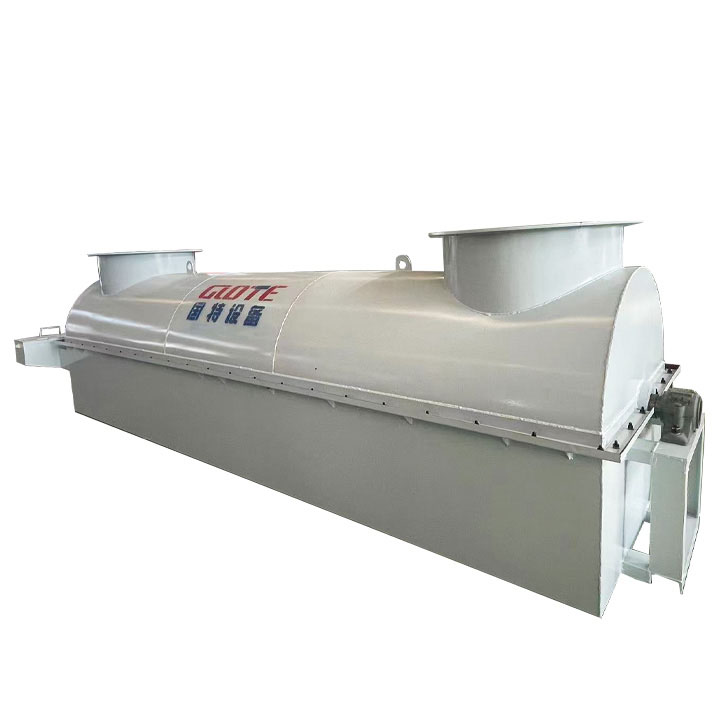
Hydraulic Classifier
[Overview]:A hydraulic classifier is a device that uses differences in particle settling velocity in a water flow to classify materials by particle size. Its core principle is Stokes' law. By controlling the water flow velocity and direction, mineral particles of different sizes are separated by their settling velocity, achieving the separation of coarse and fine particles.
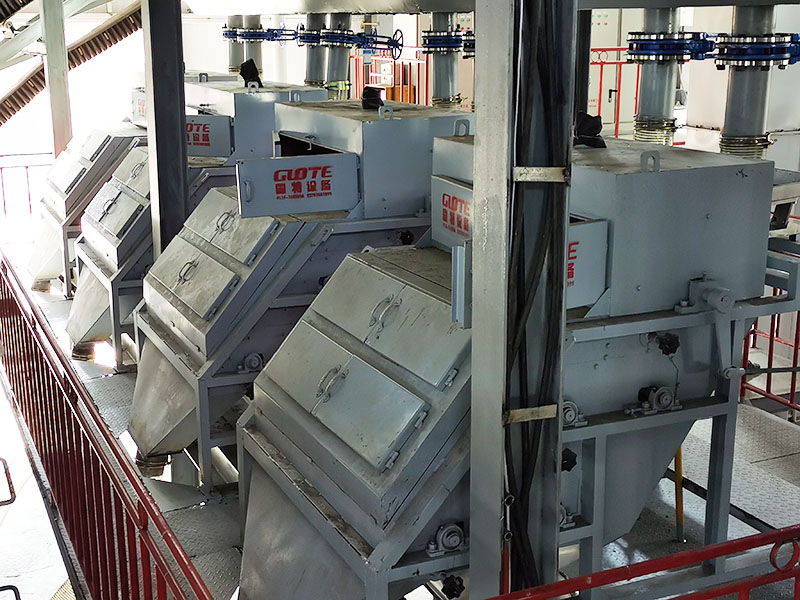
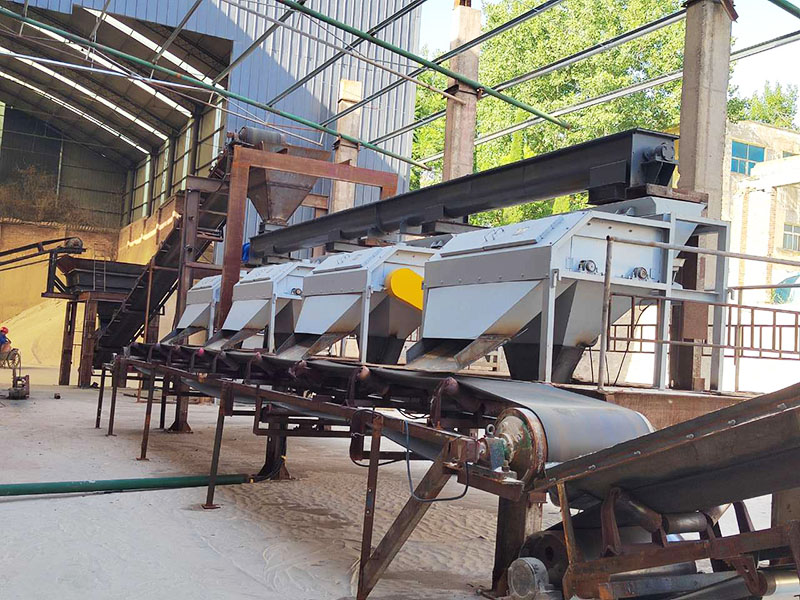
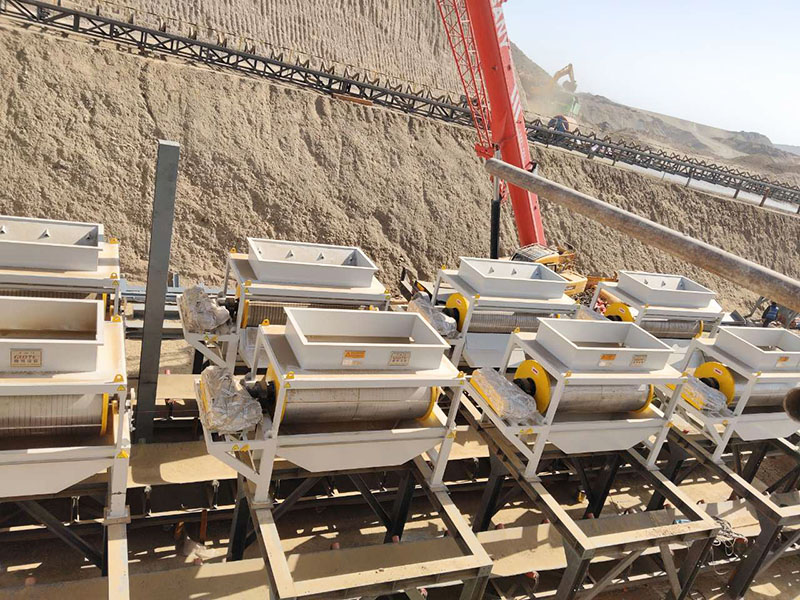
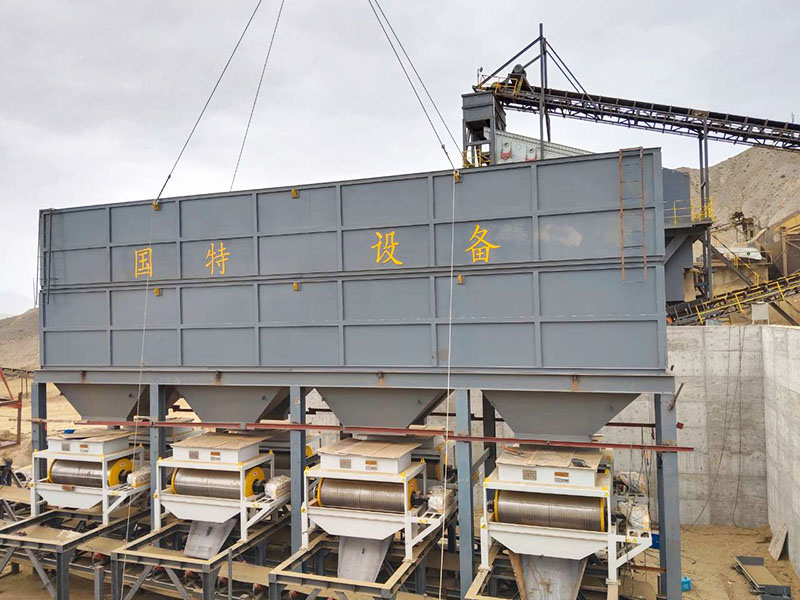
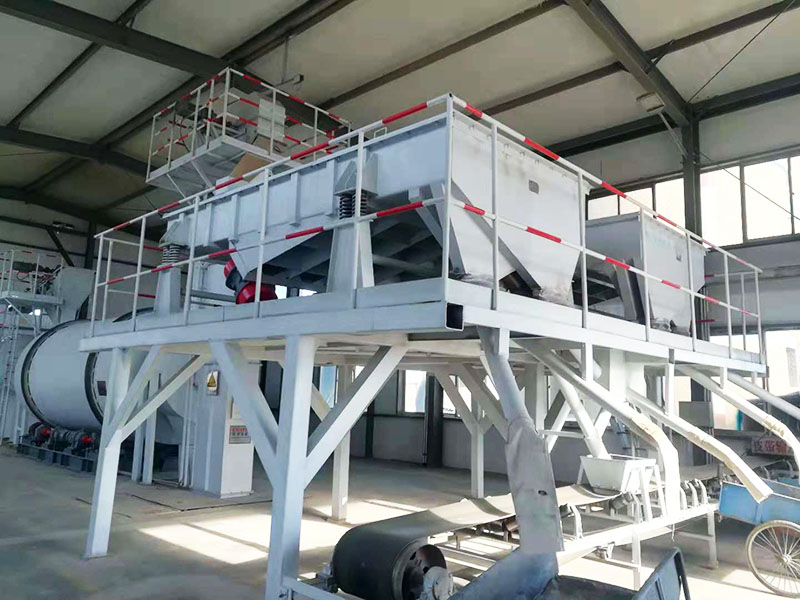
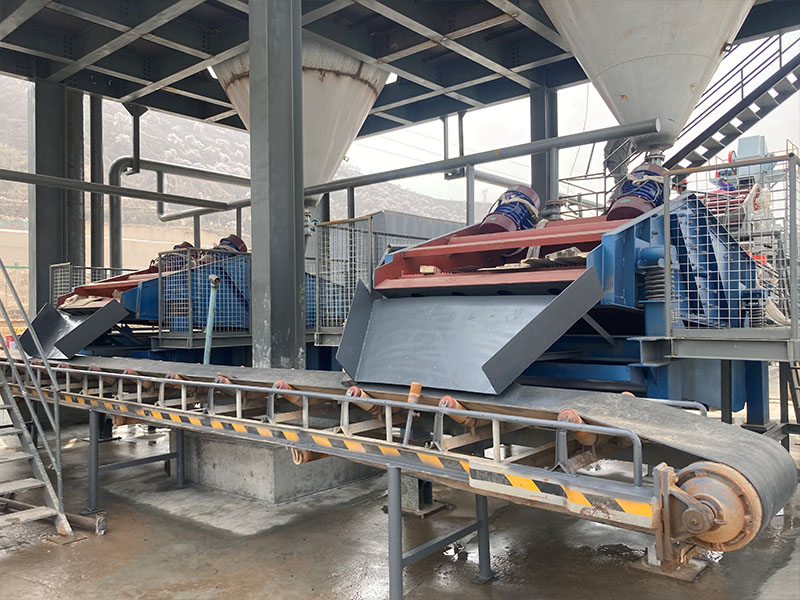
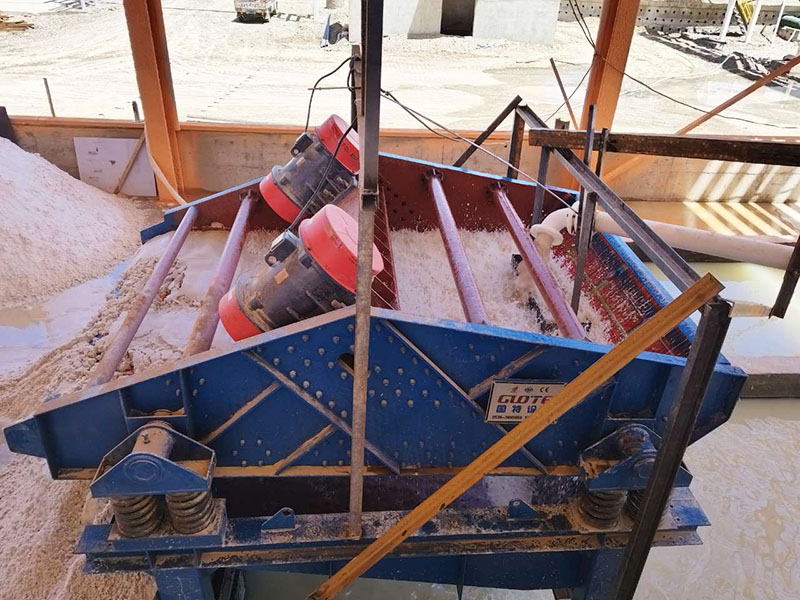
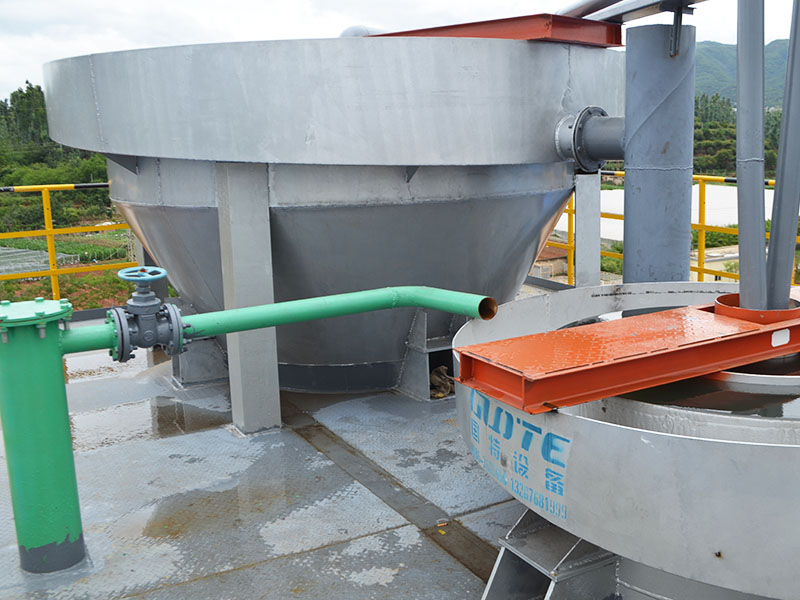
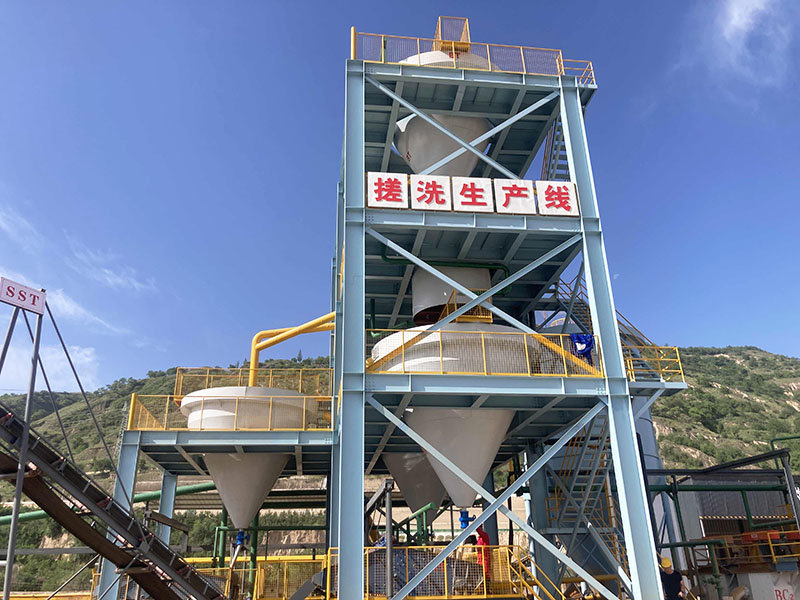
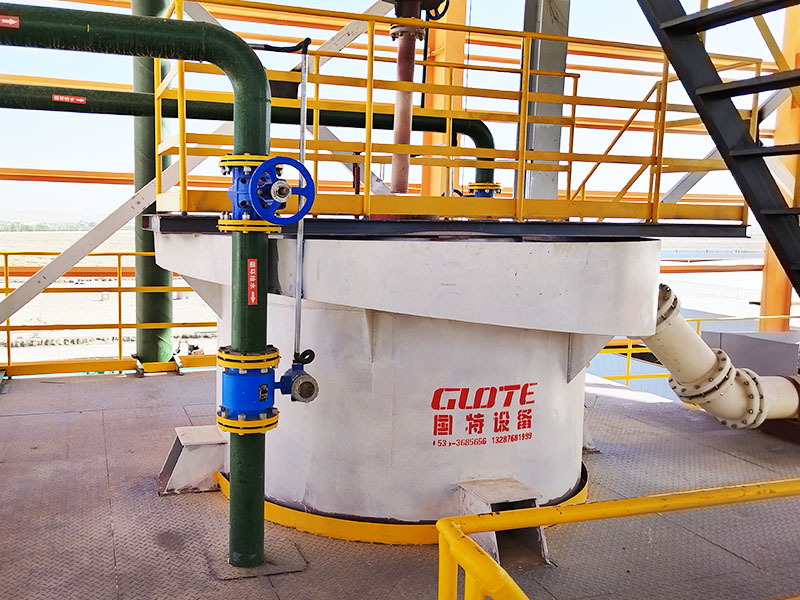
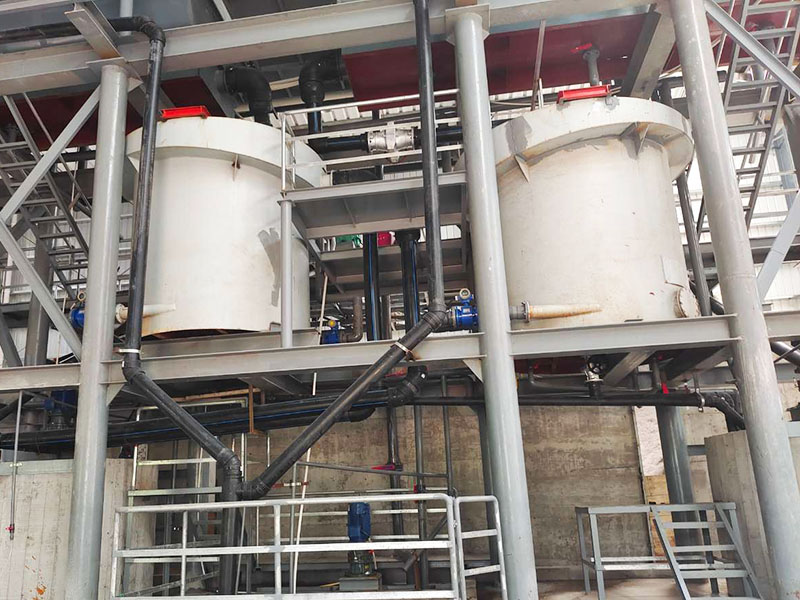
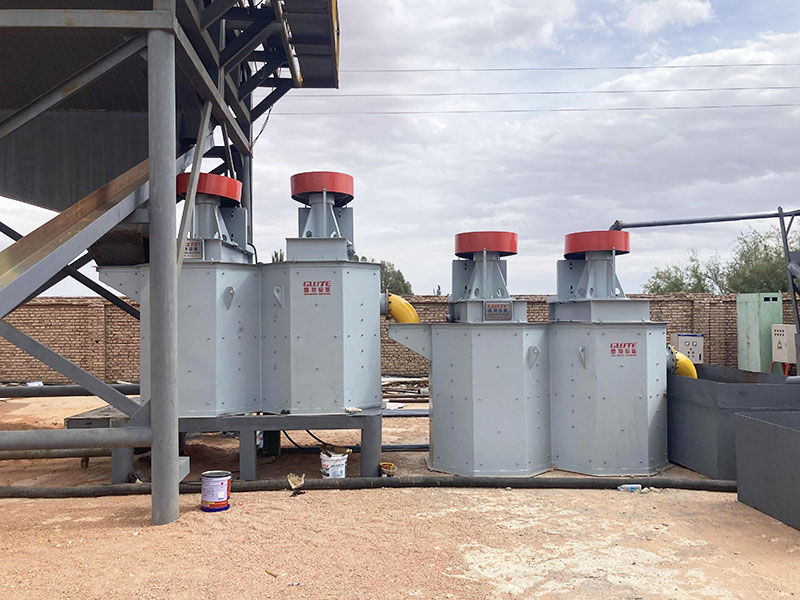
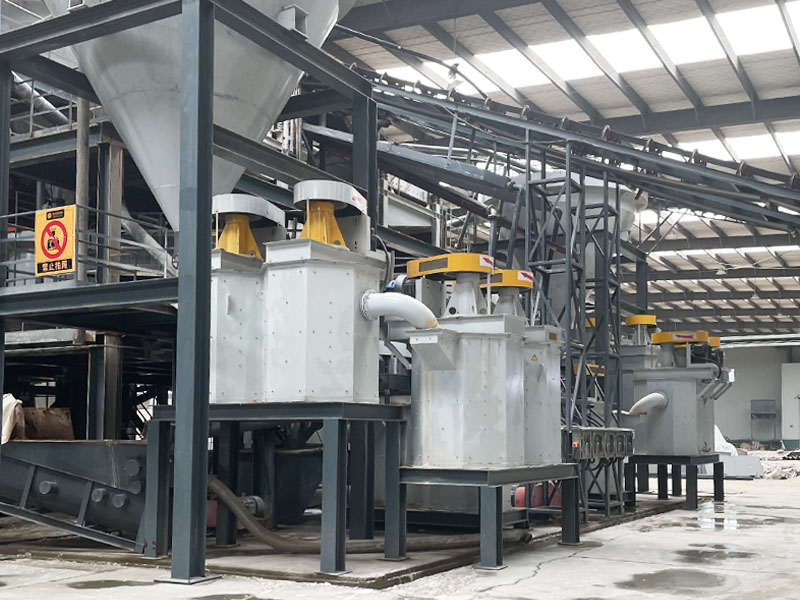
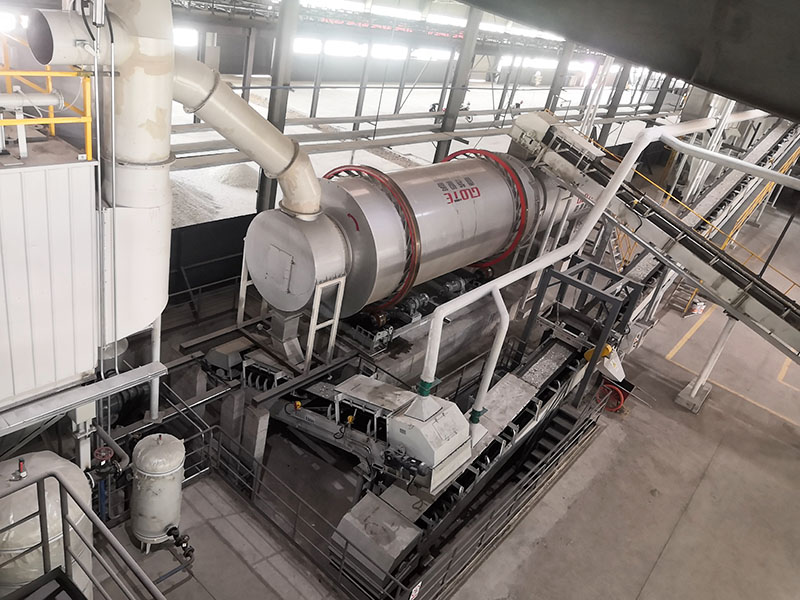
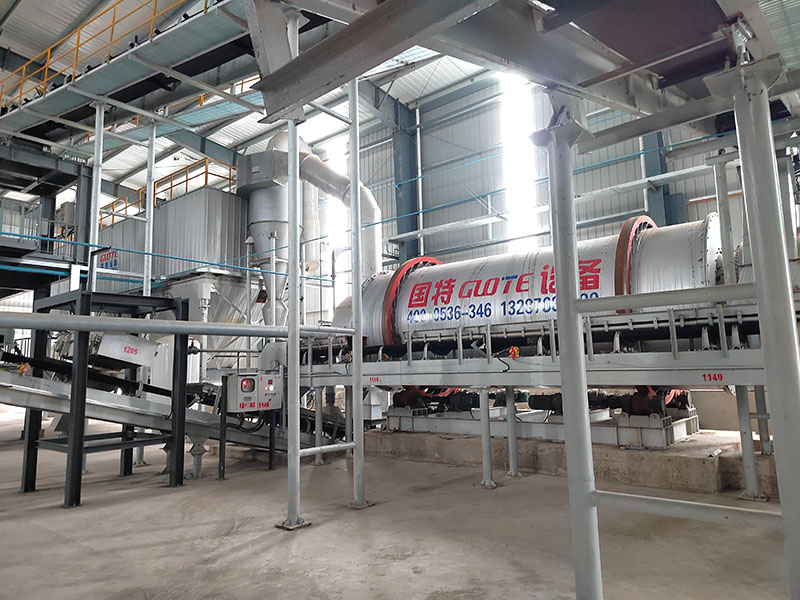
[Application Scenarios]:It is widely used in the mining, building materials, and chemical industries, and is a key piece of equipment for wet classification. Examples include particle size classification of raw materials such as quartz sand; controlling the return sand particle size in closed-circuit grinding during mineral processing to improve grinding efficiency; separating fine mud from gravel to enhance the purity of building materials; and separating grit and dewatering tailings in wastewater treatment.
ADVANTAGES
1. High efficiency and energy saving: No power machinery is required, relying on natural hydraulic classification for low energy consumption.
2. Precise particle size: Micron-level classification can be achieved through water flow regulation.
3. Simple structure: Low maintenance costs and high operational stability.
4. Strong adaptability: Capable of handling high-concentration slurries and resistant to wear.
5. Environmentally friendly: Wet processing reduces dust pollution and allows for water recycling.
 |
 |
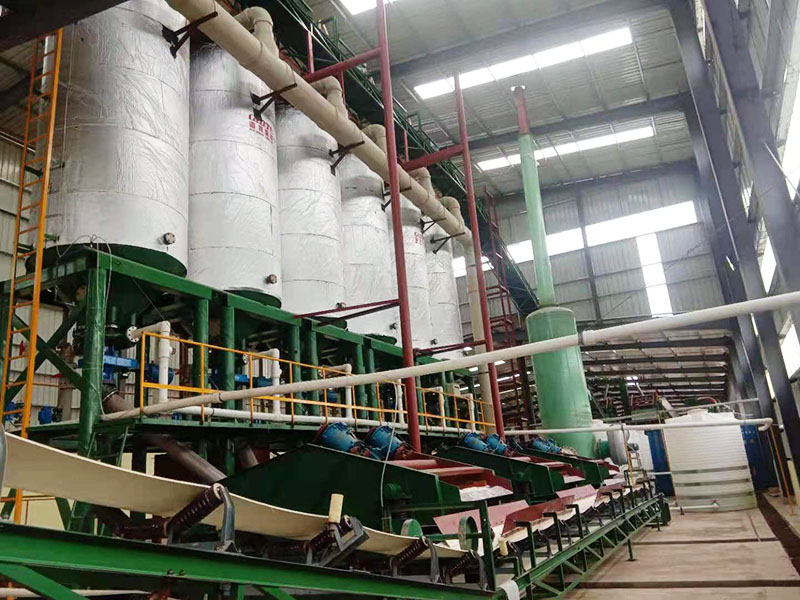
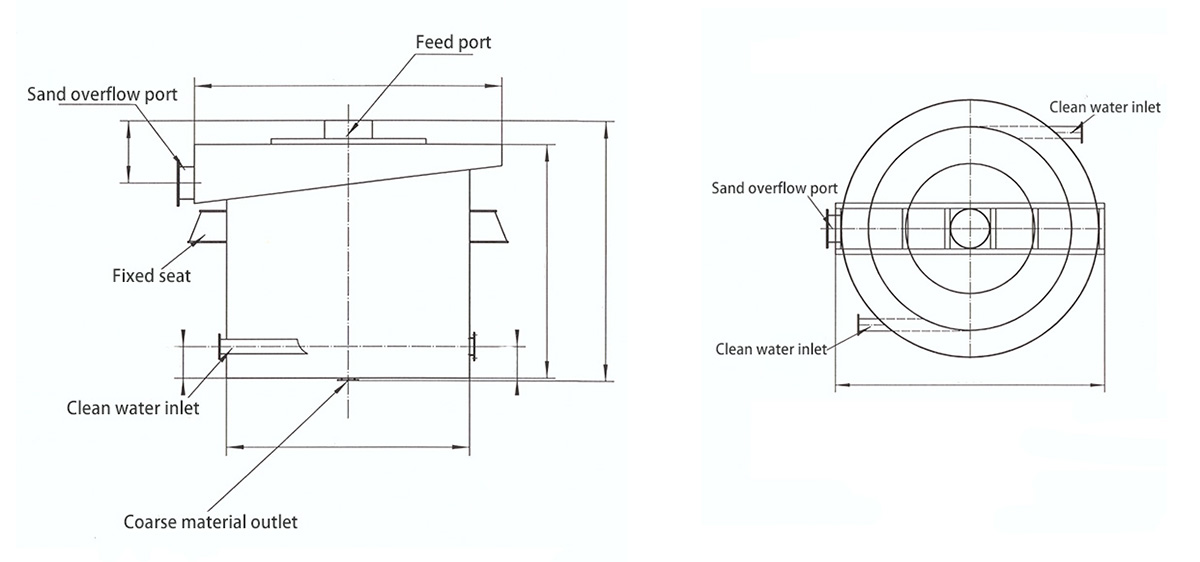
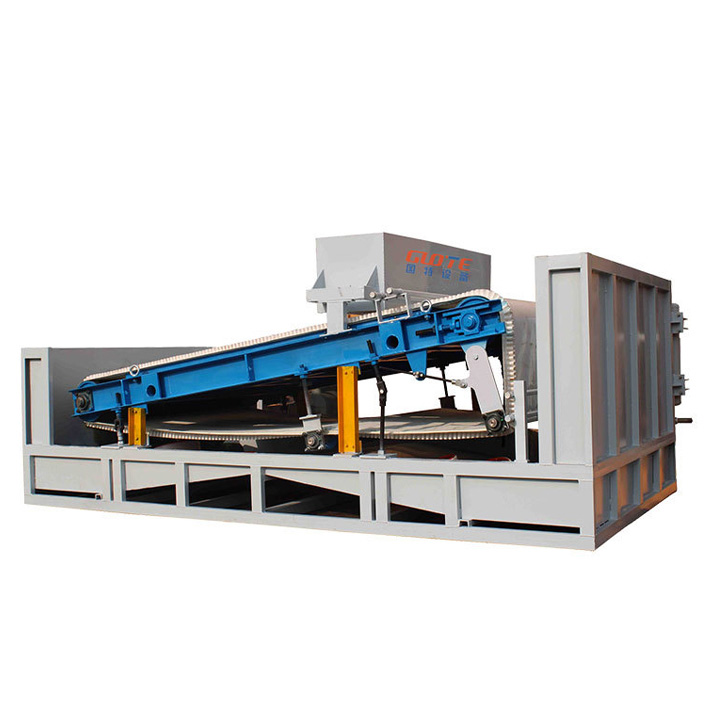
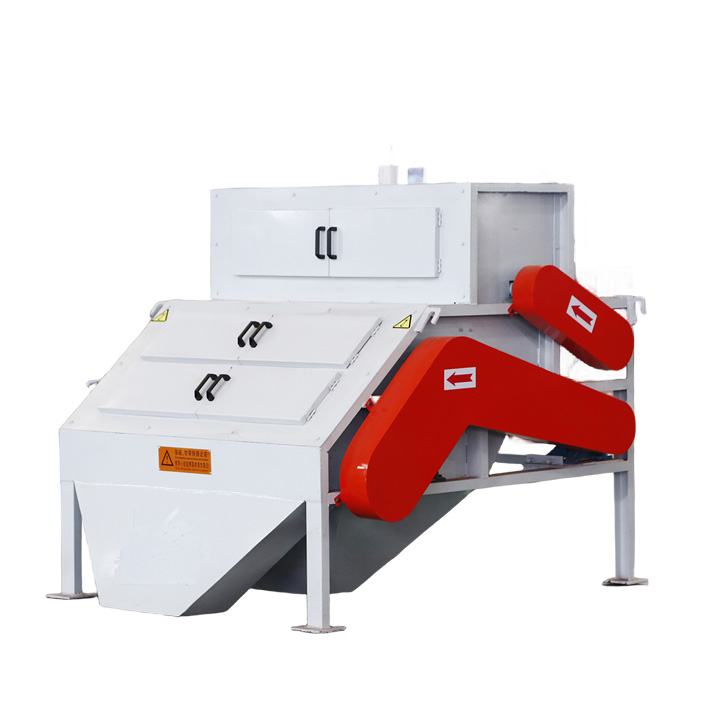
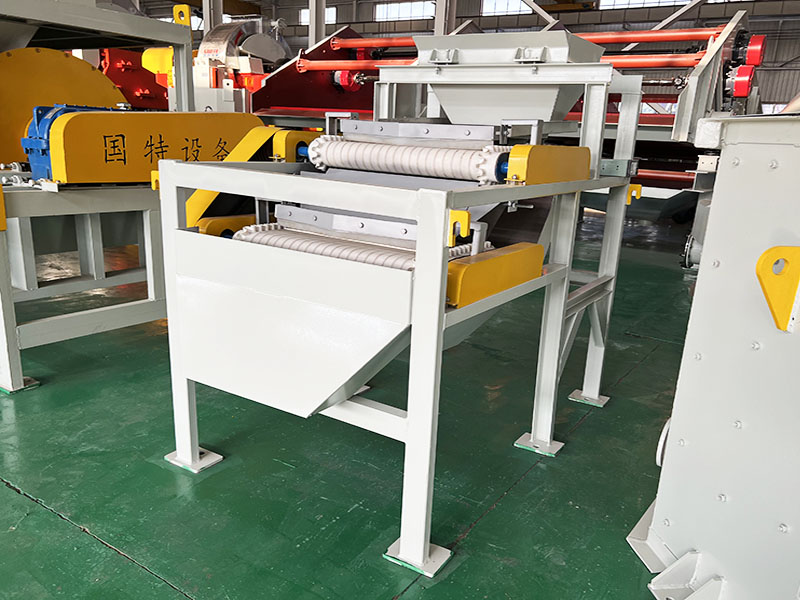
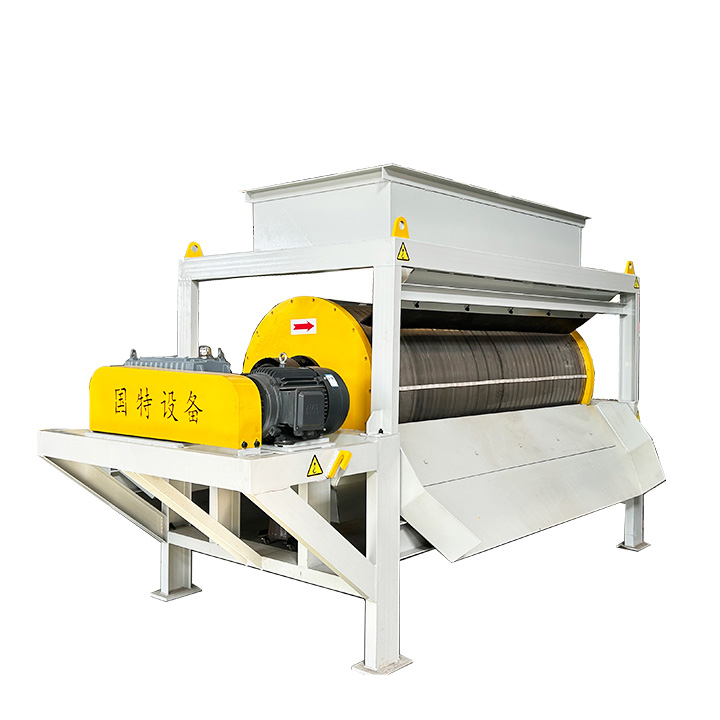
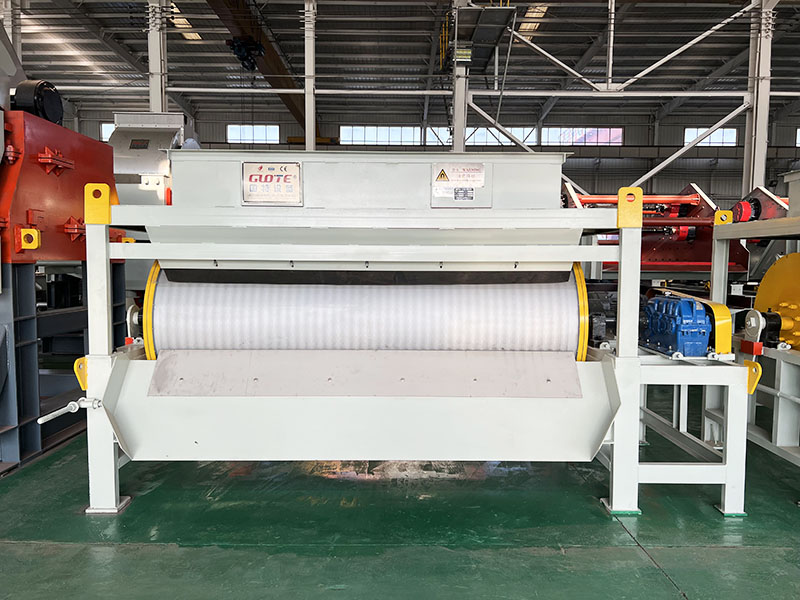
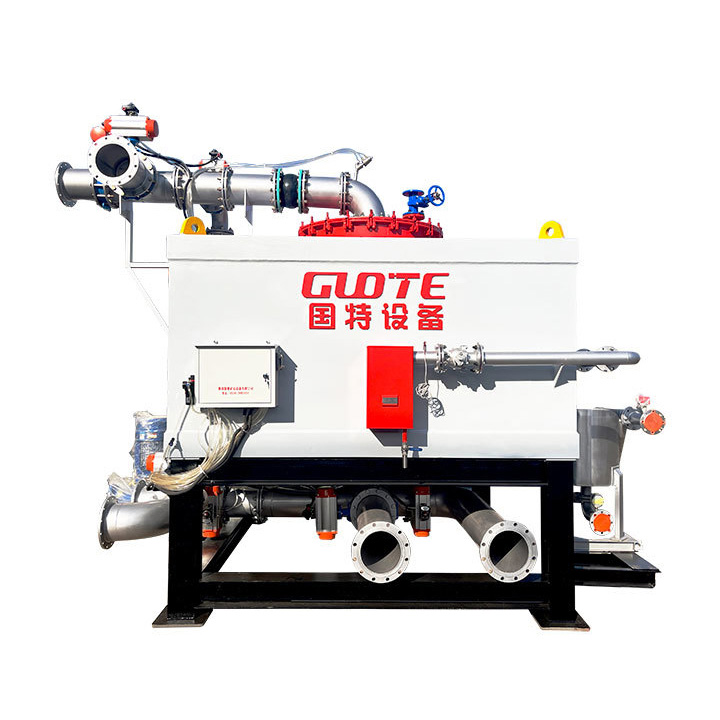
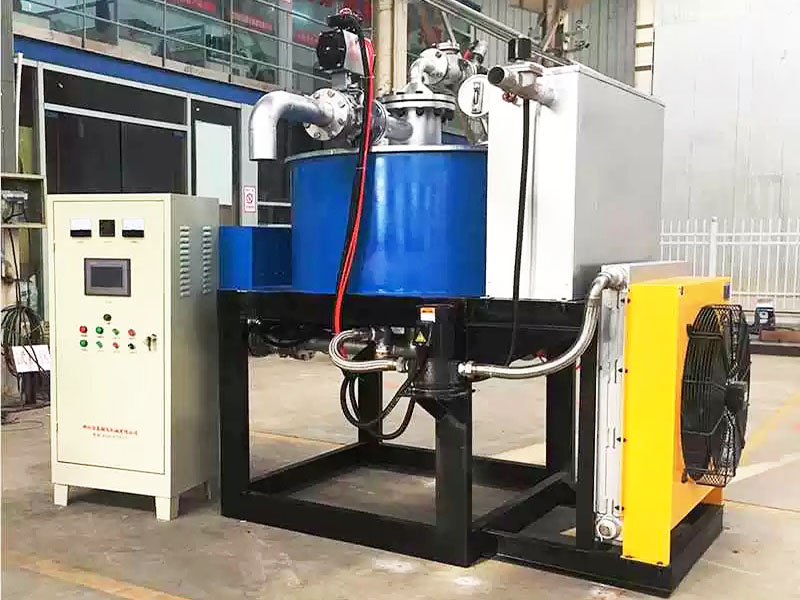
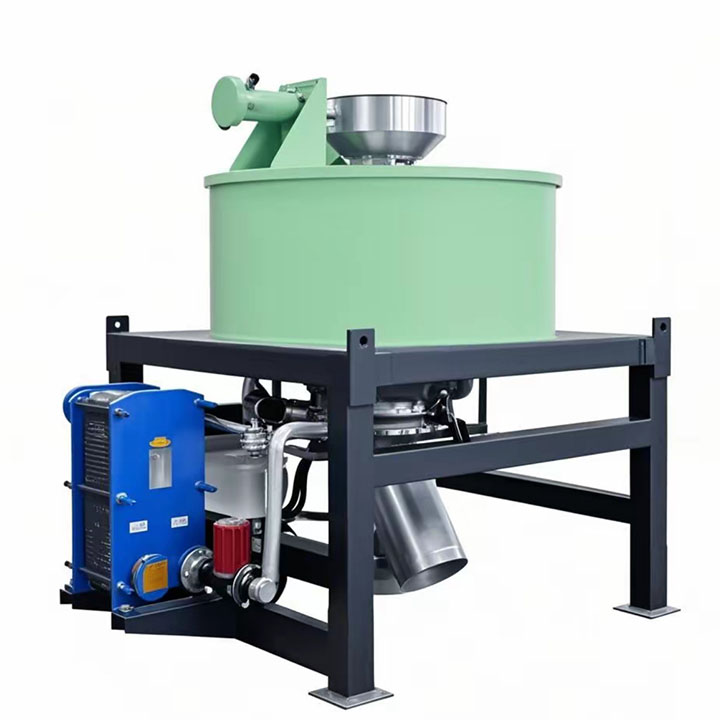
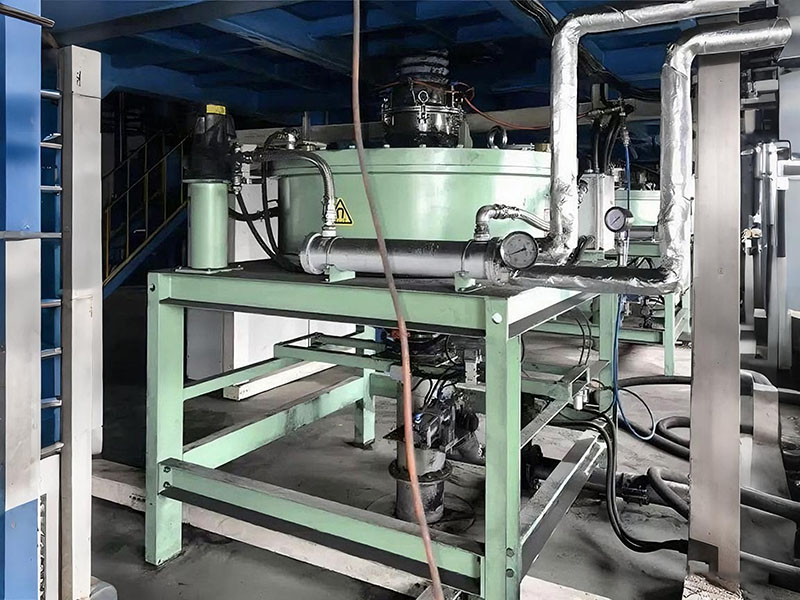
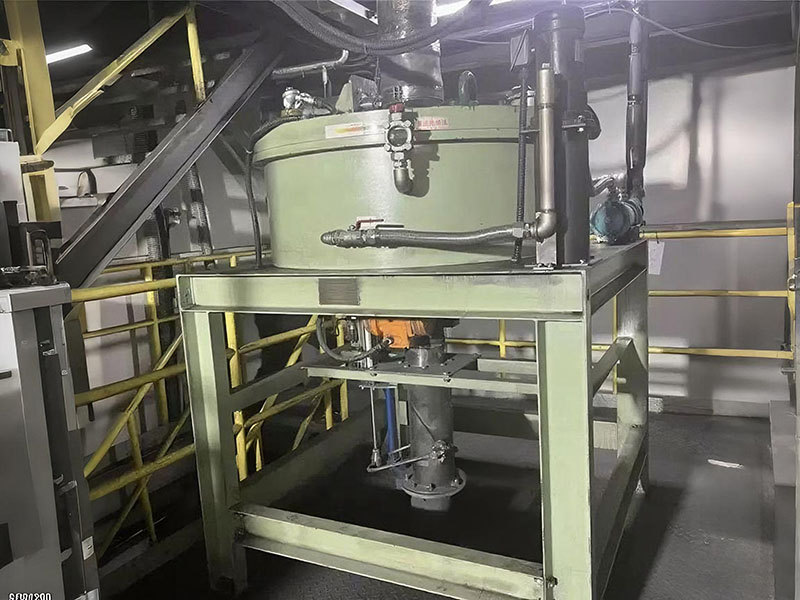
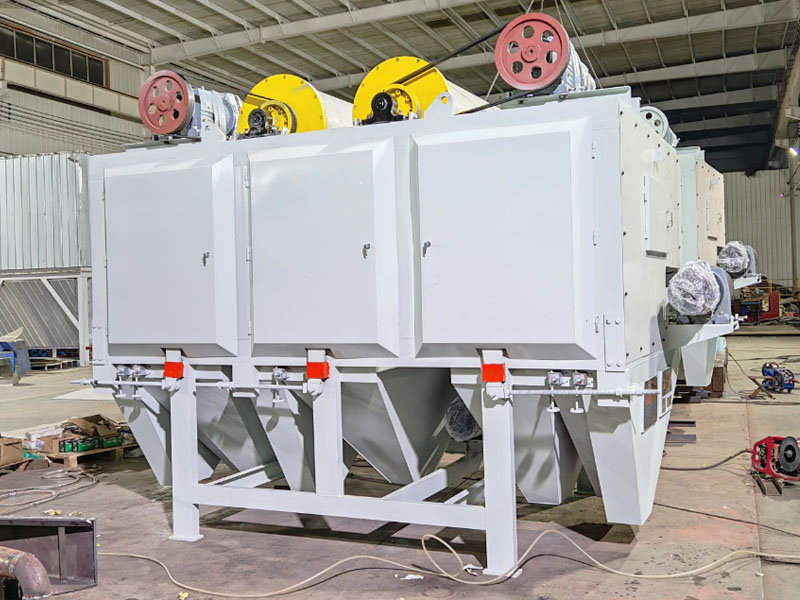
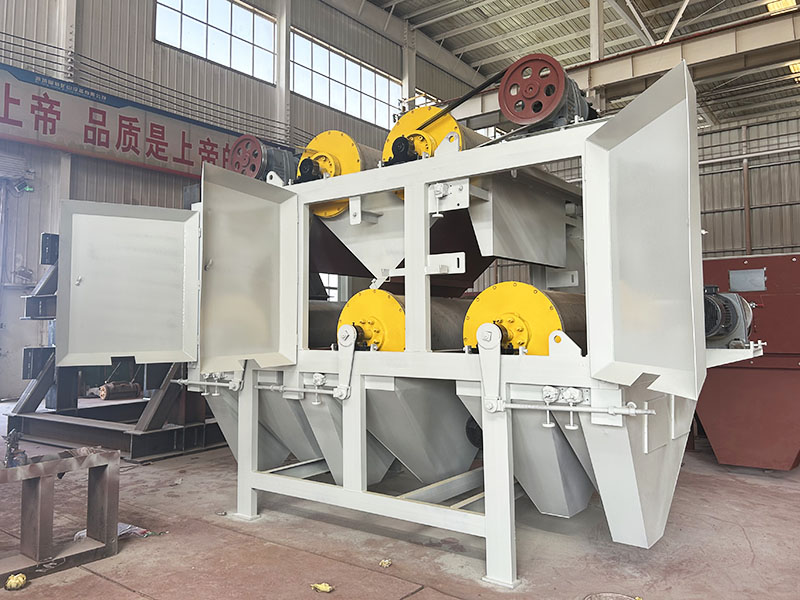
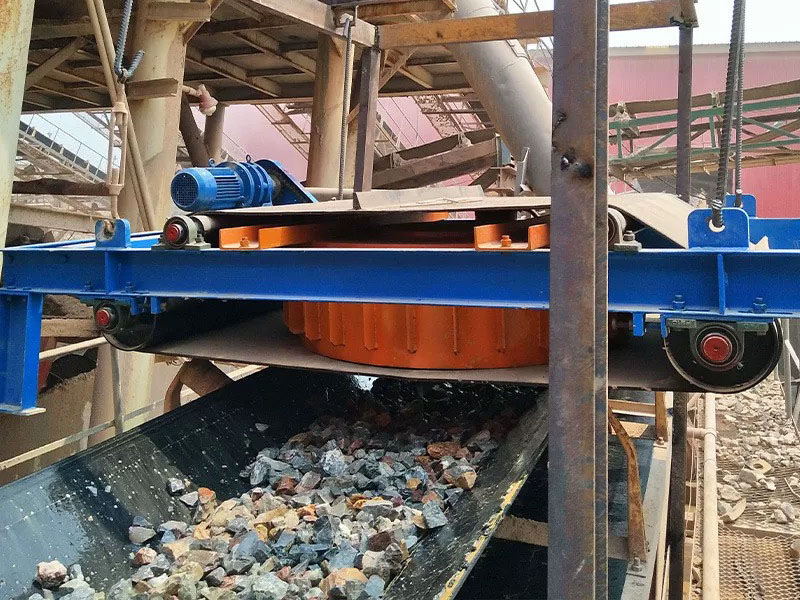
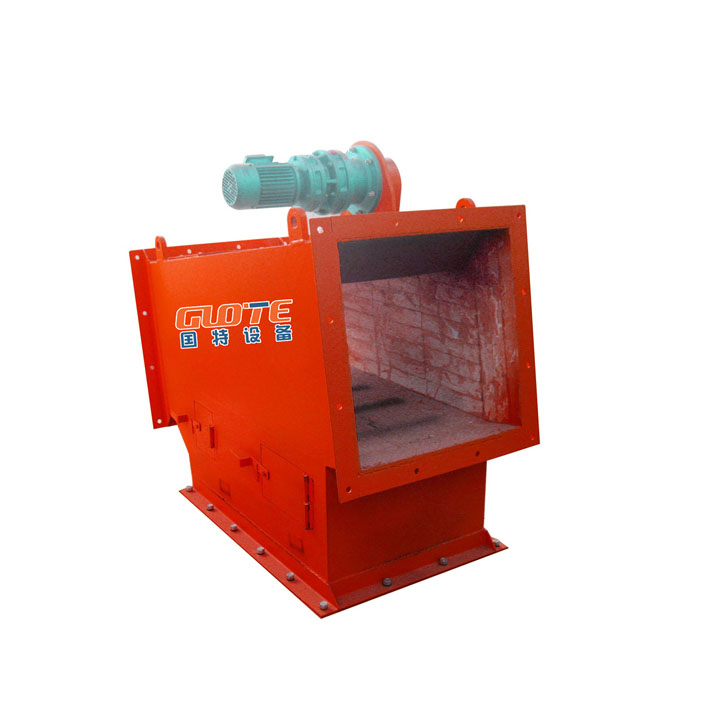
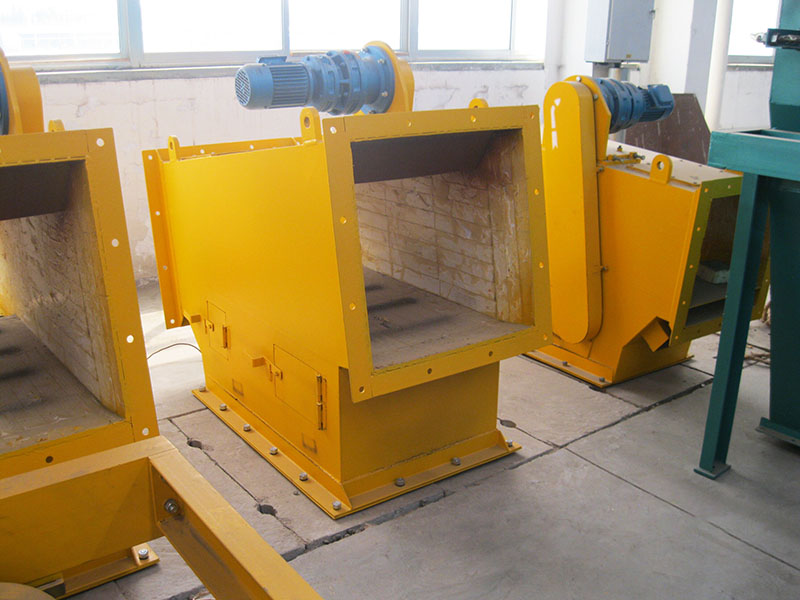
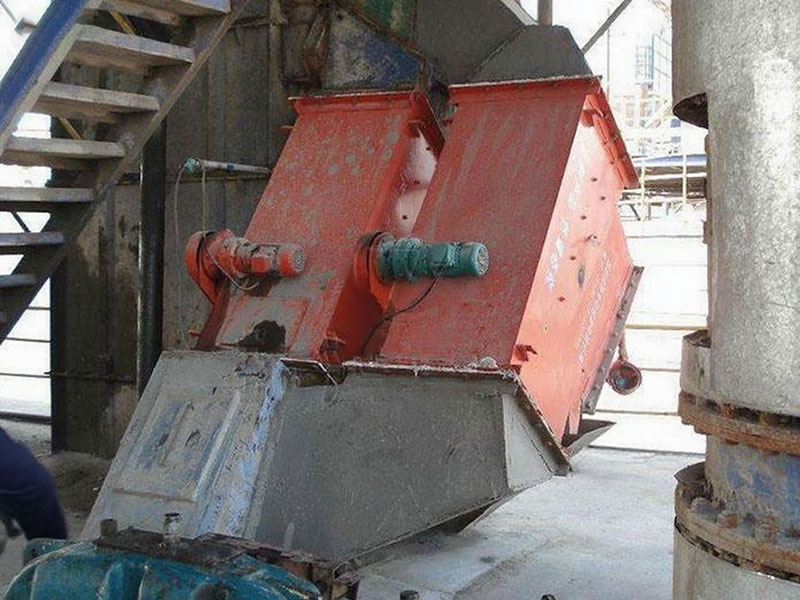
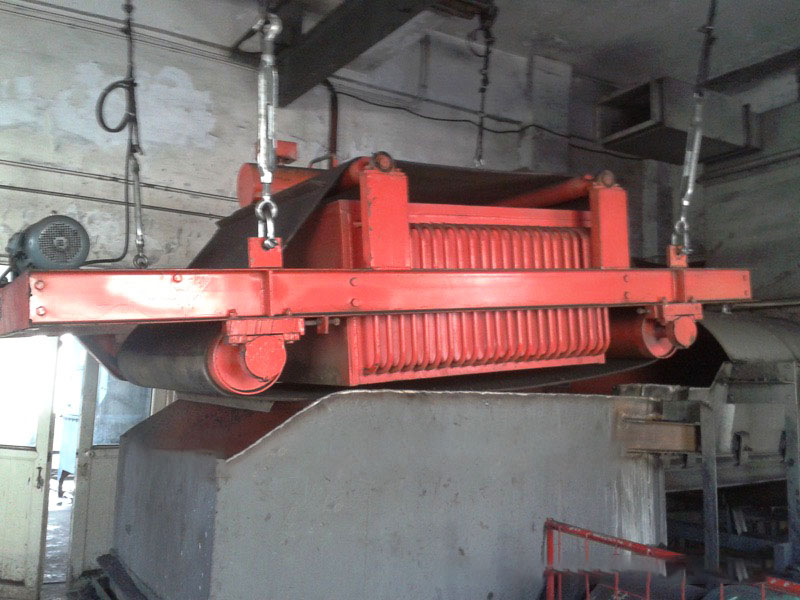
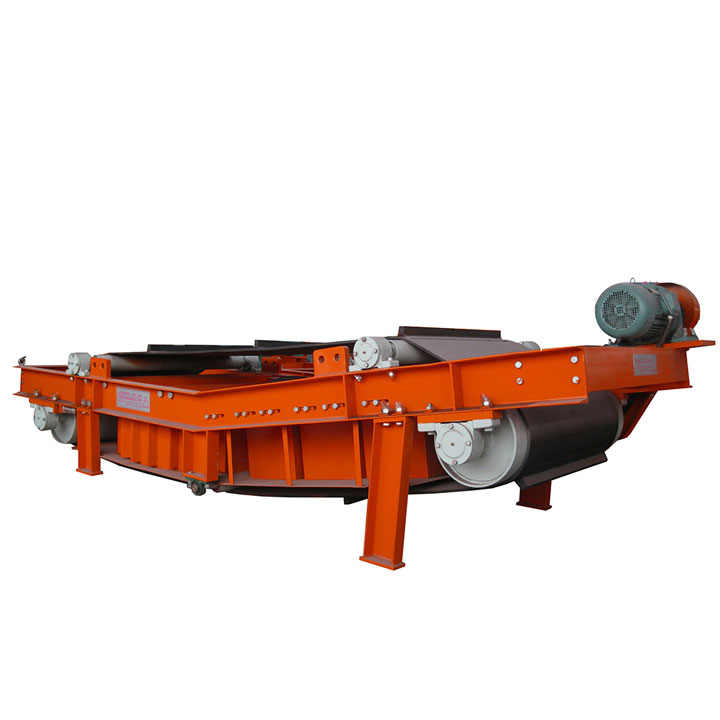
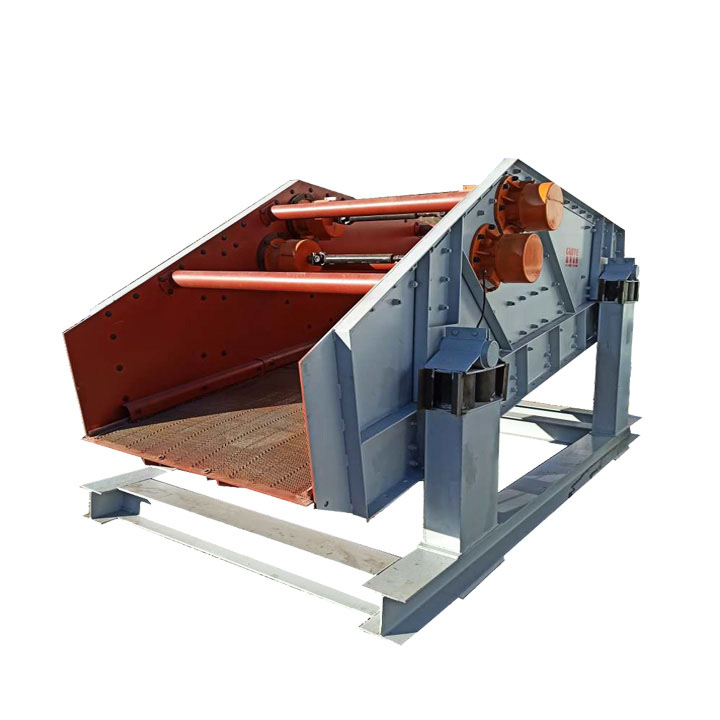
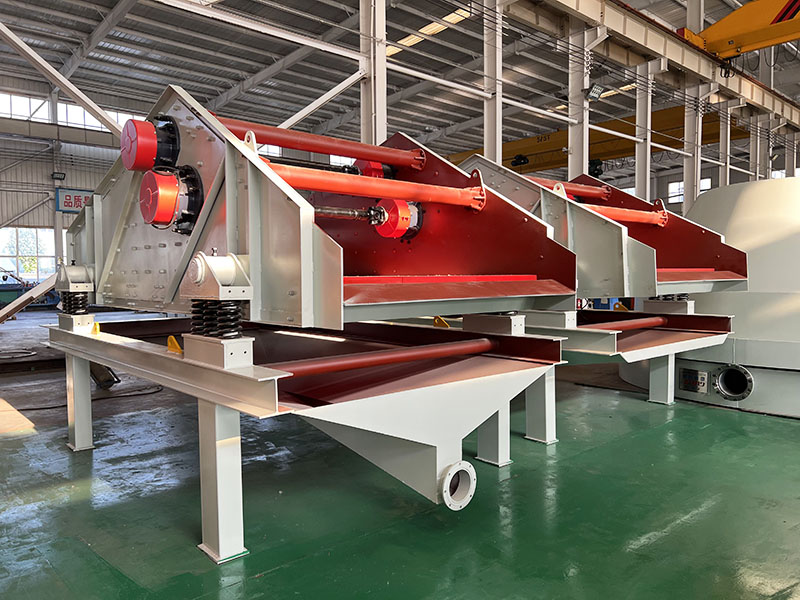
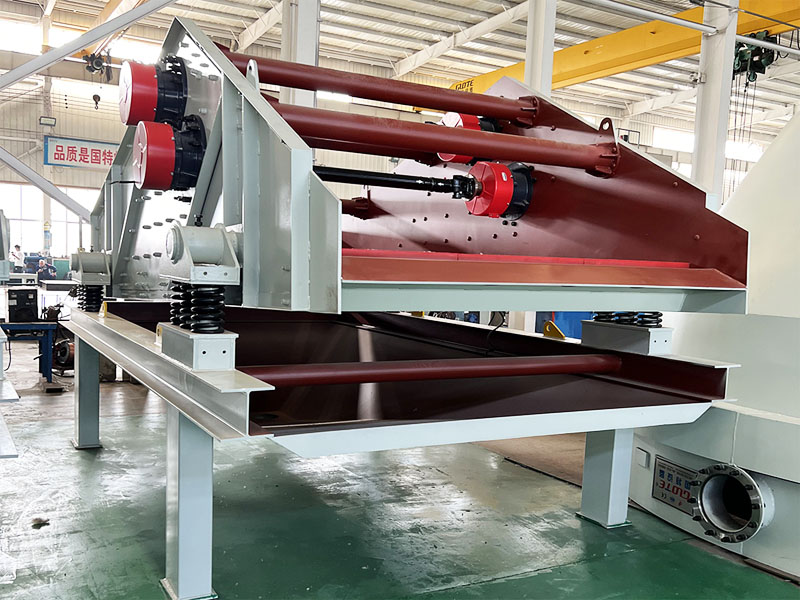
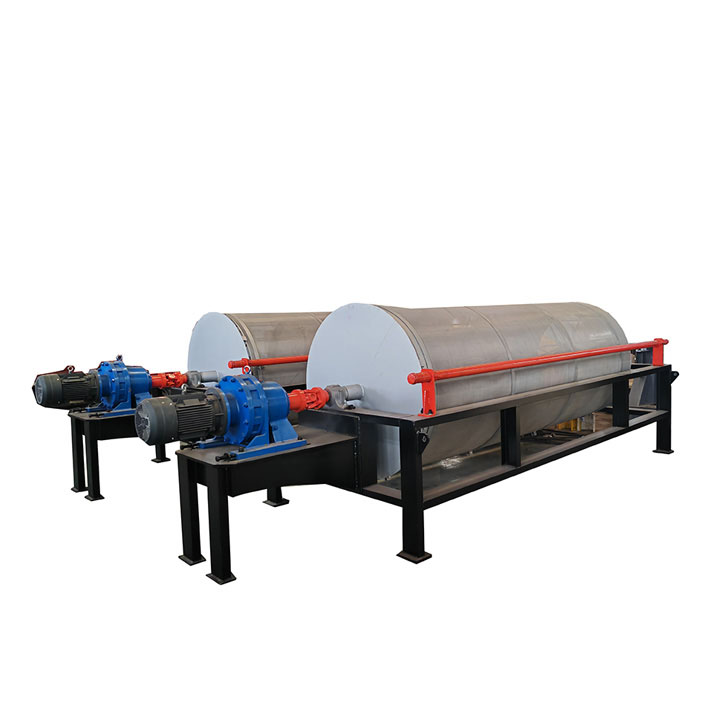
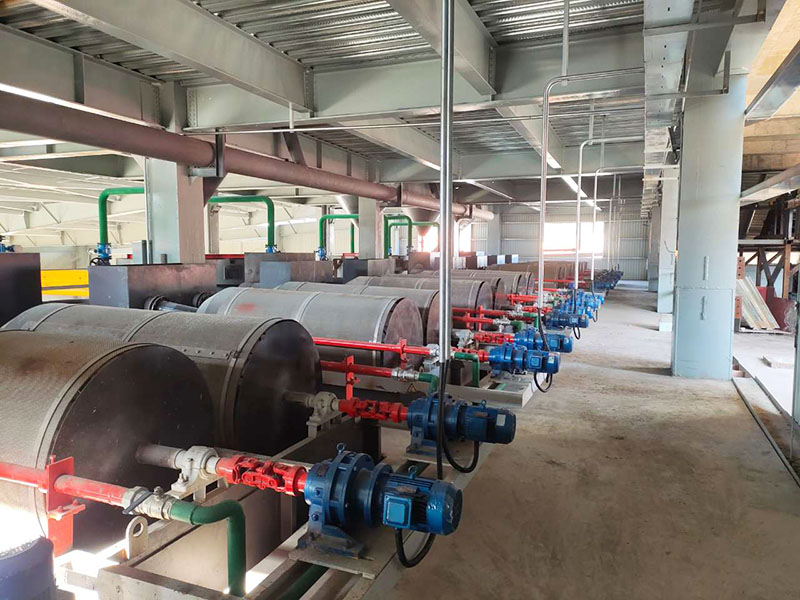
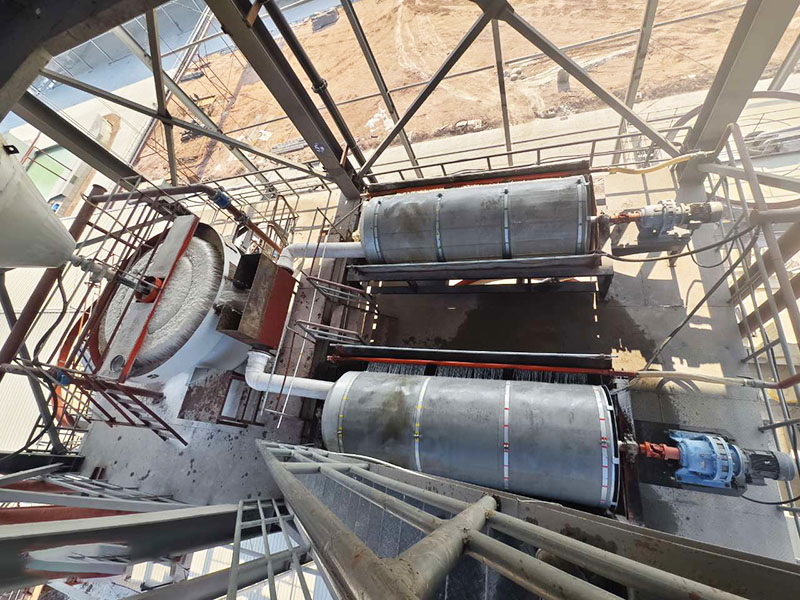
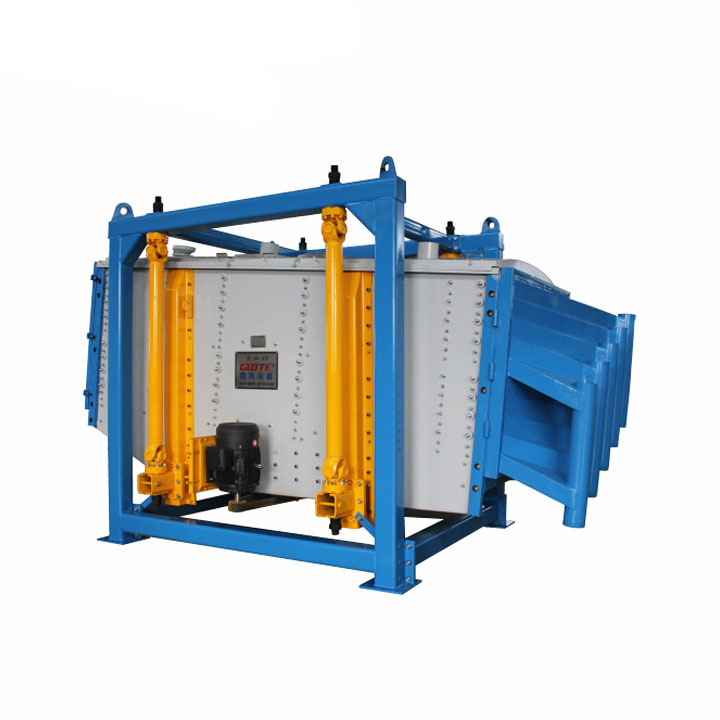
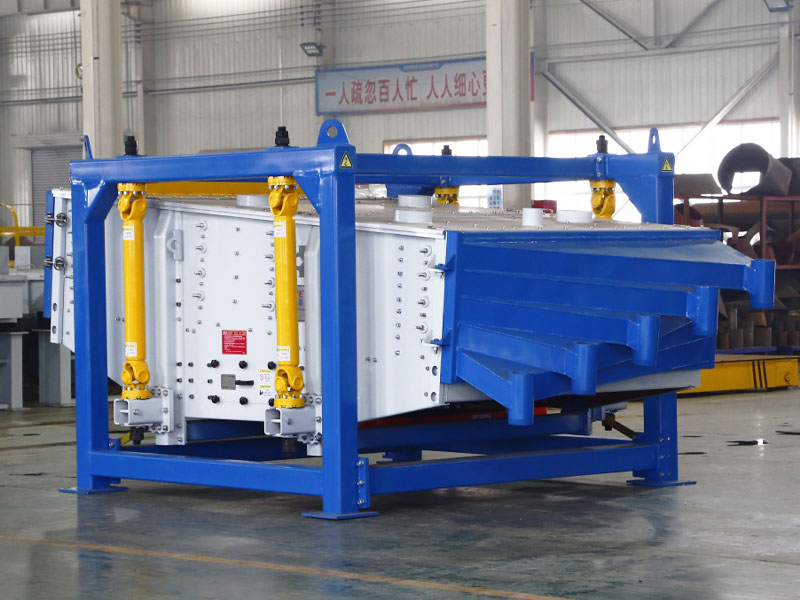
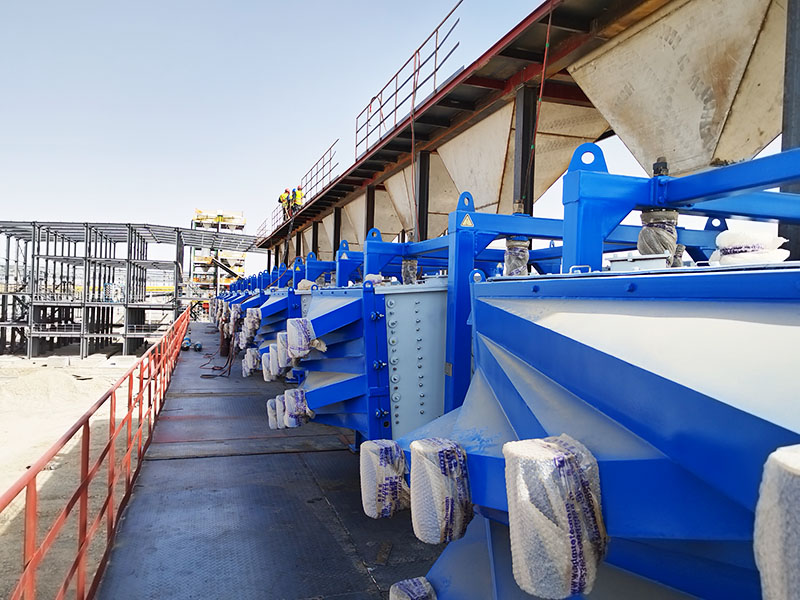
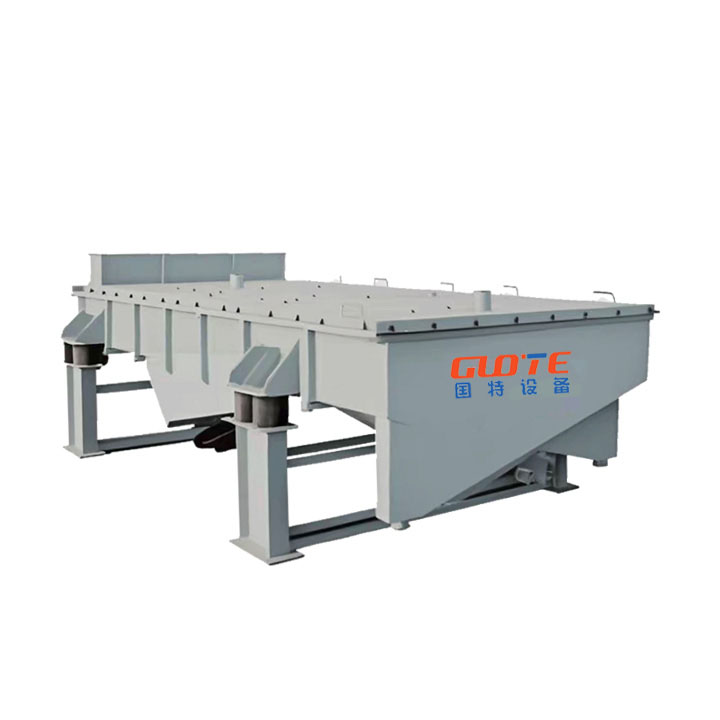
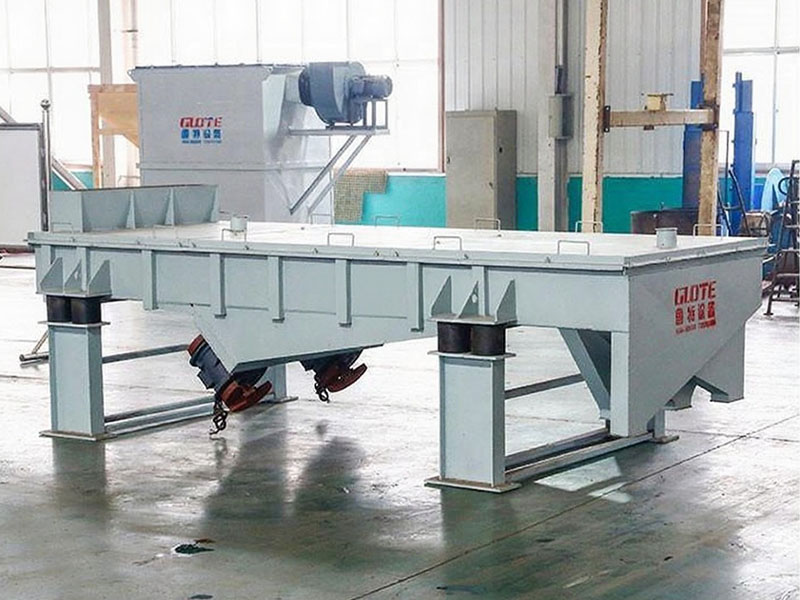
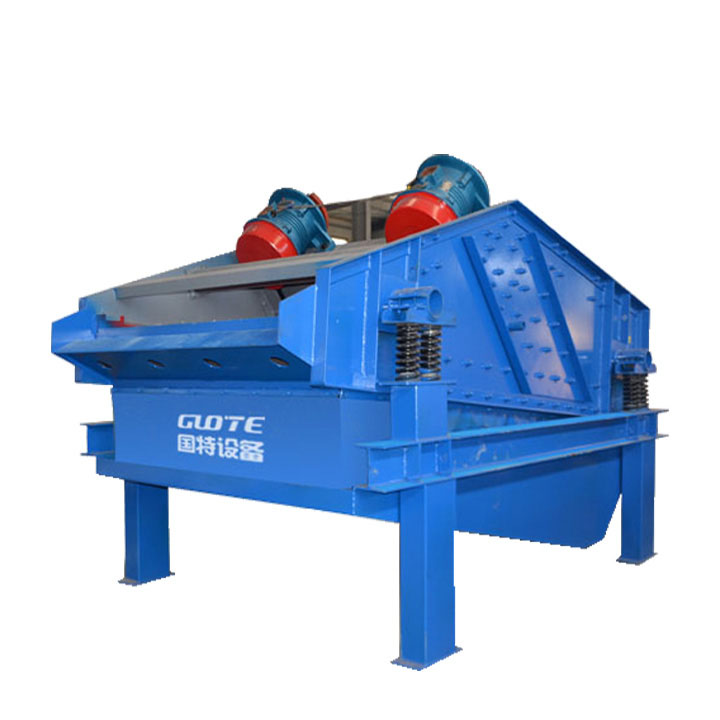
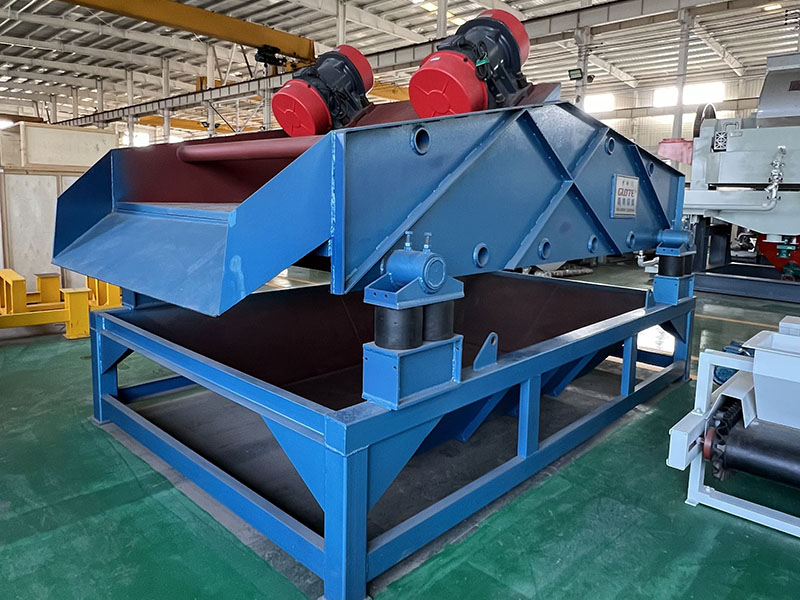
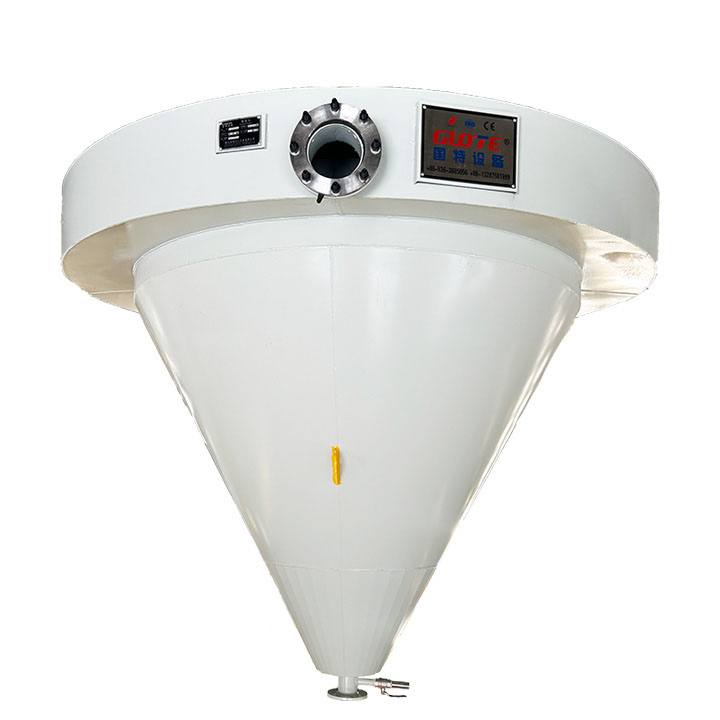
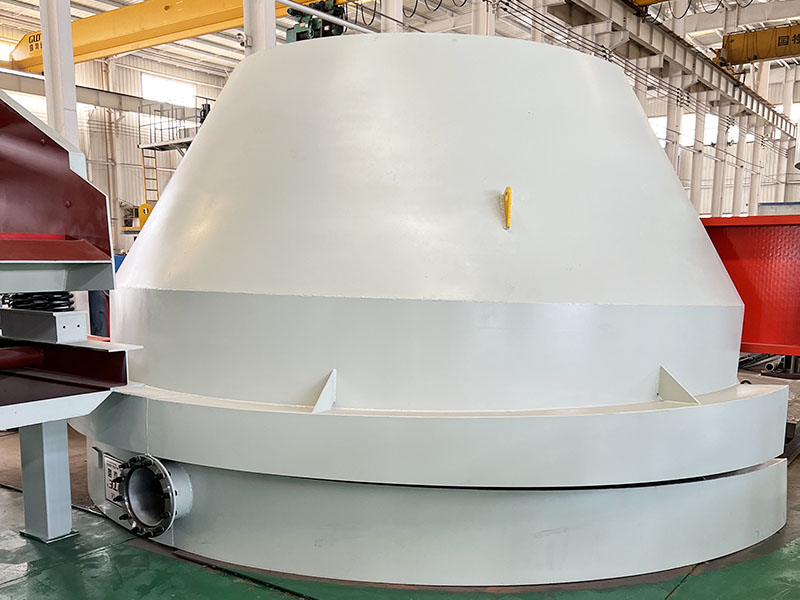
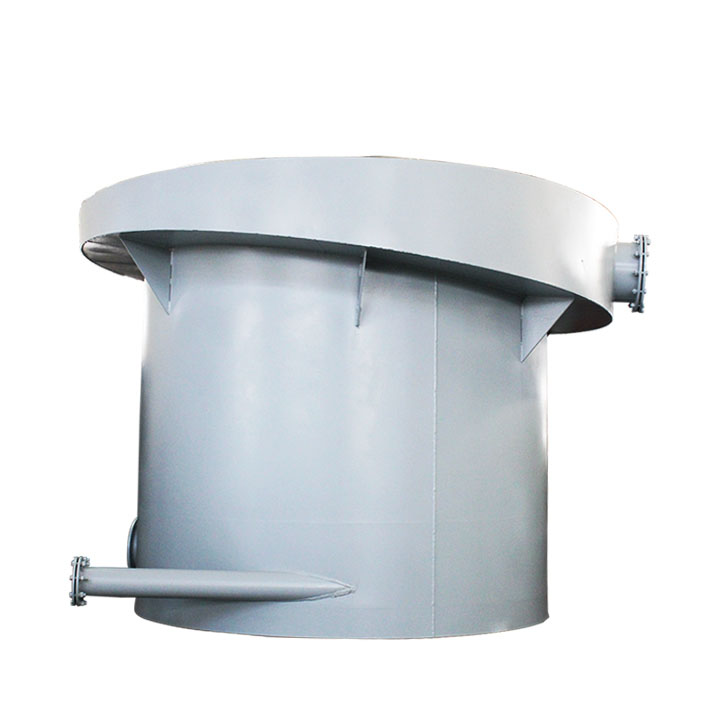
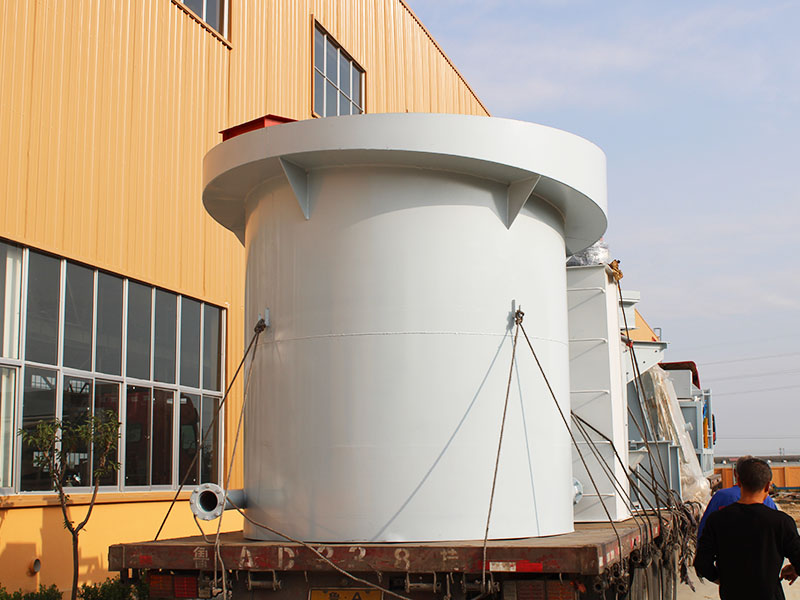
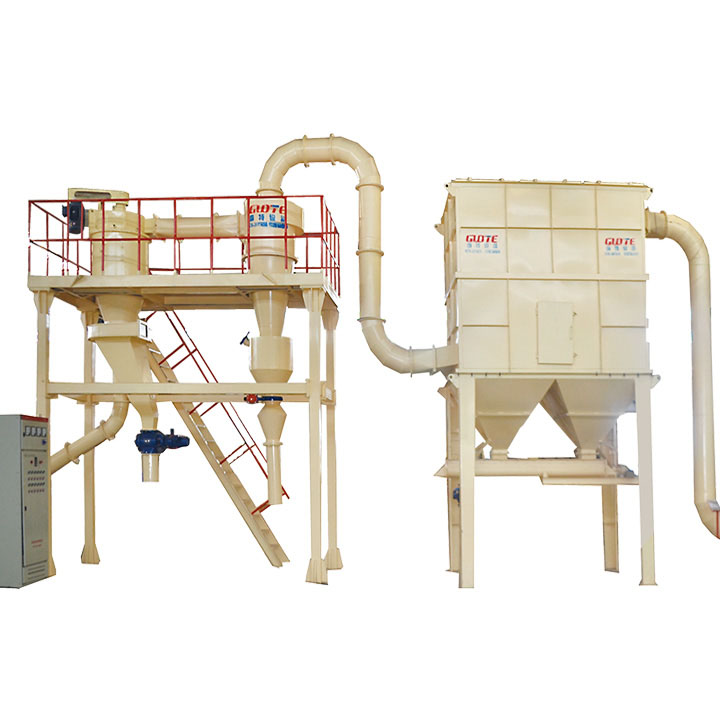
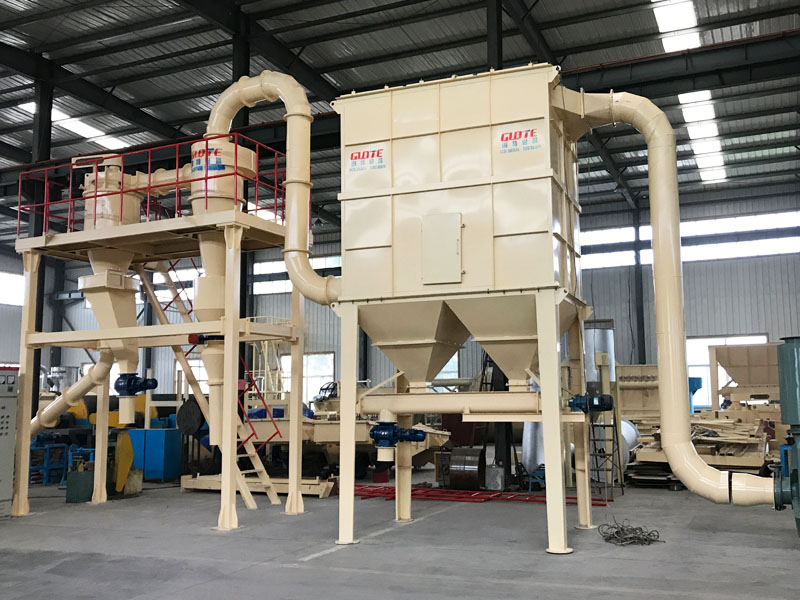
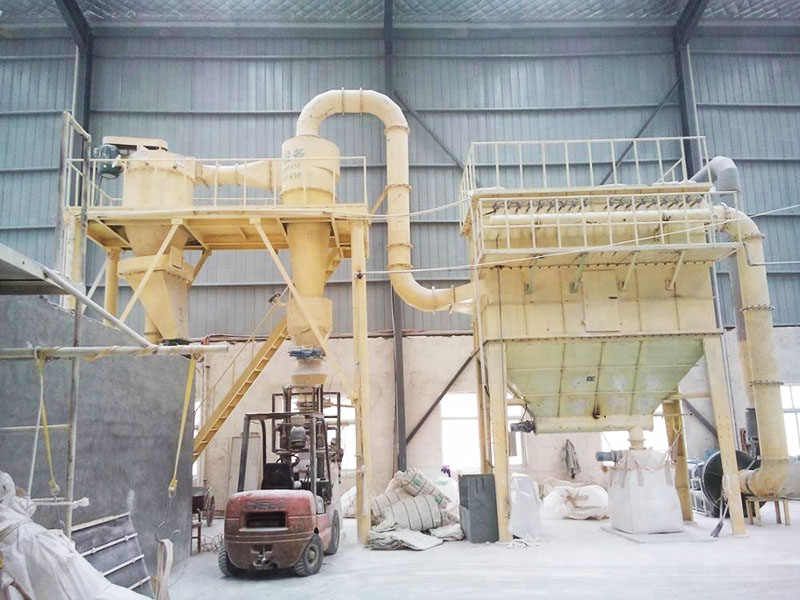
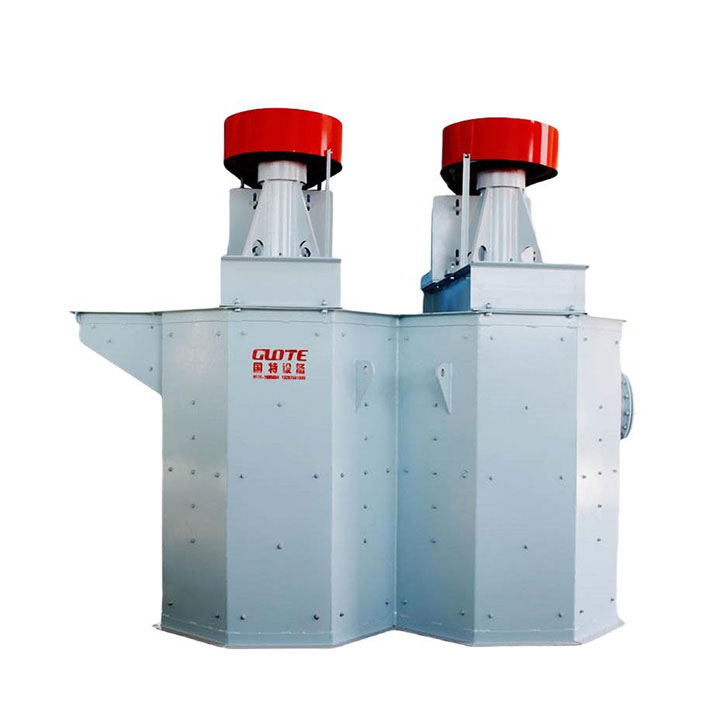
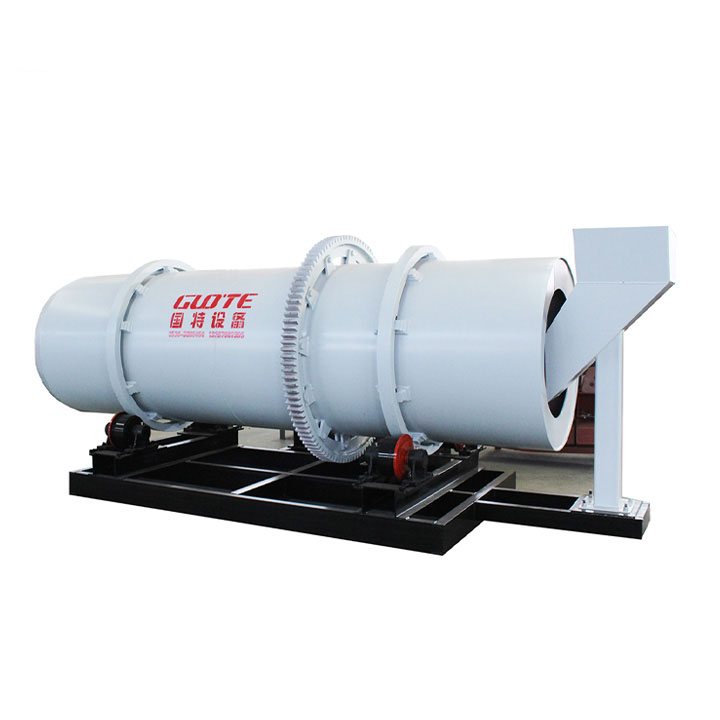
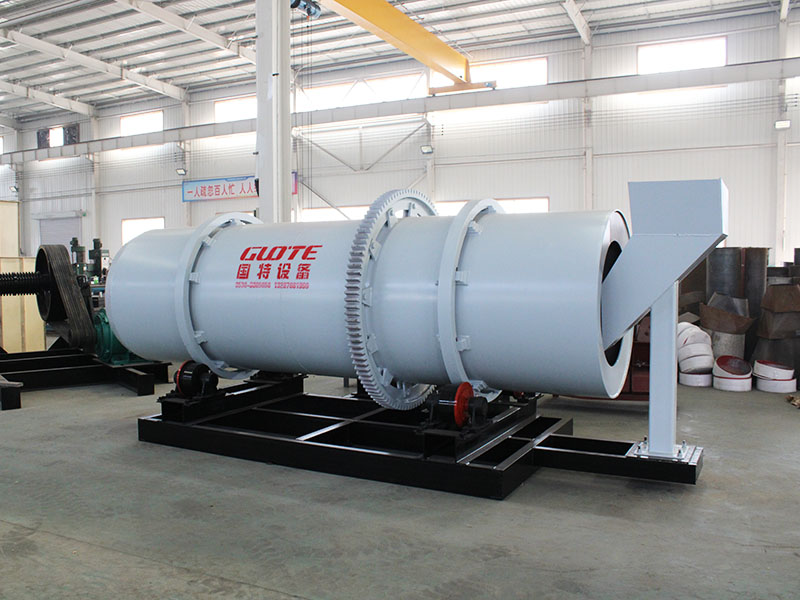
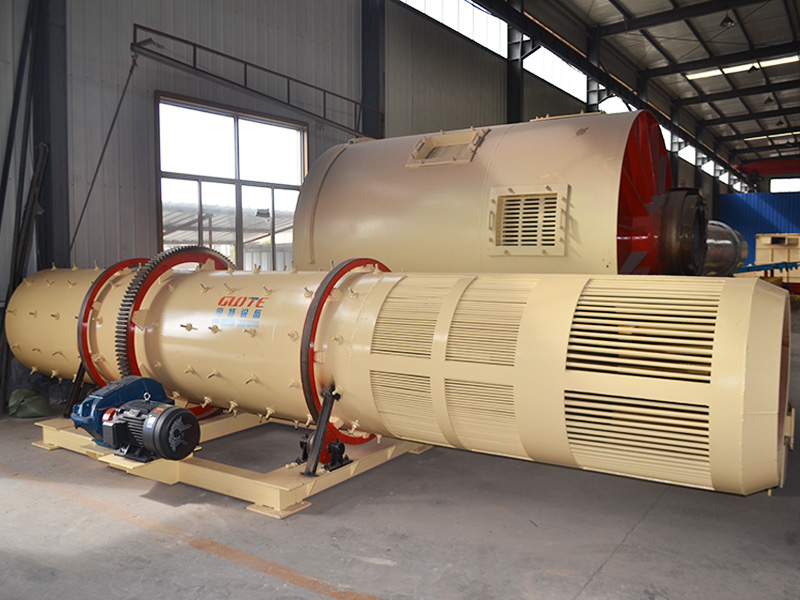
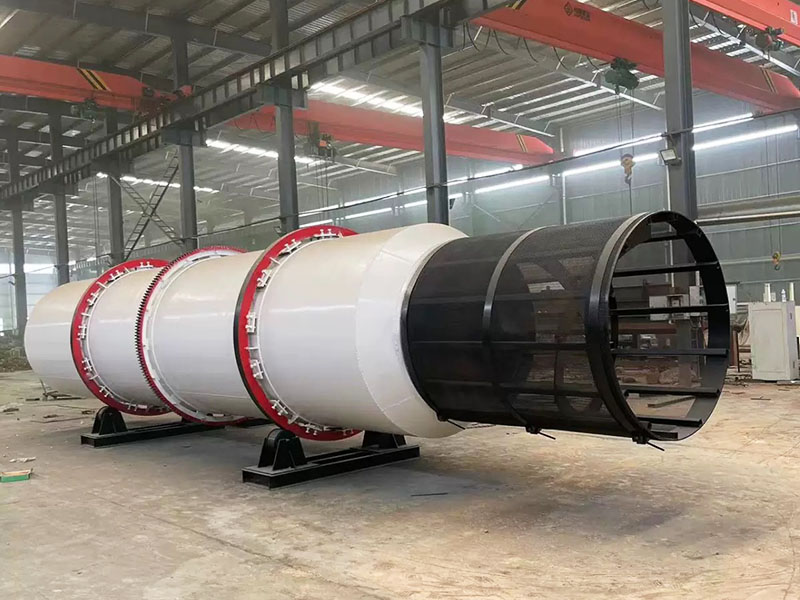
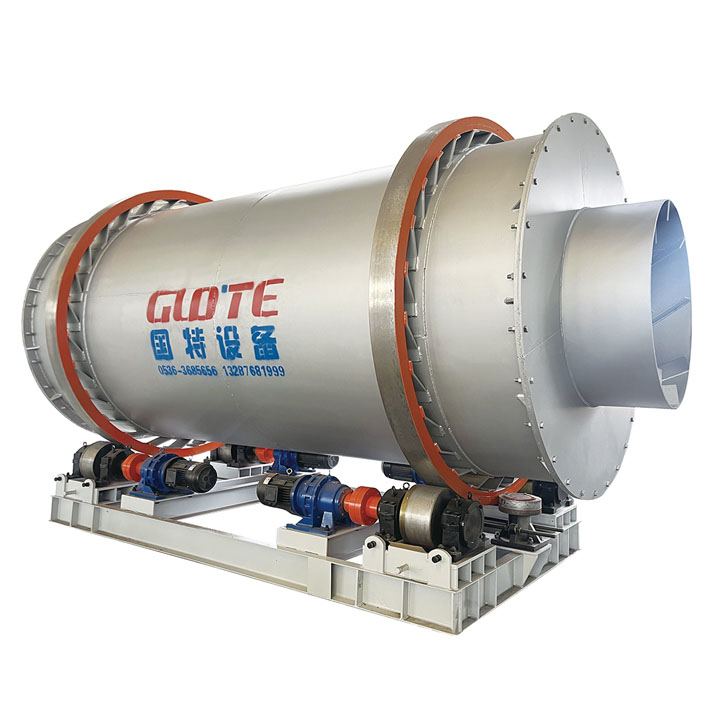
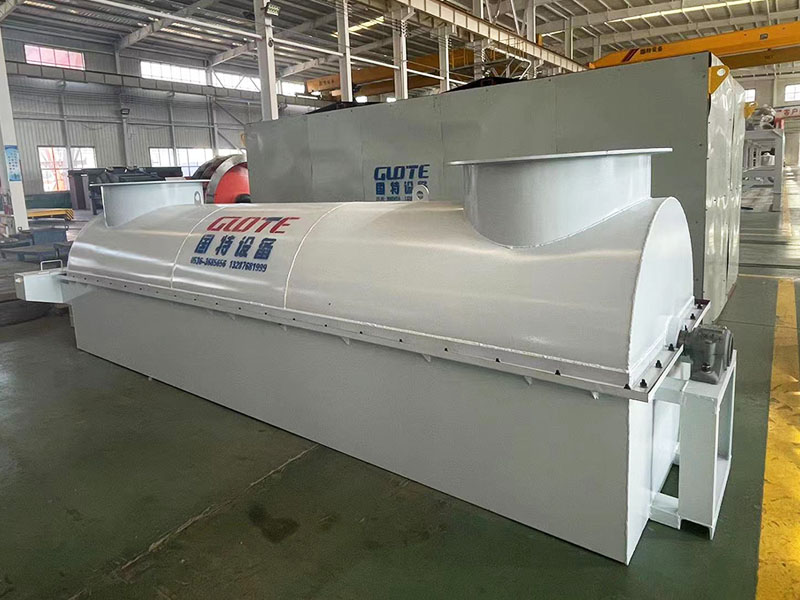
PRODUCT STRUCTURE
Introduction: The hydraulic classifier primarily consists of a grading trough, a feeding device, an overflow weir, and an underflow discharge outlet. During operation, slurry enters from above, and water flows upward or horizontally. Fine particles are discharged with the overflow water, while coarse particles, due to their rapid settling velocity, settle to the bottom and are discharged. By adjusting the water flow rate, slurry concentration, or the equipment inclination, the particle size can be precisely controlled, achieving continuous sorting.
Working principle:1. Feed: Slurry is fed into the grading tank from the top or middle of the equipment; 2. Classification and Separation: Water flows upward, and fine particles (slow settling) are discharged from the top with overflow, while coarse particles (fast settling) settle to the bottom; 3. Product Collection: The overflow (fine fraction) enters the next process (such as magnetic separation), while the underflow (coarse fraction) is recovered or reprocessed through the sand discharge port; 4. Parameter Control: Water volume, feed concentration, or baffle height are adjusted in real time to optimize classification accuracy.
TECHNICAL PARAMETERS
| Specification | Feed size (mm) | Classification range (mm) | Processing capacity (t/h) | Water consumption (m³/h) | Weight (kg) |
| GSF-1500 | <5 | 0.4—0.04 | 7—10 | 15—20 | 1200 |
| GSF-1800 | <5 | 0.4—0.04 | 10—15 | 20—30 | 1800 |
| GSF-2200 | <5 | 0.4—0.04 | 20—25 | 30—50 | 3300 |
| GSF-2400 | <5 | 0.4—0.04 | 25—40 | 40—60 | 4200 |
| GSF-2600 | <5 | 0.4—0.04 | 30—45 | 45—65 | 4300 |
| GSF-2800 | <5 | 0.4—0.04 | 35—50 | 50—70 | 4500 |
| GSF-3000 | <5 | 0.4—0.04 | 40—60 | 60—80 | 4600 |
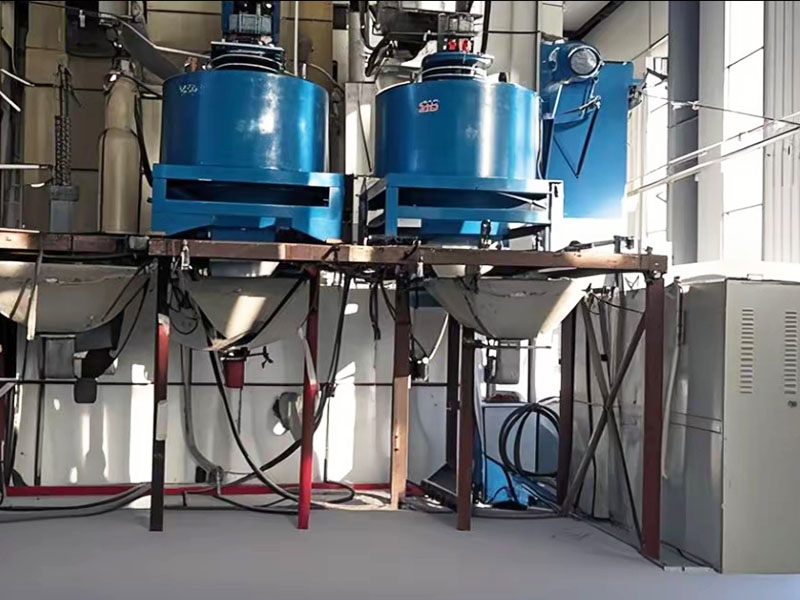
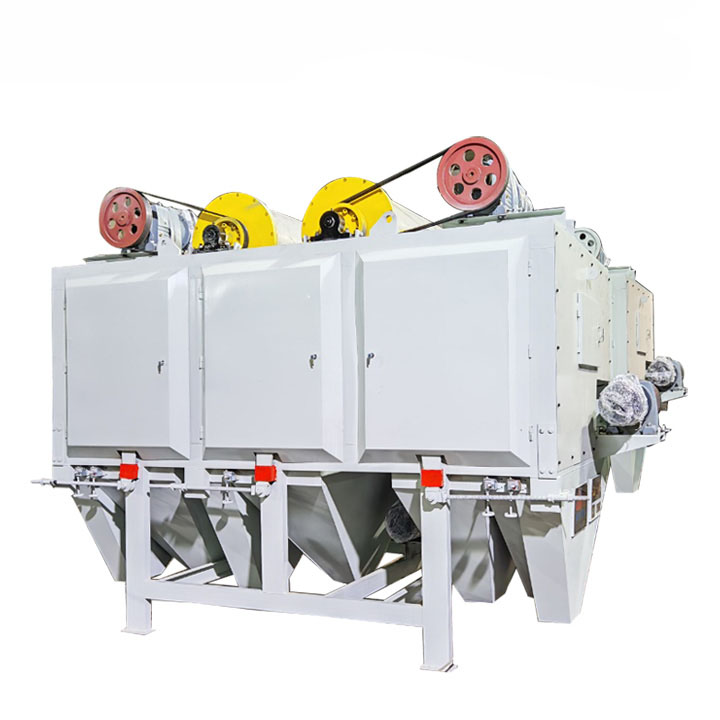
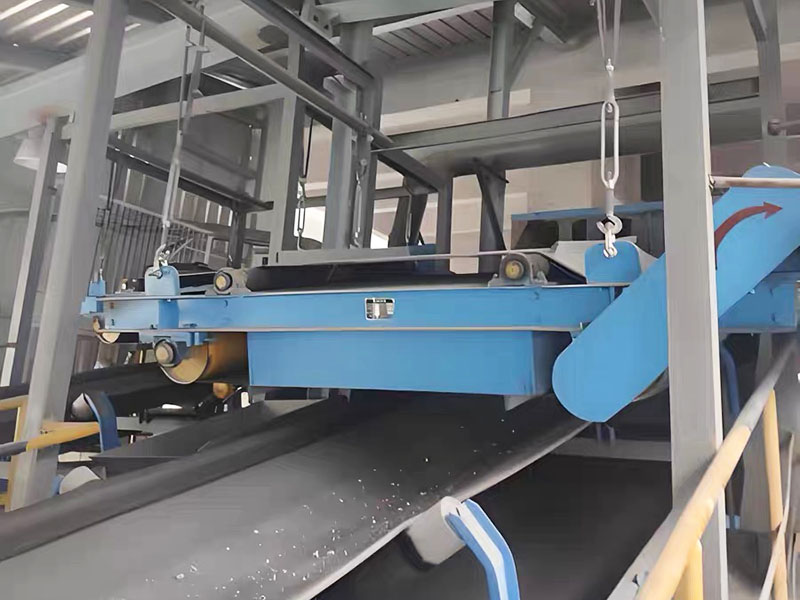
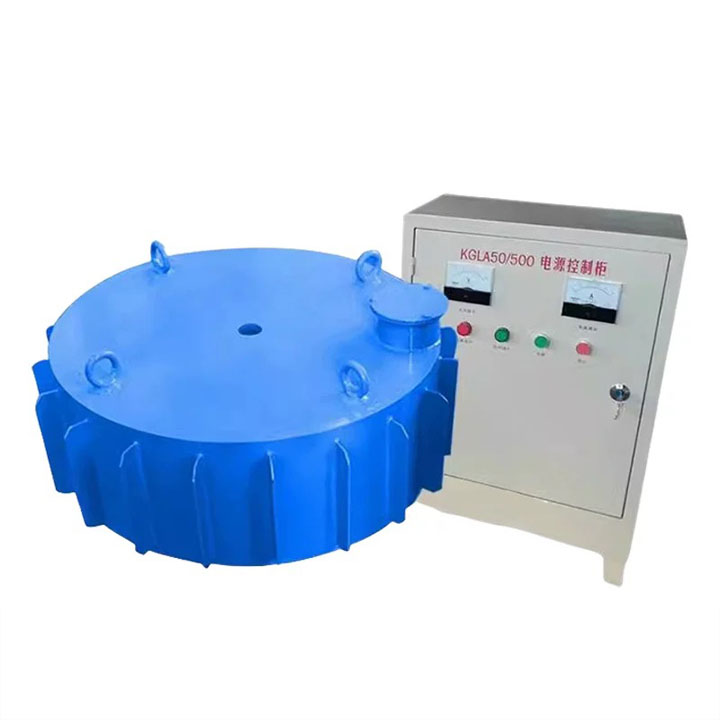
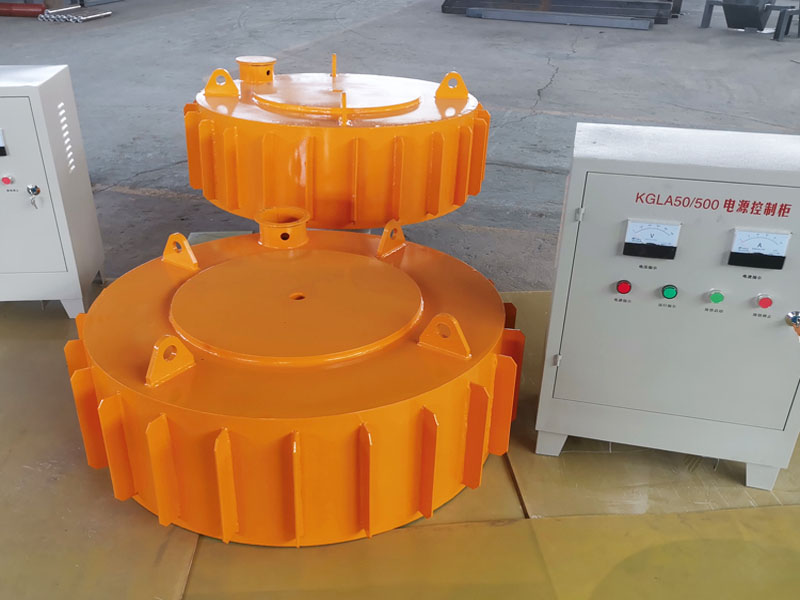
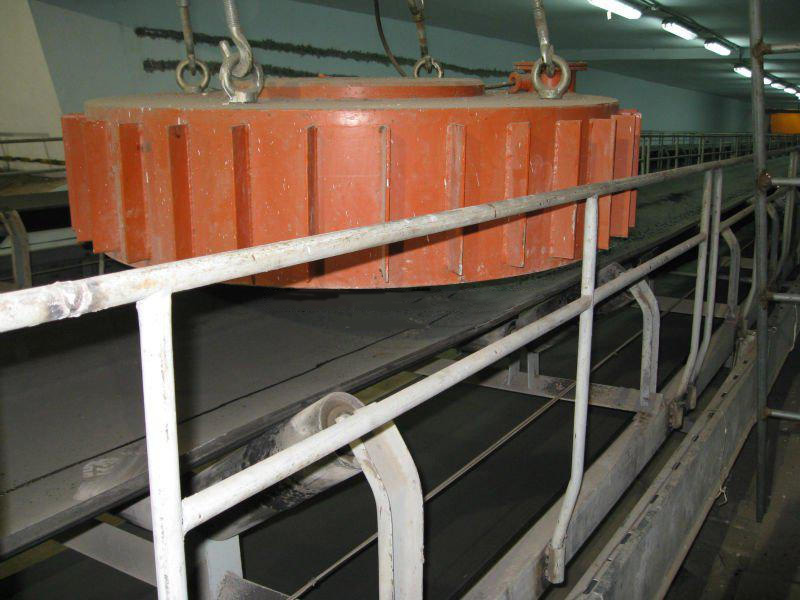
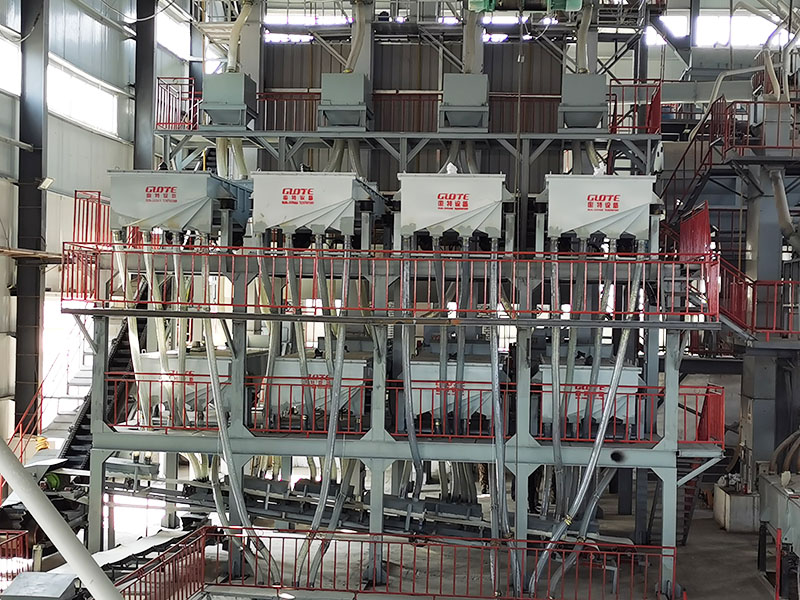
RELATED PRODUCTS
Contact Us
To find out more about our products and solutions, please fill out the form below and one of our experts will get back to you shortly.

 guotemining@gmail.com
guotemining@gmail.com  8613792666516
8613792666516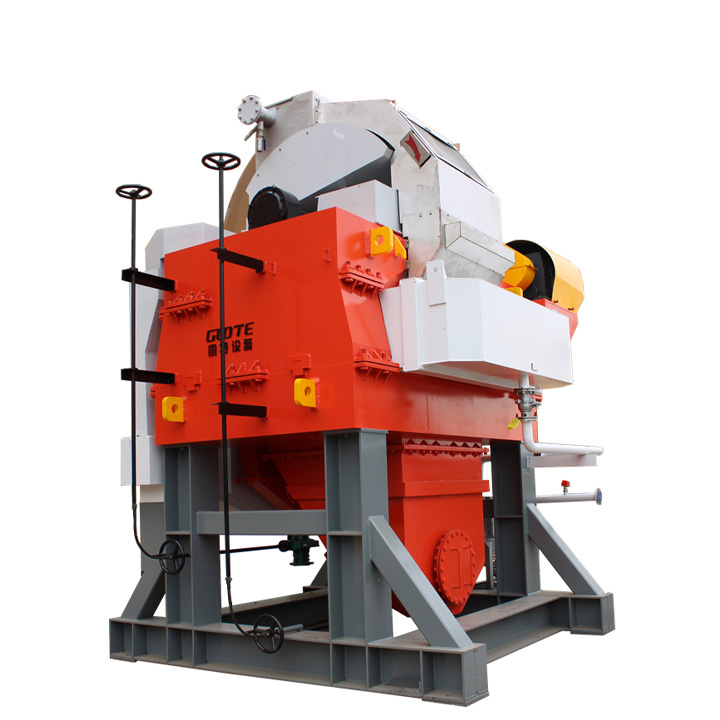 













































































































































 CHAT
CHAT MESSAGE
MESSAGE