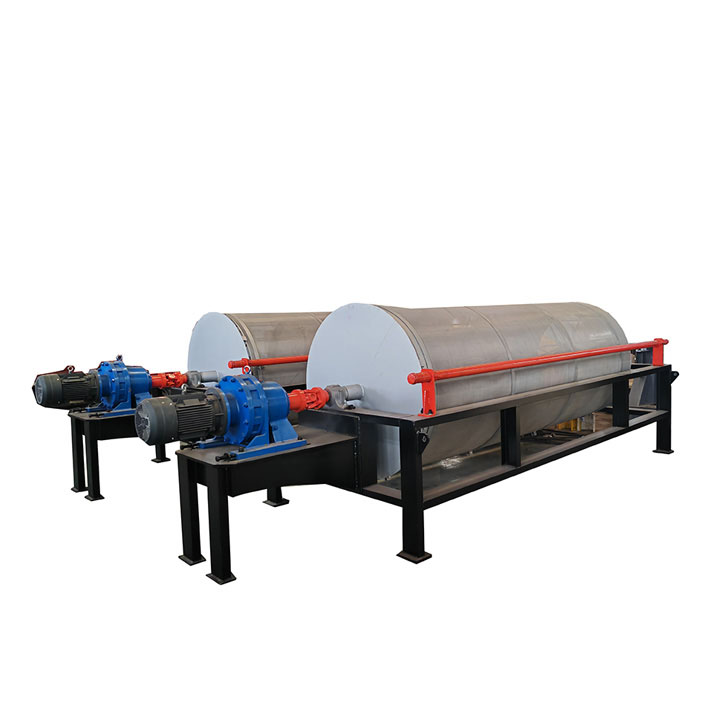
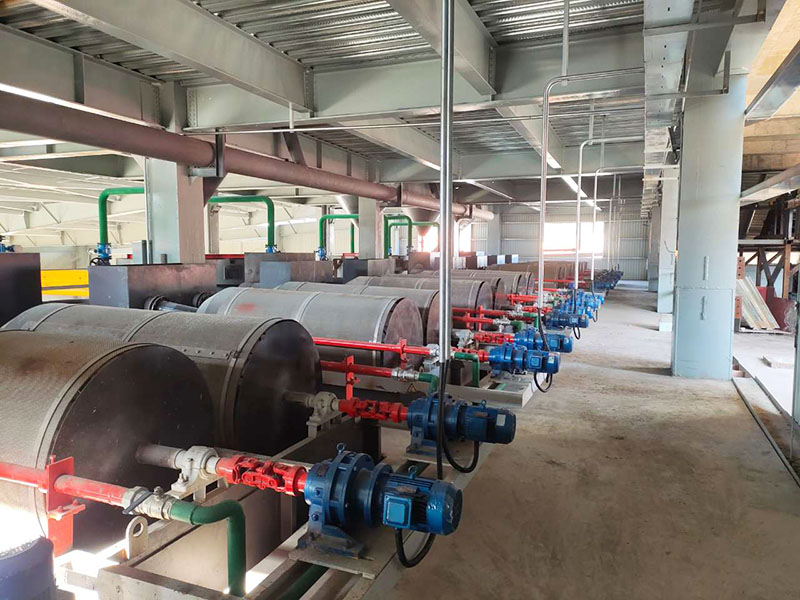
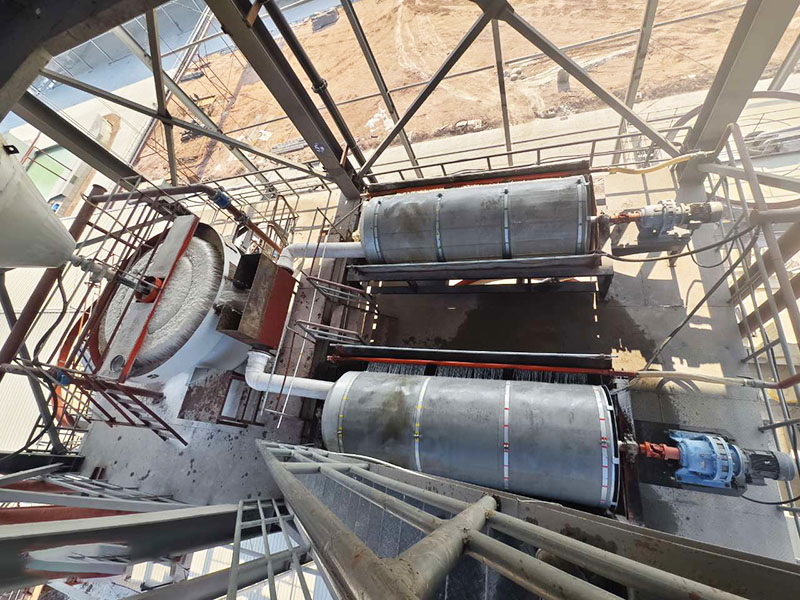
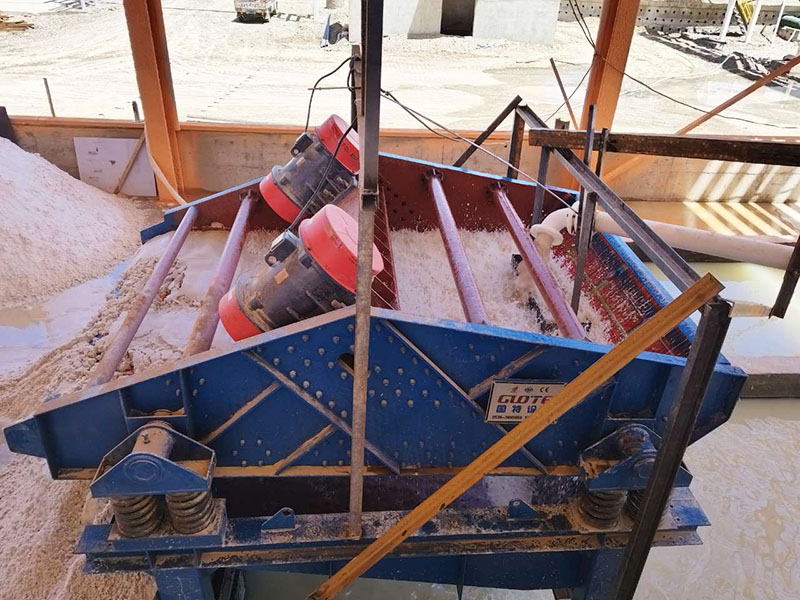
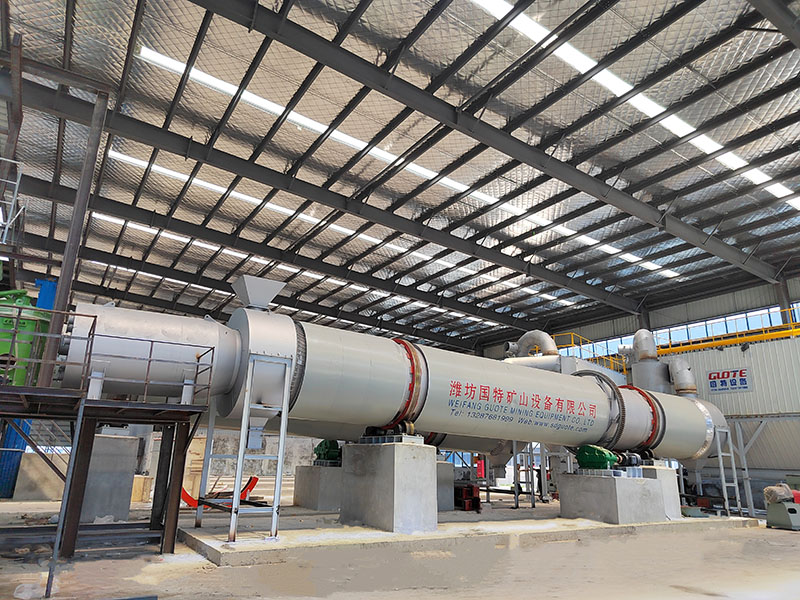
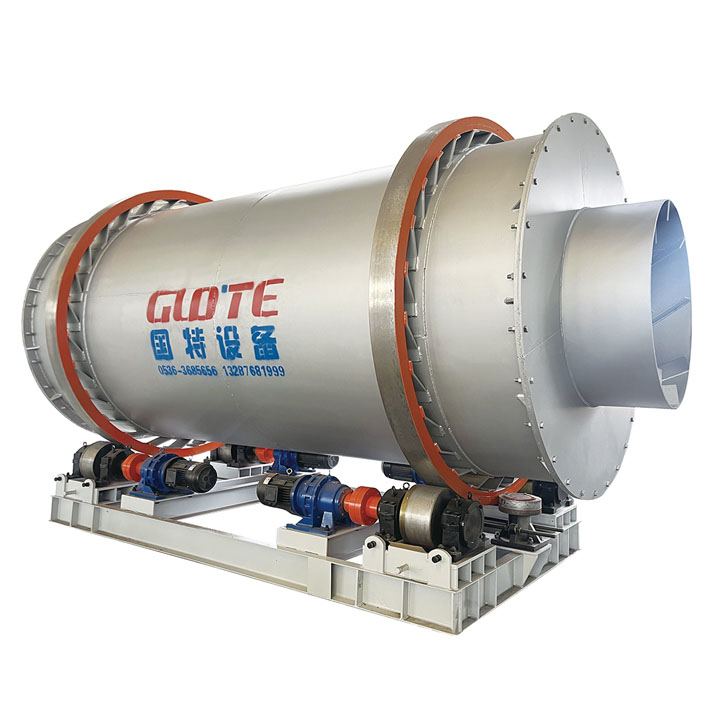
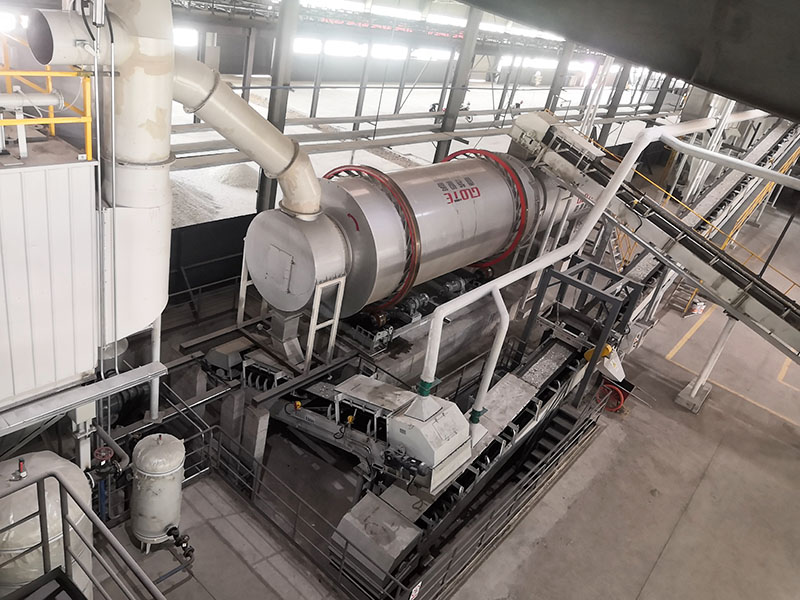
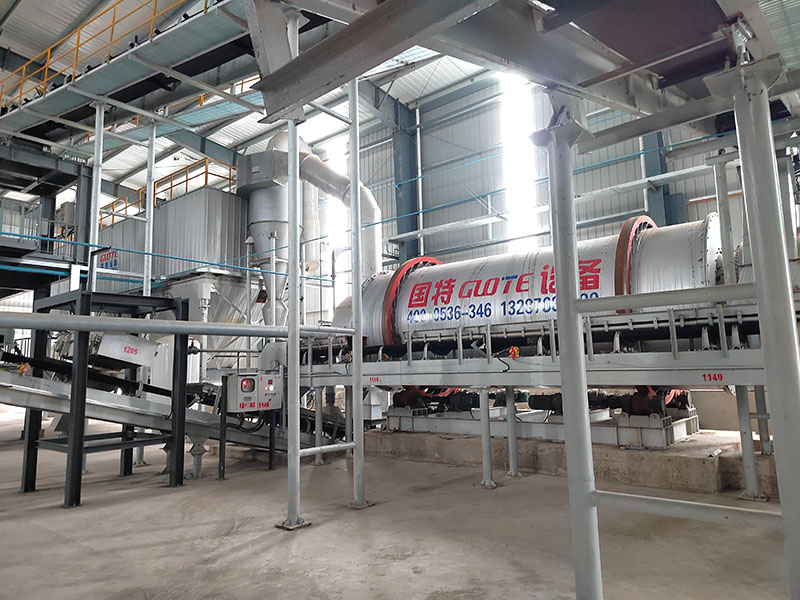
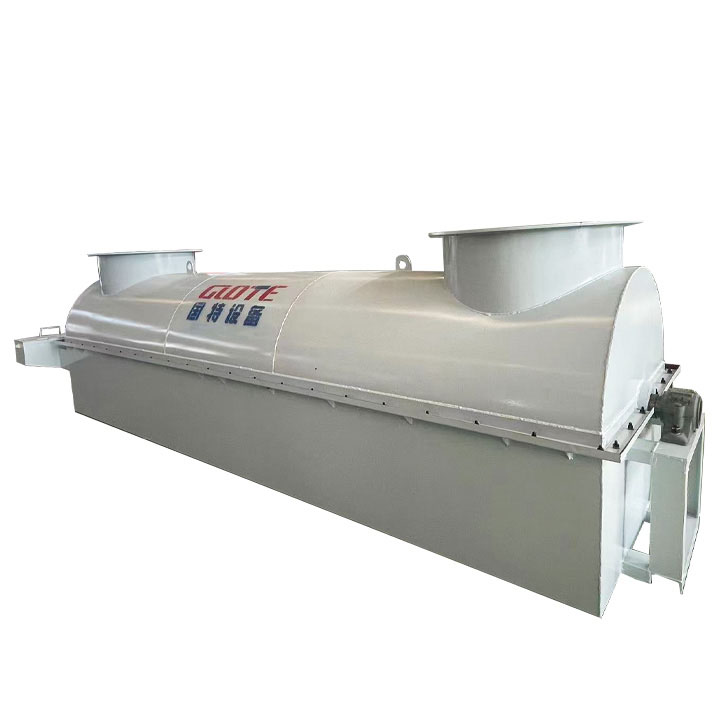
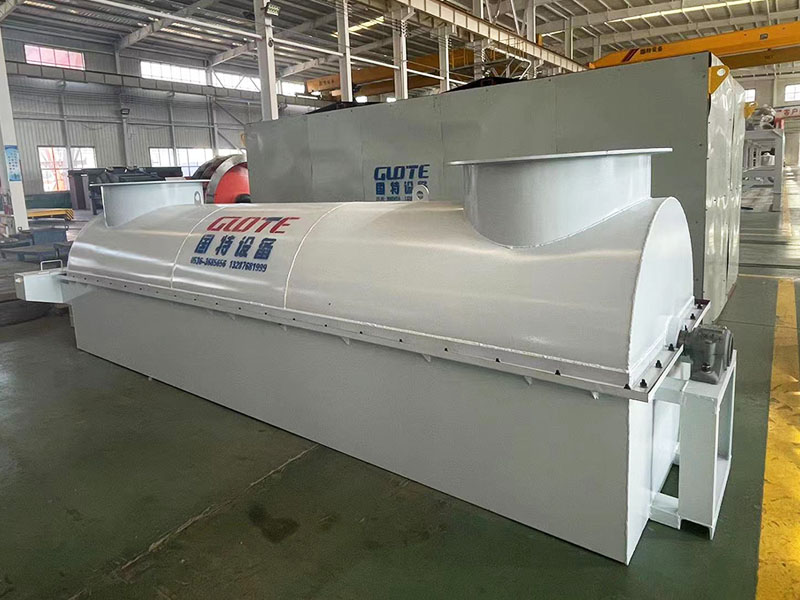
1. Drum magnetic separator:
●Structure: The core component is a non-magnetic (such as stainless steel) drum with a fixed magnetic system (permanent magnet or electromagnet) inside and rotating outside.
●Working mode: The material (dry powder or slurry) is fed to the drum surface. The magnetic particles are adsorbed on the drum surface and unloaded as the drum rotates to the non-magnetic area (or through a scraper or flushing water); non-magnetic particles are directly thrown away under the action of centrifugal force and gravity.
●Function: The most widely used. Permanent magnetic drum type is mainly used for strong magnetic mineral sorting and iron removal (wet type is used for fine sweeping and selection, and dry type is used for pre-selection and roughing); electromagnetic drum type can be used in occasions where the magnetic field needs to be adjusted.
●Wet/dry type: Both are widely used.
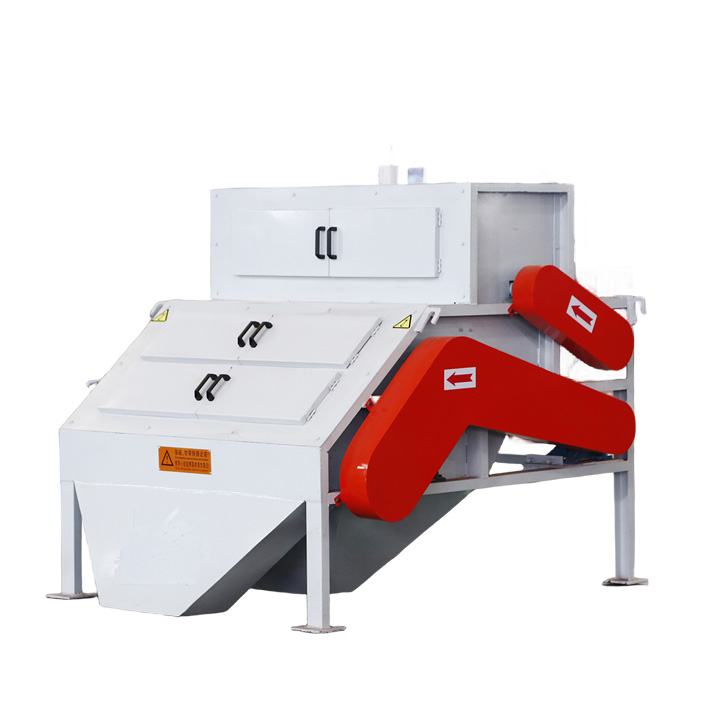
2. Roller magnetic separator:
●Structure: The core is one or more magnetic rollers (magnetic wheels) composed of permanent magnetic materials or electromagnetic coils.
●Working mode: The material (usually dry powder) is evenly fed to the surface of the magnetic roller or between the two rollers through a vibrating feeder. Magnetic materials are adsorbed on the roller surface or the trajectory is deviated, and non-magnetic materials fall freely. There are single roller, double roller (multi-stage sorting), multi-roller series and other forms.
●Function: Mainly used for dry sorting. Permanent magnetic roller is often used for iron removal and sorting of medium-sized materials (such as quartz sand, plastic particles); induction roller (strong magnetic field) is a classic dry equipment for processing weakly magnetic minerals.
●Dry type is the main method.
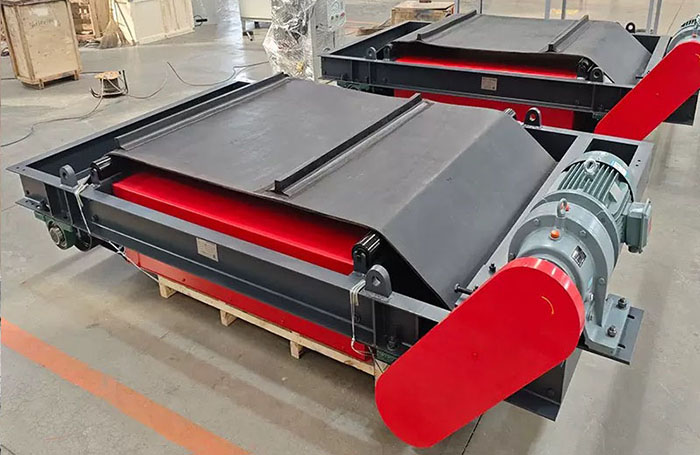
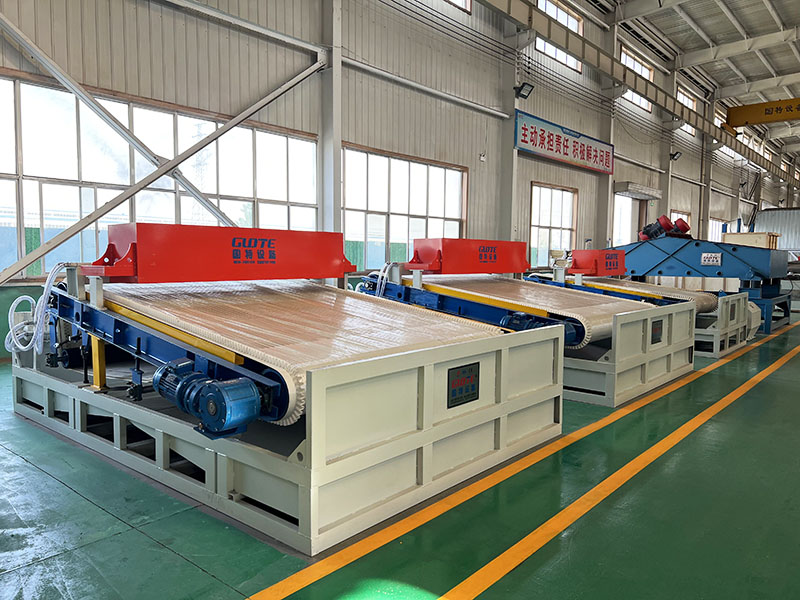
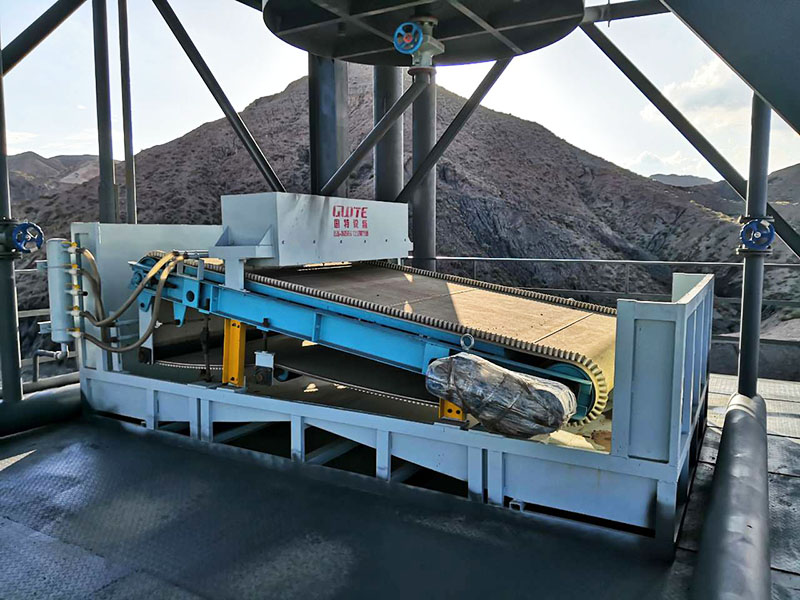
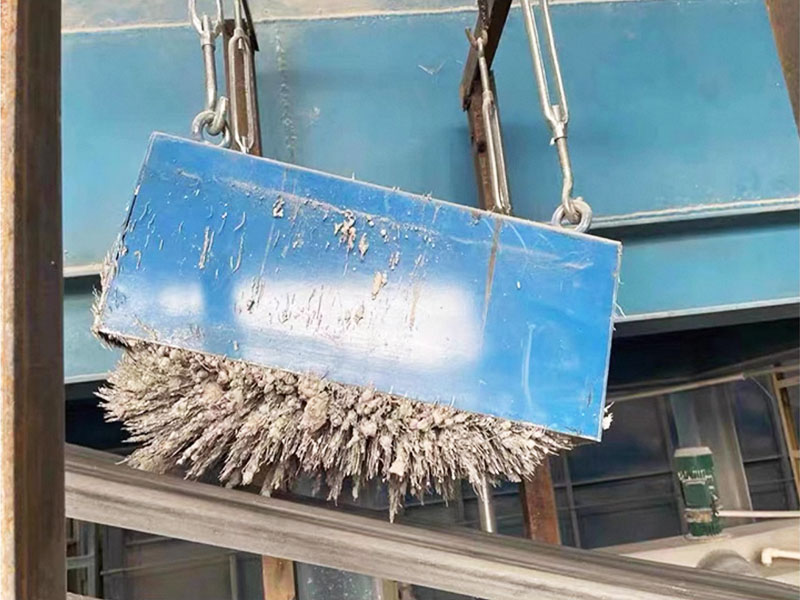
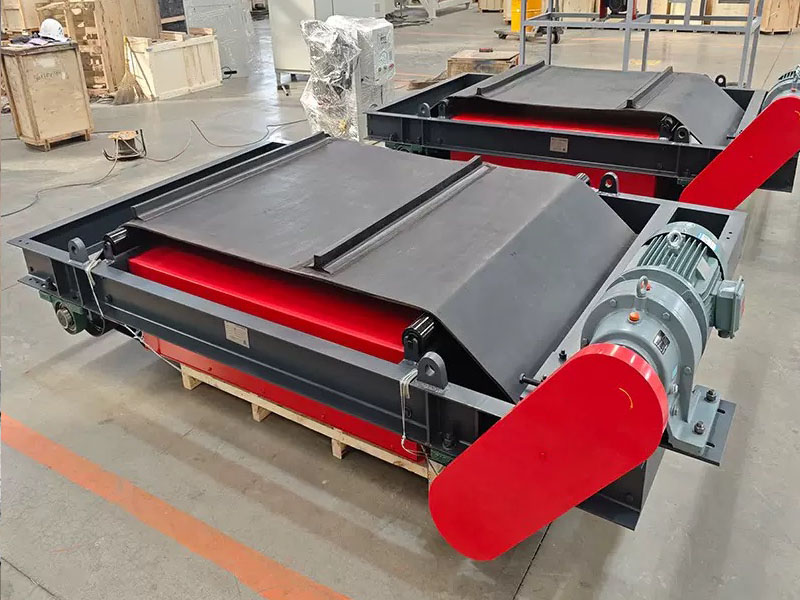
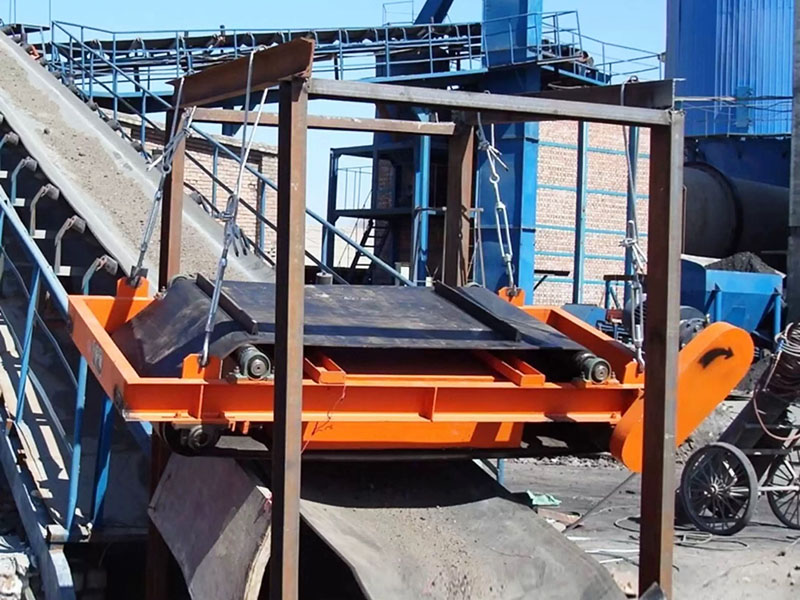
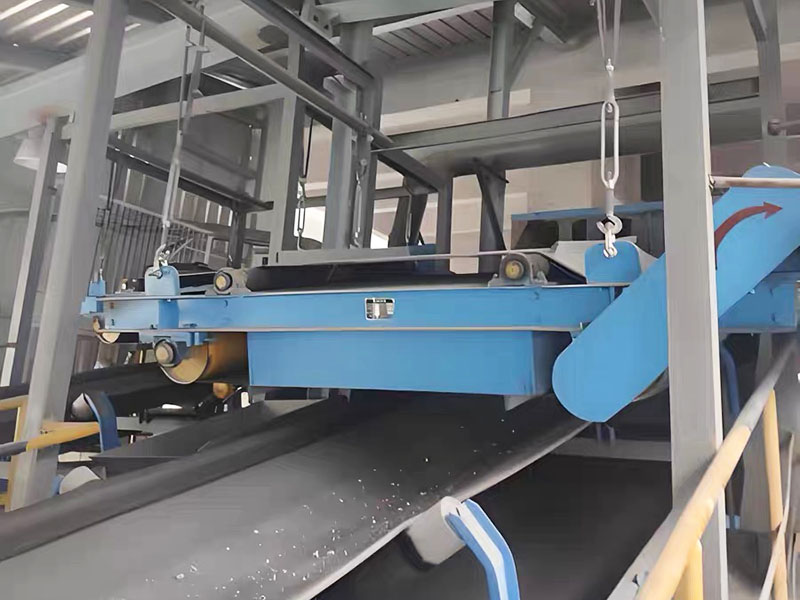
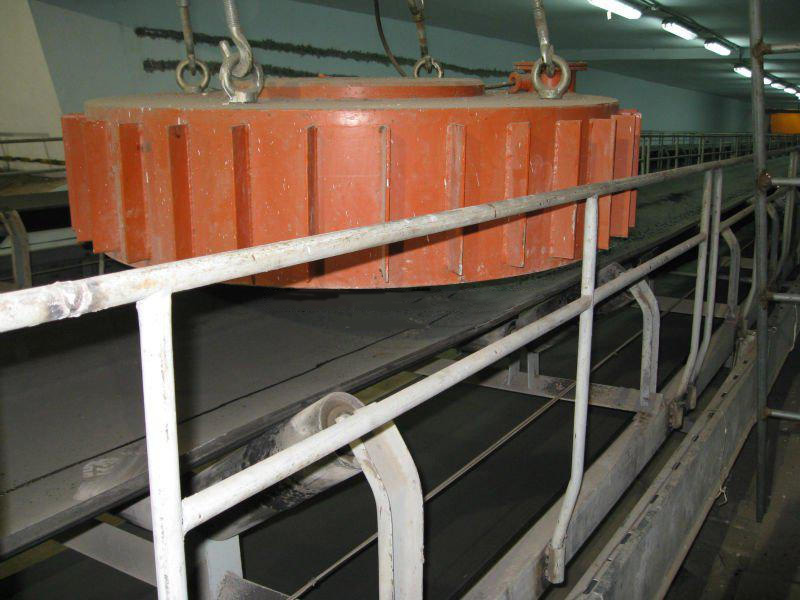
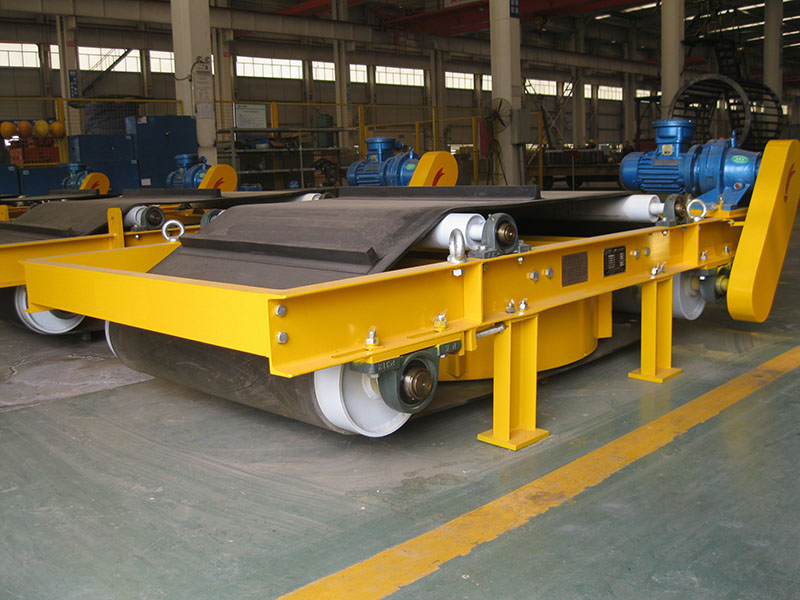
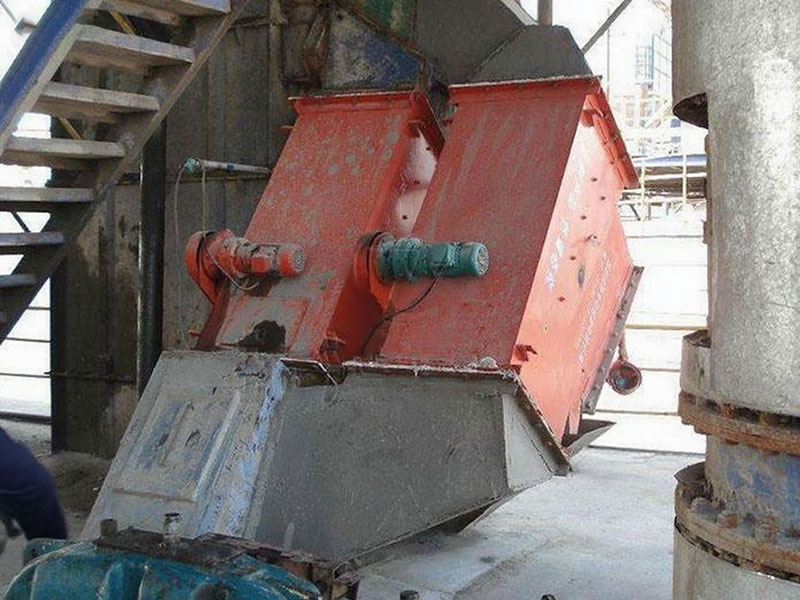
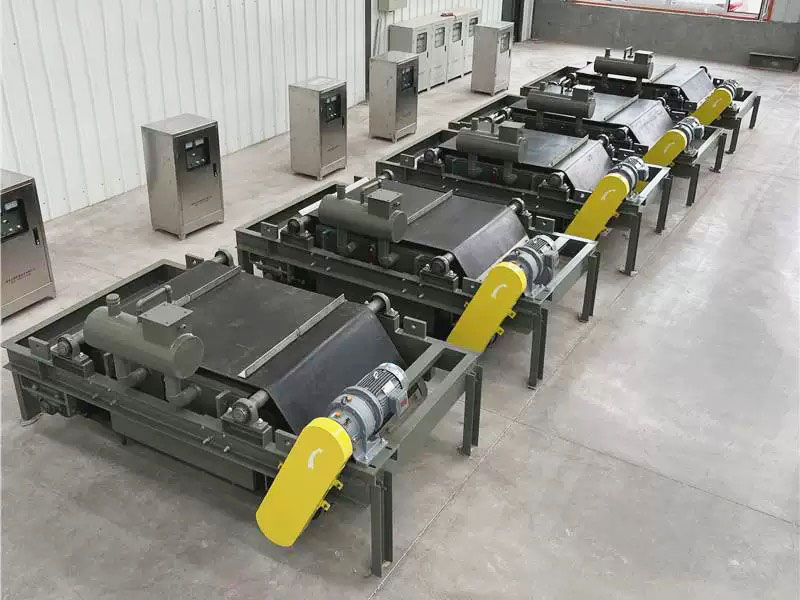
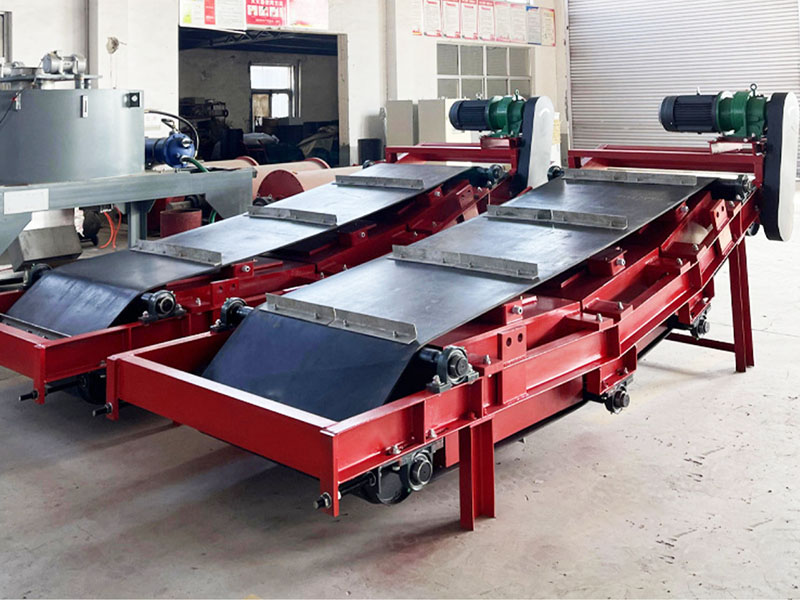
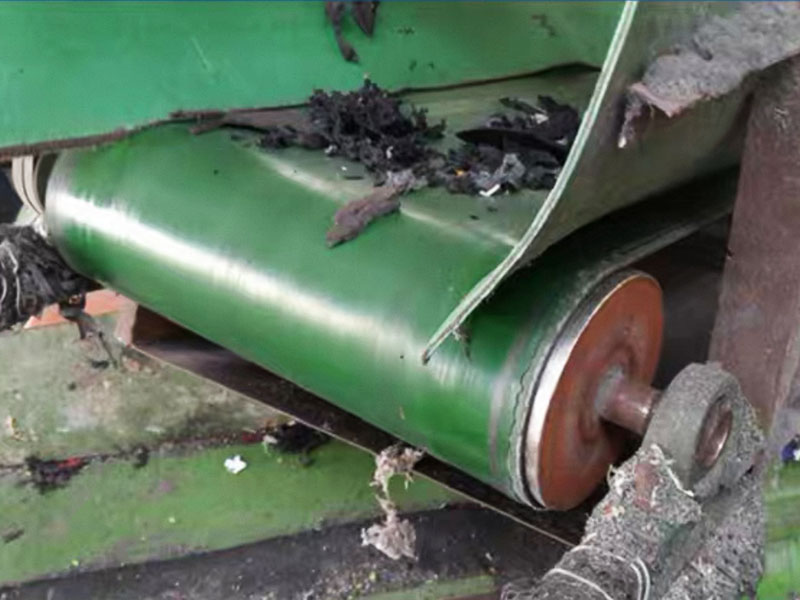
3. Belt magnetic separator/iron remover:
●Structure: including suspended iron remover (magnetic source fixed) and belt magnetic separator (magnetic source under or above the belt). Strong belt iron removers usually have built-in iron unloading belts.
●Working mode: Materials (bulk or packaged) are transported by conveyor belts passing under (suspended) or above (some belt machines). Ferromagnetic impurities are adsorbed on the surface of the iron remover or on the belt, and then taken away by the automatic iron unloading mechanism (such as the iron discarding belt).
●Function: Mainly used for iron removal protection (protection of subsequent equipment such as crushers, grinders, conveyor belts, etc.), and also used to recover ferromagnetic materials from bulk materials (such as coal, grain, chemical raw materials, garbage). It is one of the most widely used magnetic separation equipment.
●Dry type (materials are transported in the air).
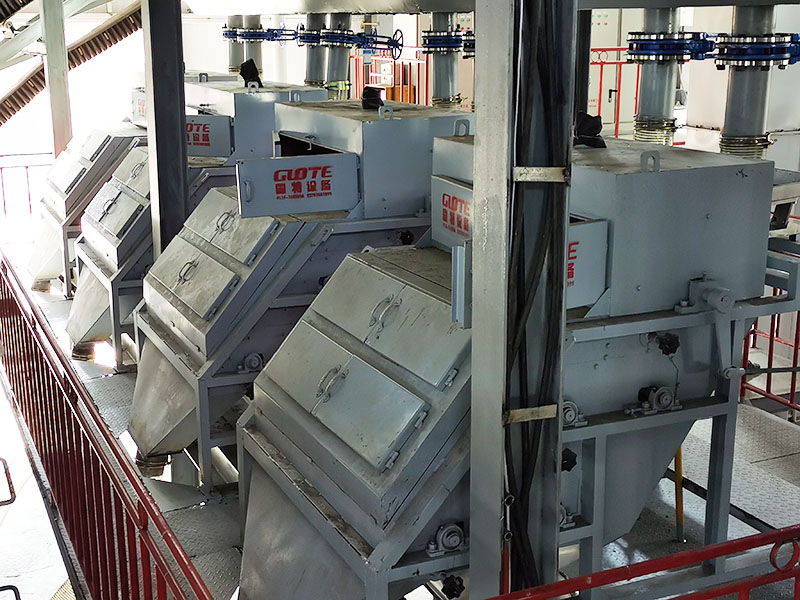
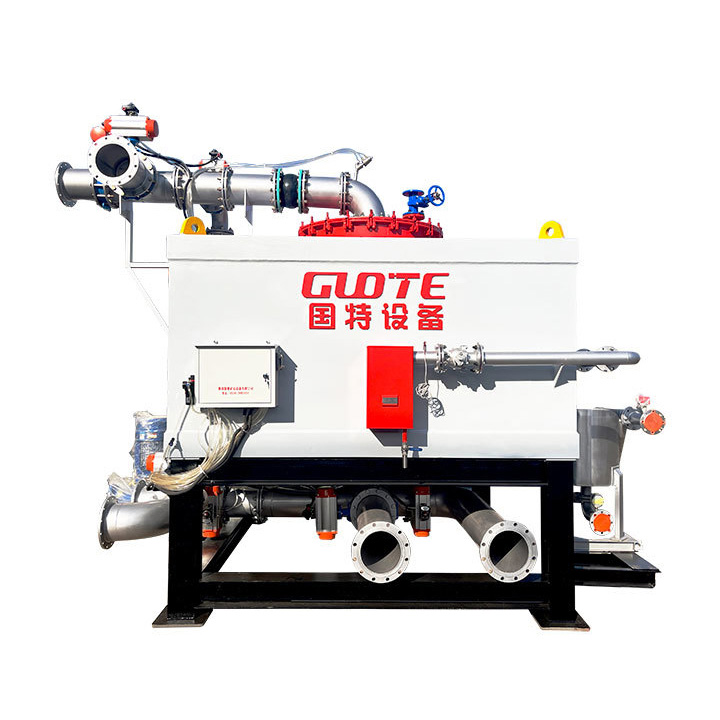
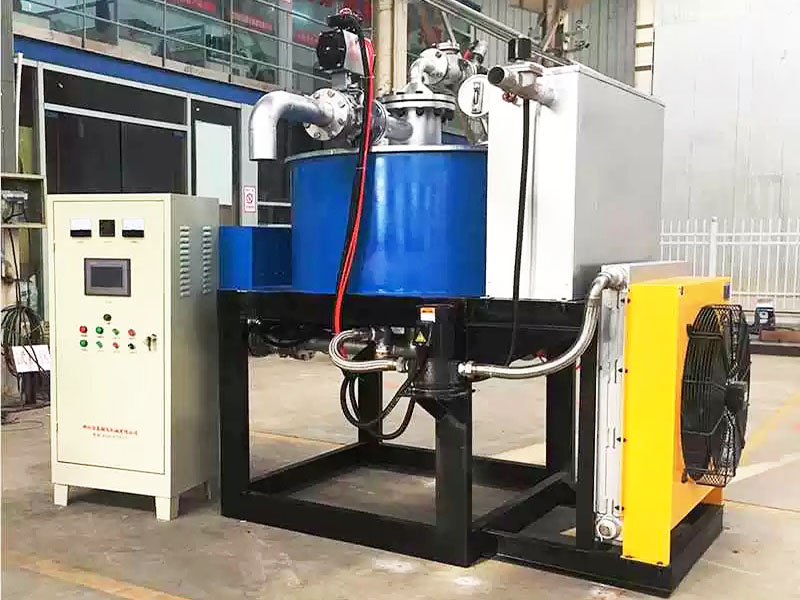
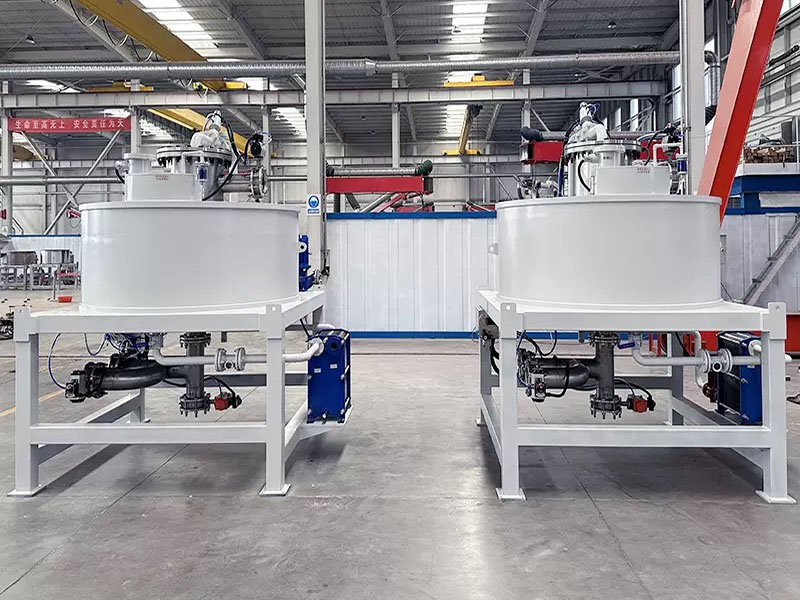
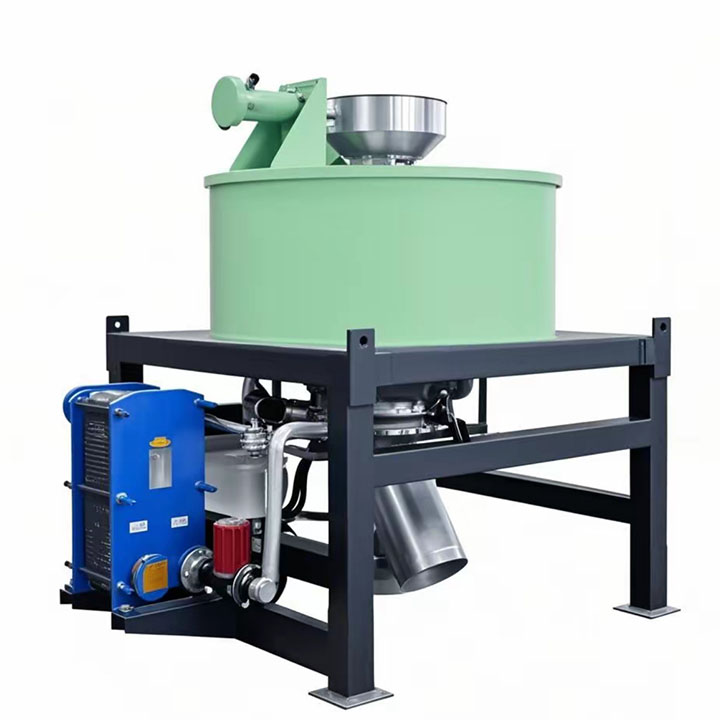
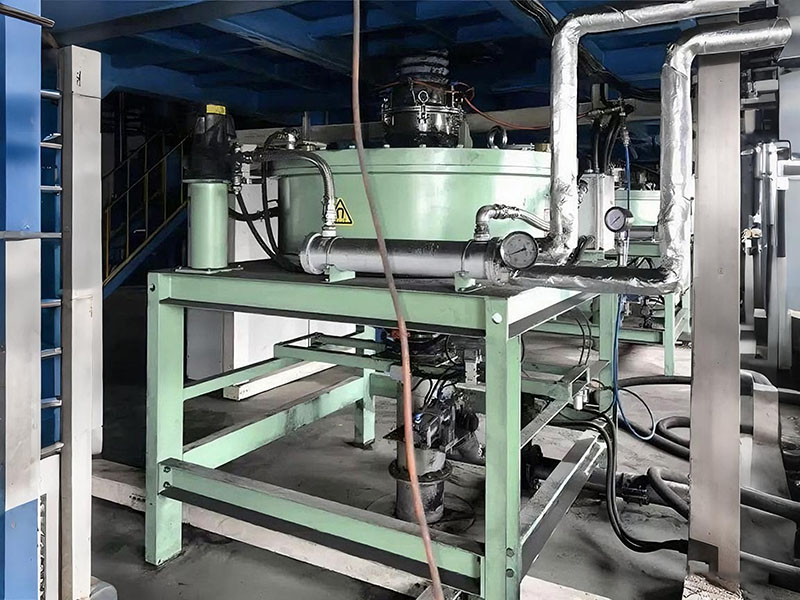
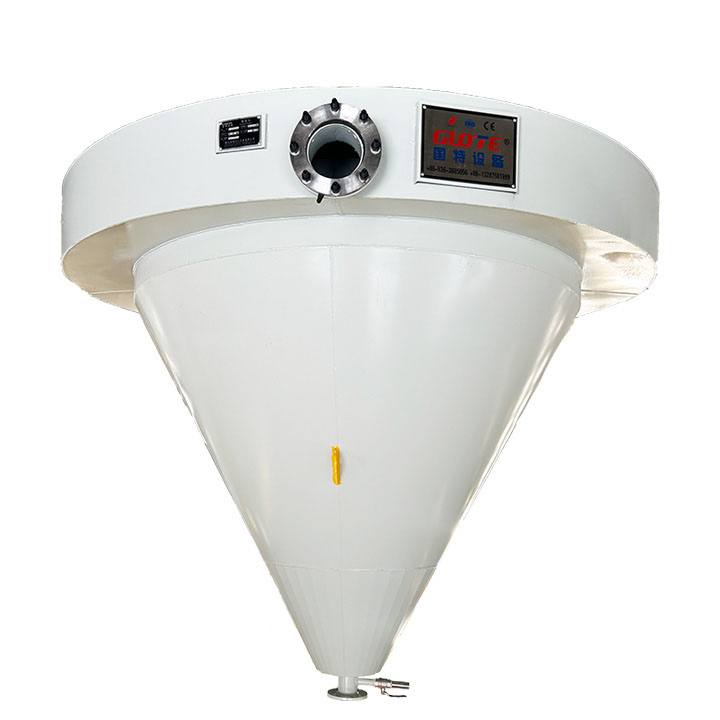
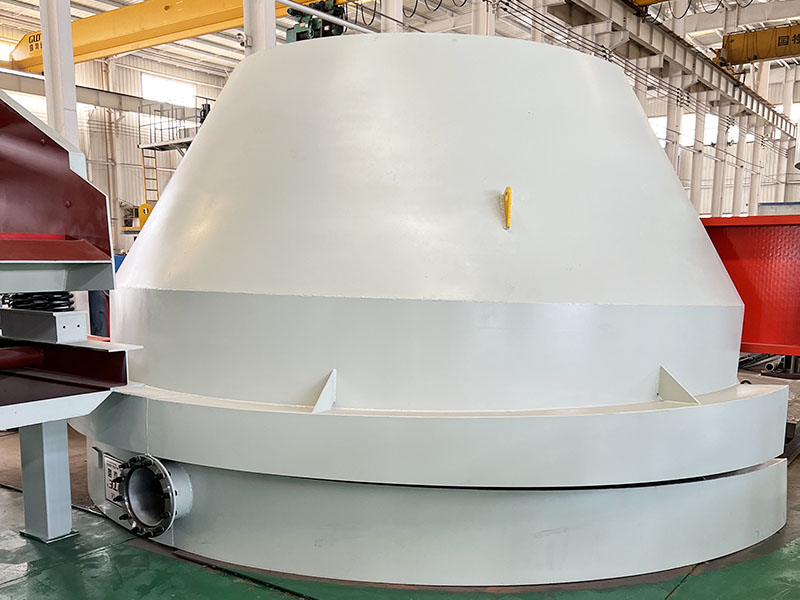
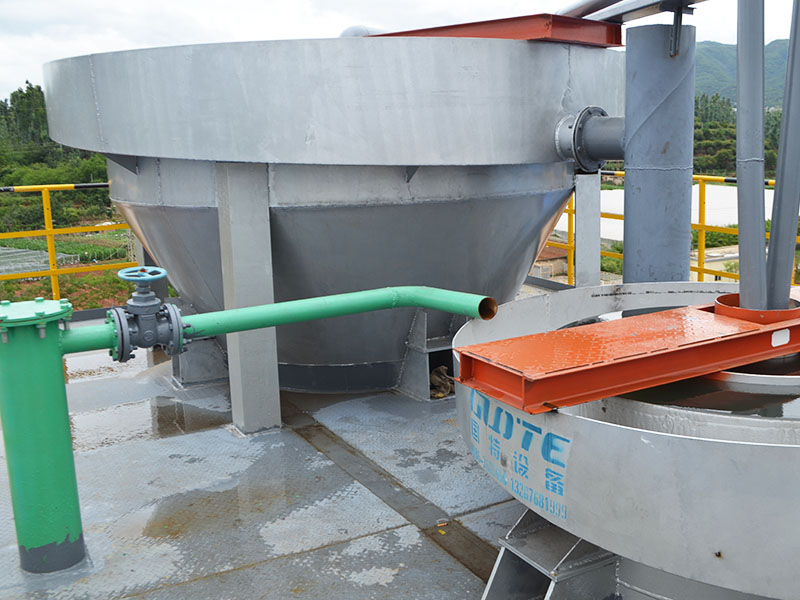
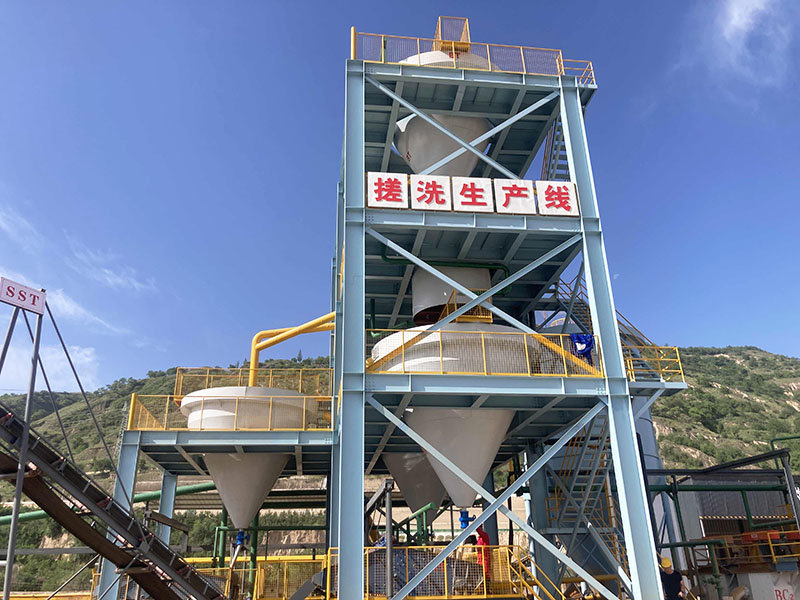
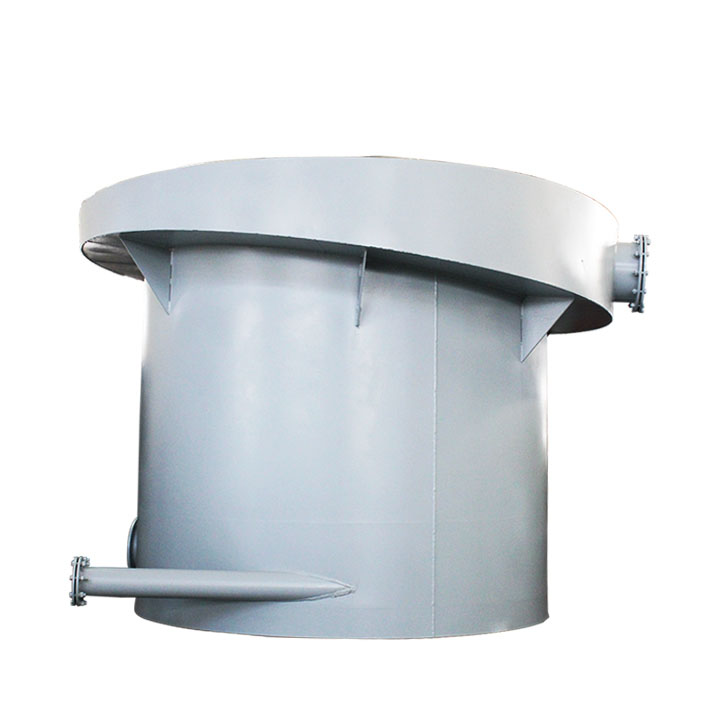
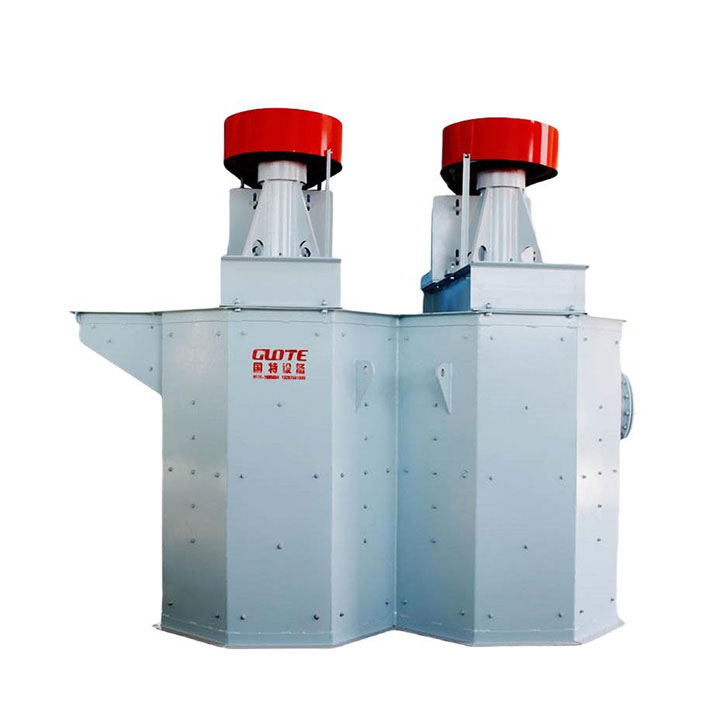
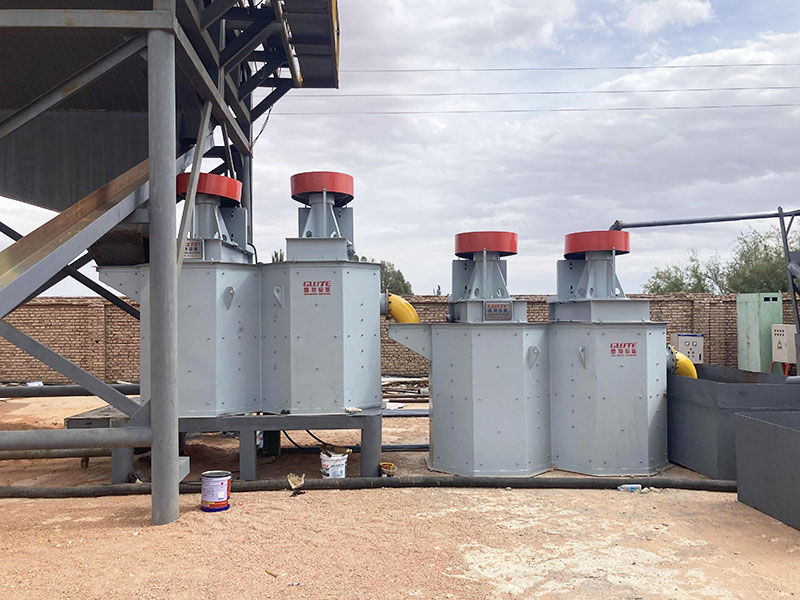
4. High gradient magnetic separator:
●Structure: The core is the magnet (mostly electromagnet) that generates the background magnetic field and the magnetic medium (such as magnetic stainless steel wool, steel plate mesh, steel balls, etc.) filled in the sorting chamber. The medium is magnetized in the magnetic field, and extremely high magnetic field gradients are generated at its tip and edge.
●Working mode: The ore pulp passes through the sorting chamber filled with the medium. Weakly magnetic particles and even paramagnetic particles are captured and adsorbed on the medium by the high gradient magnetic field; non-magnetic particles pass through. After adsorption saturation, the magnetic field is stopped (or flushed), and the captured magnetic particles are flushed down.
●Function: Specially used for sorting extremely fine (micron-level) weakly magnetic and paramagnetic minerals (such as hematite, siderite, wolframite, ilmenite) and deeply removing extremely fine weakly magnetic iron-titanium impurities (purification and impurity reduction) from non-metallic minerals such as kaolin, quartz sand, feldspar, talc, graphite, etc., with remarkable results. It is one of the key equipment for the preparation of modern ultra-pure materials.
●Wet type is the main method (there are also dry high gradient methods).
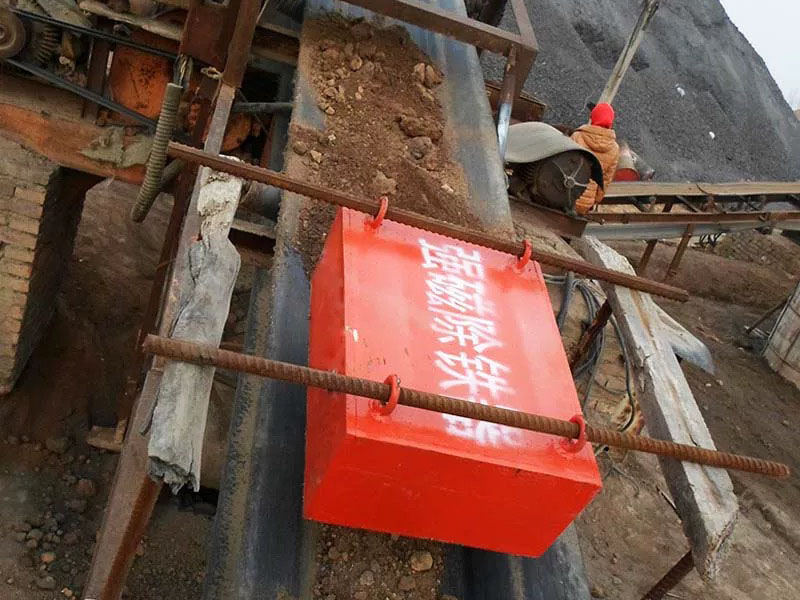
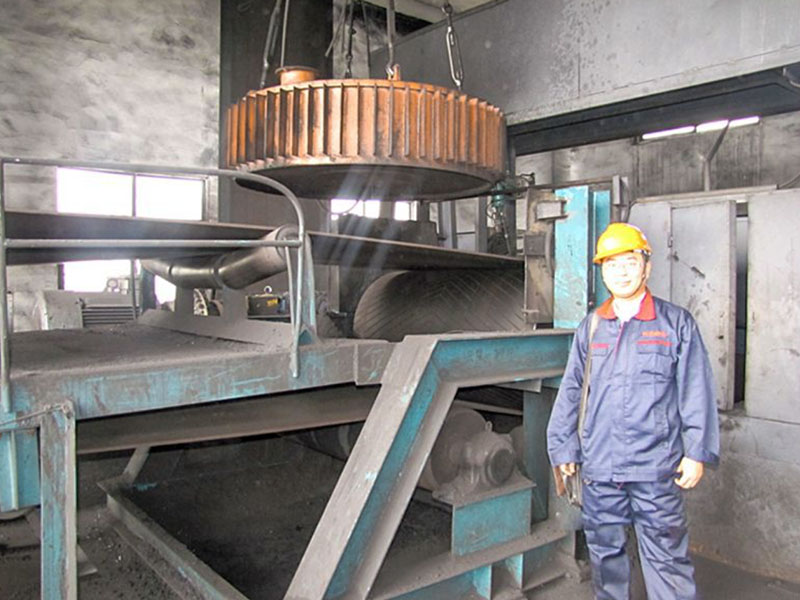
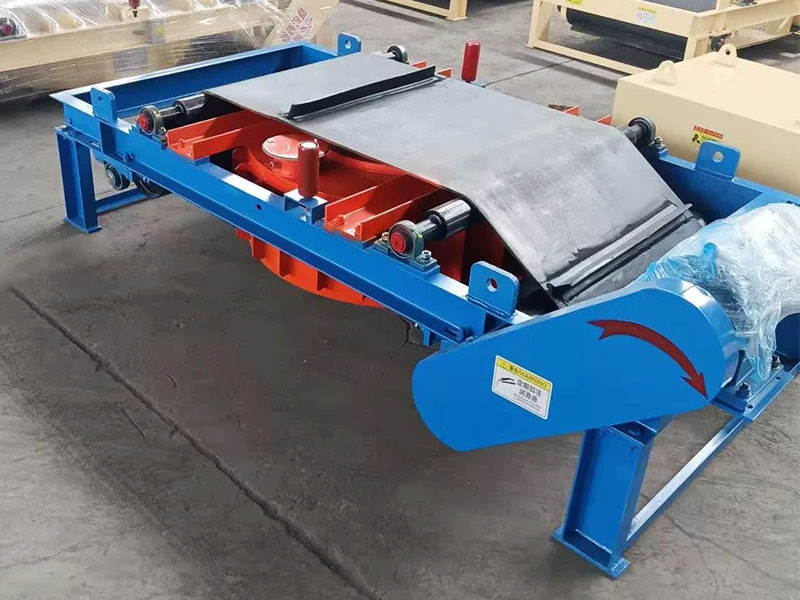
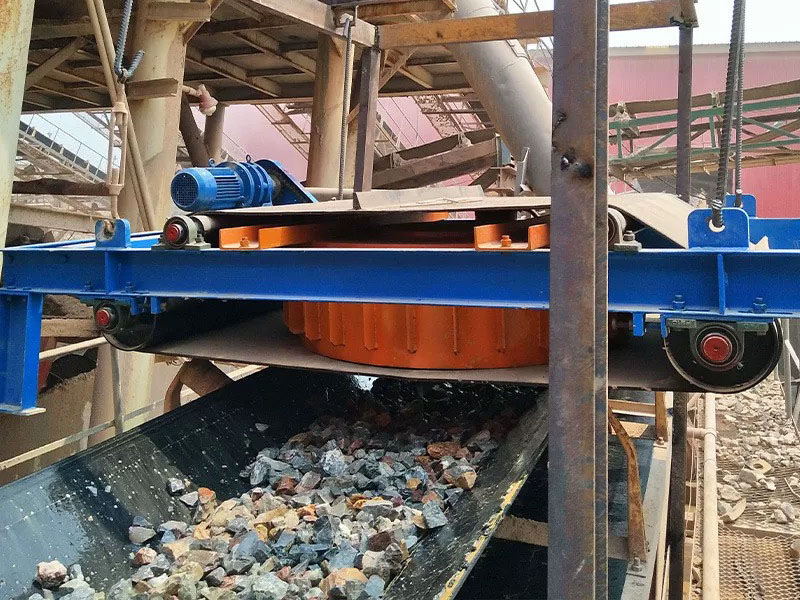
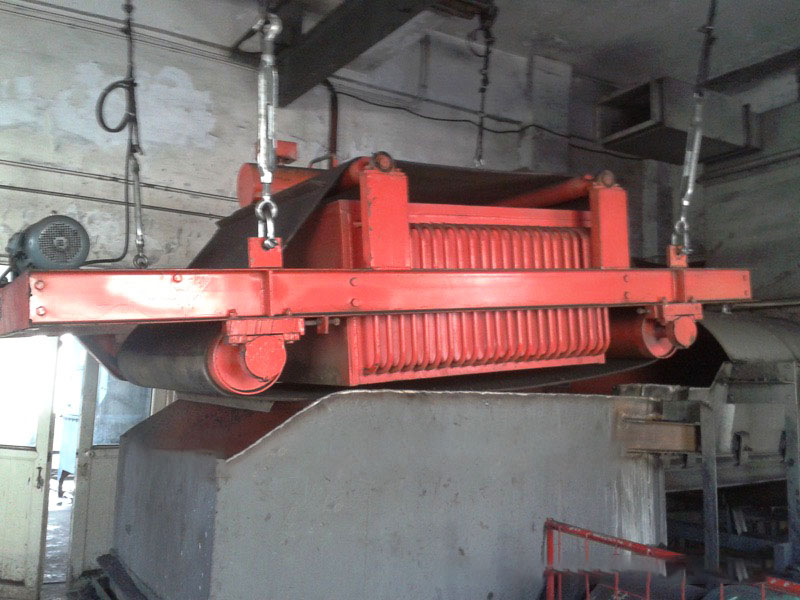
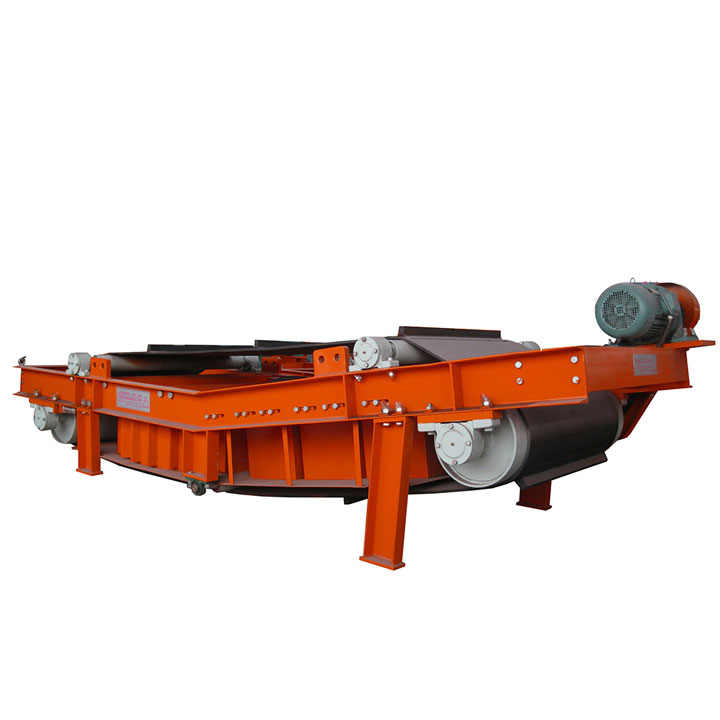
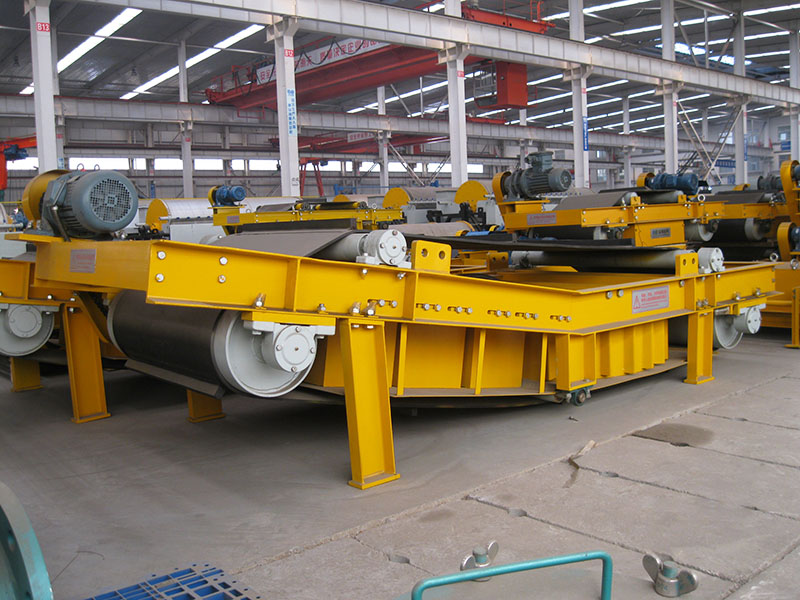
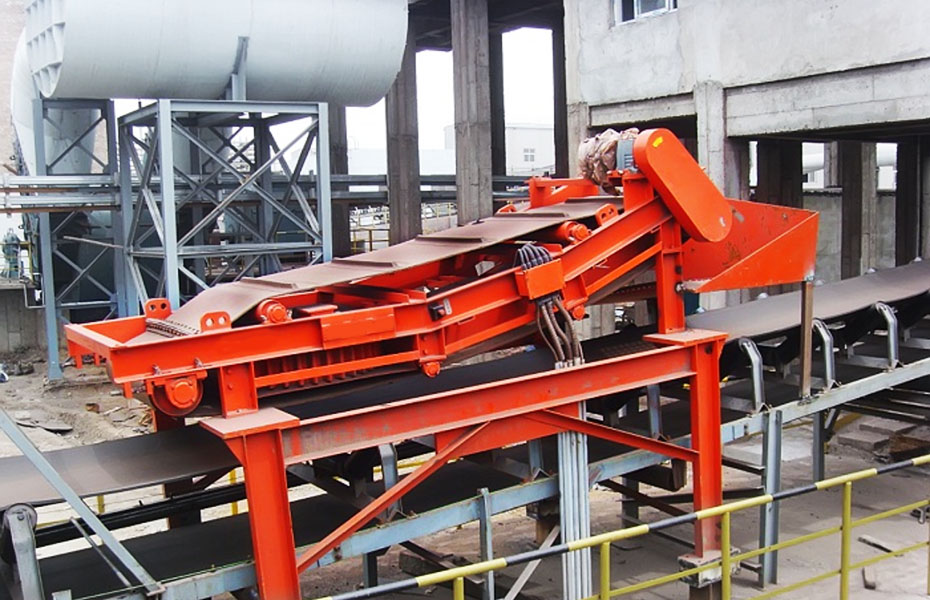
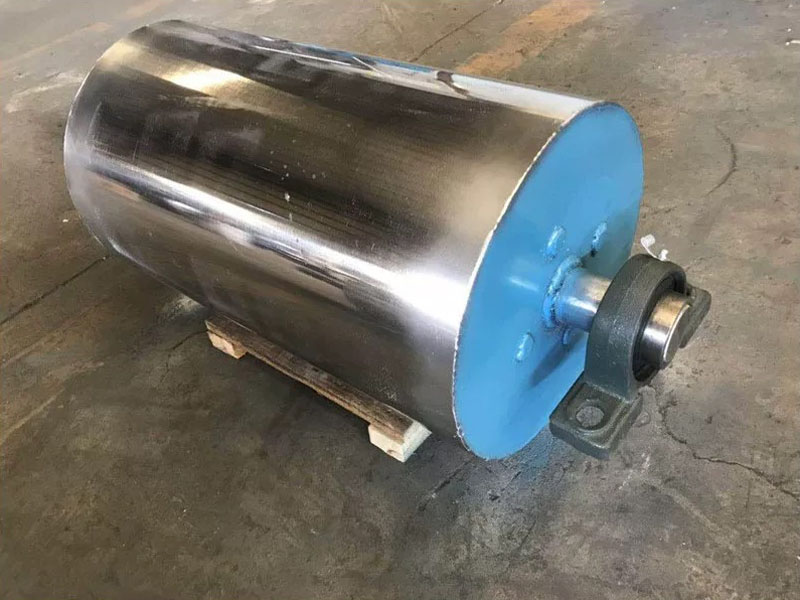
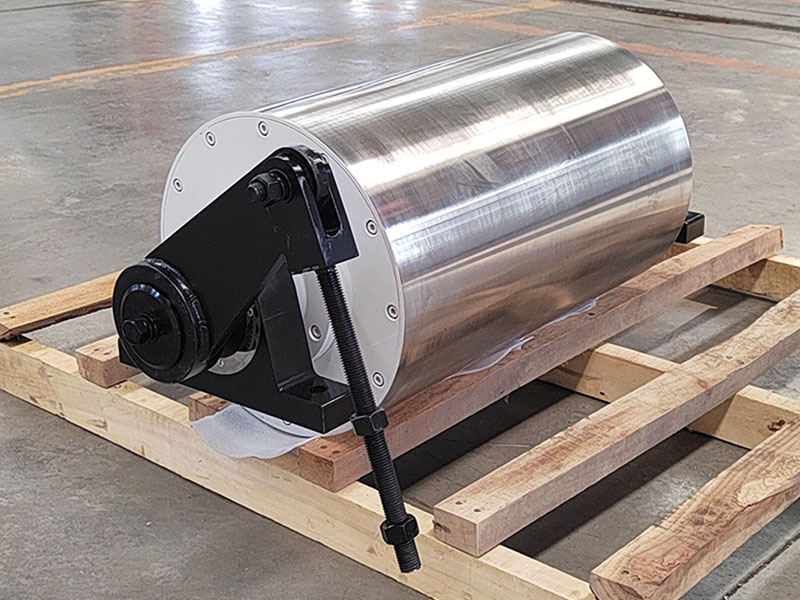
5. Magnetic roller (magnetic pulley):
●Structure: It is essentially a permanent magnetic roller, usually installed at the head of the conveyor belt (mostly belt conveyors) as a driving roller.
●Working mode: When the bulk material (such as raw ore) on the conveyor belt passes through the roller, the magnetic particles (such as large pieces of magnetite) are adsorbed on the belt and fall off with the rotation of the roller (entering the concentrate tank), and the non-magnetic particles are thrown away at the top of the roller (entering the tailings tank).
●Function: Mainly used for pre-selection and tailing of large pieces of strongly magnetic ore (>10mm), discarding a large amount of waste rock before entering the mill, improving the selection grade, and having a huge energy-saving and consumption-reducing effect.
●Dry type.
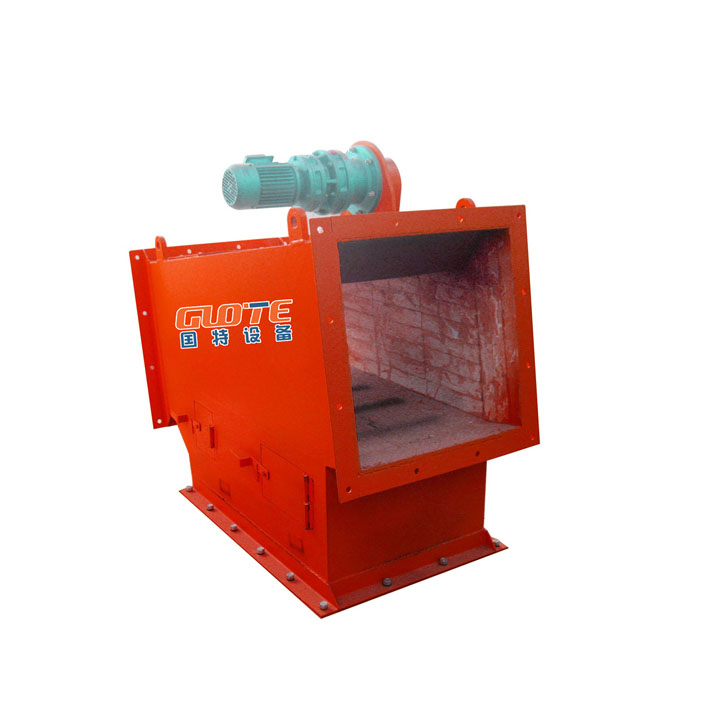
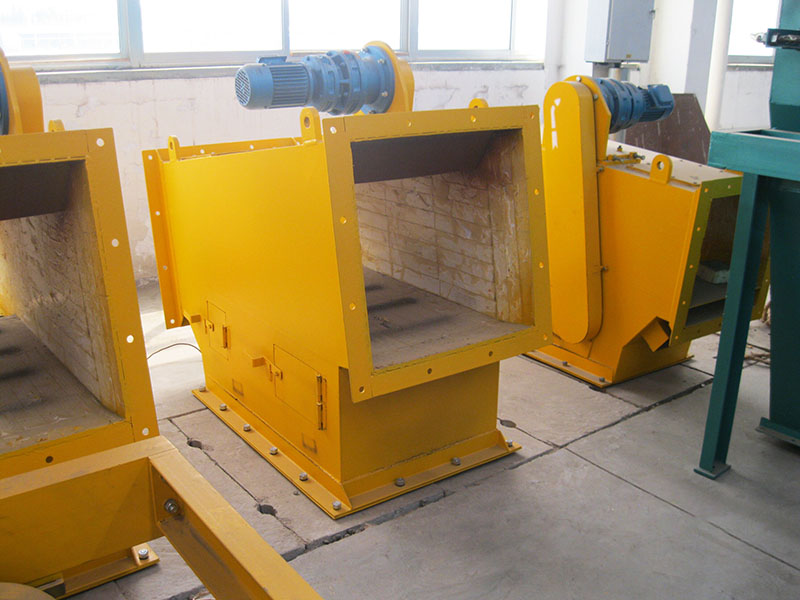
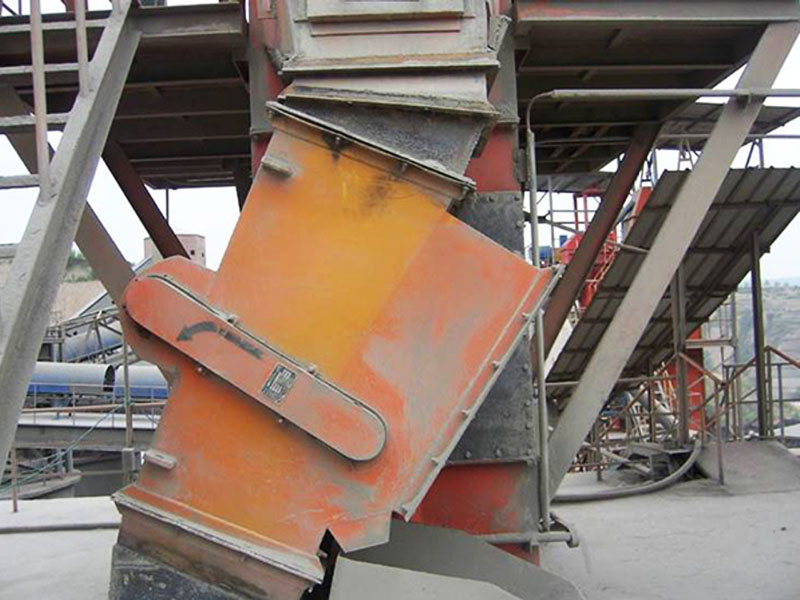
6. Pipeline iron remover:
●Structure: Permanent magnets or electromagnets are installed on the outer wall of the pipeline or made into a tube and inserted into the pipeline.
●Working mode: When powdered or slurry materials flow through the pipeline, the ferromagnetic impurities in them are adsorbed on the magnetic source on the inner wall of the pipeline.
●Function: Mainly used to protect pipelines and subsequent equipment (such as pumps, valves, nozzles), remove ferromagnetic impurities mixed in fluids (gas/liquid), commonly used in food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, ceramics and other industries.
●Structure: The core component is a non-magnetic (such as stainless steel) drum with a fixed magnetic system (permanent magnet or electromagnet) inside and rotating outside.
●Working mode: The material (dry powder or slurry) is fed to the drum surface. The magnetic particles are adsorbed on the drum surface and unloaded as the drum rotates to the non-magnetic area (or through a scraper or flushing water); non-magnetic particles are directly thrown away under the action of centrifugal force and gravity.
●Function: The most widely used. Permanent magnetic drum type is mainly used for strong magnetic mineral sorting and iron removal (wet type is used for fine sweeping and selection, and dry type is used for pre-selection and roughing); electromagnetic drum type can be used in occasions where the magnetic field needs to be adjusted.
●Wet/dry type: Both are widely used.
2. Roller magnetic separator:
●Structure: The core is one or more magnetic rollers (magnetic wheels) composed of permanent magnetic materials or electromagnetic coils.
●Working mode: The material (usually dry powder) is evenly fed to the surface of the magnetic roller or between the two rollers through a vibrating feeder. Magnetic materials are adsorbed on the roller surface or the trajectory is deviated, and non-magnetic materials fall freely. There are single roller, double roller (multi-stage sorting), multi-roller series and other forms.
●Function: Mainly used for dry sorting. Permanent magnetic roller is often used for iron removal and sorting of medium-sized materials (such as quartz sand, plastic particles); induction roller (strong magnetic field) is a classic dry equipment for processing weakly magnetic minerals.
●Dry type is the main method.
3. Belt magnetic separator/iron remover:
●Structure: including suspended iron remover (magnetic source fixed) and belt magnetic separator (magnetic source under or above the belt). Strong belt iron removers usually have built-in iron unloading belts.
●Working mode: Materials (bulk or packaged) are transported by conveyor belts passing under (suspended) or above (some belt machines). Ferromagnetic impurities are adsorbed on the surface of the iron remover or on the belt, and then taken away by the automatic iron unloading mechanism (such as the iron discarding belt).
●Function: Mainly used for iron removal protection (protection of subsequent equipment such as crushers, grinders, conveyor belts, etc.), and also used to recover ferromagnetic materials from bulk materials (such as coal, grain, chemical raw materials, garbage). It is one of the most widely used magnetic separation equipment.
●Dry type (materials are transported in the air).
4. High gradient magnetic separator:
●Structure: The core is the magnet (mostly electromagnet) that generates the background magnetic field and the magnetic medium (such as magnetic stainless steel wool, steel plate mesh, steel balls, etc.) filled in the sorting chamber. The medium is magnetized in the magnetic field, and extremely high magnetic field gradients are generated at its tip and edge.
●Working mode: The ore pulp passes through the sorting chamber filled with the medium. Weakly magnetic particles and even paramagnetic particles are captured and adsorbed on the medium by the high gradient magnetic field; non-magnetic particles pass through. After adsorption saturation, the magnetic field is stopped (or flushed), and the captured magnetic particles are flushed down.
●Function: Specially used for sorting extremely fine (micron-level) weakly magnetic and paramagnetic minerals (such as hematite, siderite, wolframite, ilmenite) and deeply removing extremely fine weakly magnetic iron-titanium impurities (purification and impurity reduction) from non-metallic minerals such as kaolin, quartz sand, feldspar, talc, graphite, etc., with remarkable results. It is one of the key equipment for the preparation of modern ultra-pure materials.
●Wet type is the main method (there are also dry high gradient methods).
5. Magnetic roller (magnetic pulley):
●Structure: It is essentially a permanent magnetic roller, usually installed at the head of the conveyor belt (mostly belt conveyors) as a driving roller.
●Working mode: When the bulk material (such as raw ore) on the conveyor belt passes through the roller, the magnetic particles (such as large pieces of magnetite) are adsorbed on the belt and fall off with the rotation of the roller (entering the concentrate tank), and the non-magnetic particles are thrown away at the top of the roller (entering the tailings tank).
●Function: Mainly used for pre-selection and tailing of large pieces of strongly magnetic ore (>10mm), discarding a large amount of waste rock before entering the mill, improving the selection grade, and having a huge energy-saving and consumption-reducing effect.
●Dry type.
6. Pipeline iron remover:
●Structure: Permanent magnets or electromagnets are installed on the outer wall of the pipeline or made into a tube and inserted into the pipeline.
●Working mode: When powdered or slurry materials flow through the pipeline, the ferromagnetic impurities in them are adsorbed on the magnetic source on the inner wall of the pipeline.
●Function: Mainly used to protect pipelines and subsequent equipment (such as pumps, valves, nozzles), remove ferromagnetic impurities mixed in fluids (gas/liquid), commonly used in food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, ceramics and other industries.
●Both dry and wet types are available (depending on the medium in the pipeline).

-
PRE
No Record
-
NEX
Weifang Guote Mining Equipment Co., Ltd.
Weifang Guote Mining Equipment Co., Ltd. is located in Weifang City, Shandong Province, China. The c…
Contact Us
To find out more about our products and solutions, please fill out the form below and one of our experts will get back to you shortly.

 guotemining@gmail.com
guotemining@gmail.com  8613792666516
8613792666516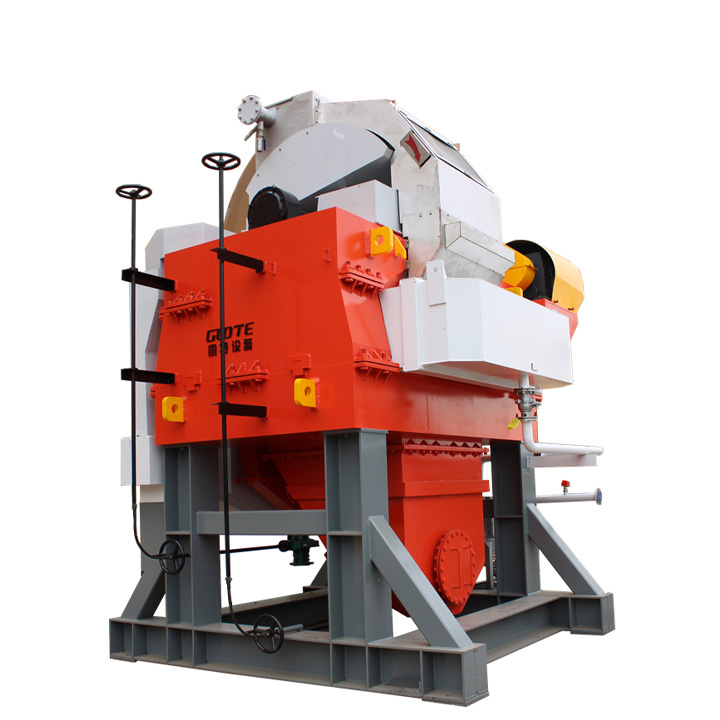 












































































































































 CHAT
CHAT MESSAGE
MESSAGE
